A `` robot that is as good at collecting blood as humans '' has the potential to significantly reduce the need for re-sticking of the injection needle during blood collection
Intravenous injection is one of the most common clinical procedures performed 1.4 billion times a year in the United States, and many people have experienced it. However, those with thin blood vessels in the arm may have had a painful thought of having their needles re-inserted many times because of the failure of the blood collection performed during the medical checkup and blood donation. A robot that can perform such blood collection and injection better than humans has appeared.
First-in-human evaluation of a hand-held automated venipuncture device for rapid venous blood draws | TECHNOLOGY
New Robot Does Superior Job Sampling Blood | Rutgers Today
https://news.rutgers.edu/new-robot-does-superior-job-sampling-blood/20200204#.XkTzESNUtph
New Medical Robot to Take Blood Samples- Rutgers University Scientists
https://www.biotecnika.org/2020/02/new-medical-robot-to-take-blood-samples-rutgers-university-scientists/
Establish intravenous lines when administering drugs or drawing blood from a vein . However, if the blood vessels are difficult to see, puncturing the needle many times may fail to secure the line, which may result in phlebitis, thrombus, or infection at the site where the needle was stabbed. There is also. As a result, blood vessels at high risk for securing the line, such as arteries and thicker veins, must be treated. Intravenous injection is one of the leading causes of injury to both patients and clinicians, and inefficiencies due to delays in securing lines have resulted in a loss of $ 4 billion annually in the United States. That there is.
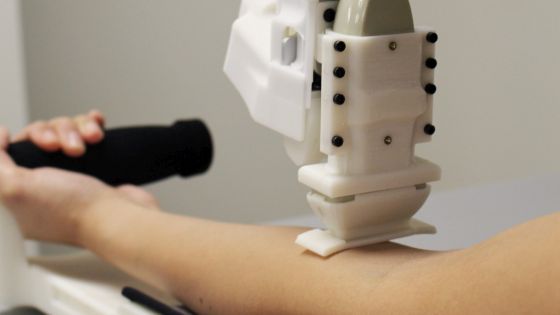
A research team led by Rutgers University has developed a robot that can easily secure such vein lines. The robot is equipped with an image guidance device using ultrasonic waves, and the state of blood flowing through blood vessels can be seen from the skin. It is expected to be a new blood collection method that replaces blood collection with needles by doctors and nurses.
Doctors and nurses report a 74% to 88% success rate when collecting blood from adults (PDF) . On the other hand, when using a blood collection robot developed by the research team, the blood collection success rate with an arm with raised blood vessels is 97%, and even with an arm with no blood vessels raised, the success rate is 87%, equivalent to humans Was recorded. In the future, he plans to improve the robot using artificial intelligence and continue to study it so that it can be used when securing venous catheters and arterial lines.

According to Josh Leipheimer , a member of the research team, 'the pain and complications of re-sticking can be prevented with our robots. Doctors and nurses can be assured that their blood samples are safe, It's a device that can be collected quickly. '
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log