What is the 'virtual retina display technology' that projects images directly on the retina?

In recent years, devices using the technology called '
The Smallest Large Display Is Projected Straight Onto Your Retina | Hackaday
https://hackaday.com/2020/04/15/the-smallest-large-display-is-projected-straight-onto-your-retina/
To know about VRD, we first need to review the human eye. The most basic function of the eye is to focus on an object using a crystalline lens. Therefore, the eye uses muscles called ciliary muscles to change the shape of the crystalline lens, and at the same time it has the function of adjusting the amount of light entering the eye with the iris to change the focal length of the eye. The central part of the image captured by the eye is projected onto the area called the fovea, which has the most photoreceptor cells in the retina, and the peripheral visual field is projected onto the rest of the retina. The basic mechanism of VRD is to scan red, green, and blue lasers on the fovea.
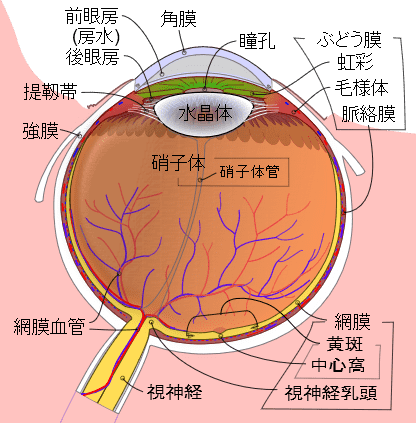
by Rhcastilhos And Jmarchn
As a technology close to VRD, there is a head-mounted display (HMD) type smart glass represented by Google Glass and Microsoft's HoloLens . This is an augmented reality (AR) technology that projects an image onto a semi-transparent display in front of you rather than projecting the image directly on the retina and superimposing it on the actual image.
HMD type smart glasses are epoch-making in that they can obtain information without looking at the screen of a smartphone or the like, but they are bulky because they still require a display. It is also not suitable for outdoor use on sunny days or midsummer. VRD solves these problems.
However, when irradiating three kinds of lasers on the eyes, safety is inevitable. In fact, at the large-scale outdoor festival ' Burning Man ' held in the Nevada Desert in the United States, there is an accident that the staff loses their eyesight with a portable type laser generator brought by someone.
The answer to these concerns is that we are using very low power lasers. With VRD, the retina is directly illuminated, so you do not have to worry about getting caught in bright sunlight, and you can exhibit sufficient performance with the minimum required laser output. For example, the BML500P, developed by electronic control equipment maker Bosch, works with a very small output of less than 15 microwatts.
The BML500P is explained in detail in the following articles.
A movie of the latest smart glass technology `` BML500P '' that directly displays mail and navigation on the eyes is on sale-GIGAZINE

It's a safe and bulky VRD, but it has the drawback that you can't use it immediately after buying it. With VRD, you have to project the image accurately in the fovea region of the retina, so you will not be able to see anything if you do not fit it a little. Therefore, products such as BML500P that have been introduced so far require a process to be adjusted according to the user.
Another disadvantage is that VRD products are expensive. For example, even the AR technology Google Glass Enterprise Edition 2 will be priced at 999 dollars (about 110,000 yen) as of 2020, and Microsoft HoloLens 2 will be $ 3,500 (about 390,000 yen).
Hackaday added, “As with VR a long time ago, much research and technological development will allow VRDs to be reasonably priced and reliable. There are many possibilities for VRD, so I'm looking forward to seeing what will come in the next few years, 'he said.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1l_ks






