Cells that were thought to have 'no particular role' in the brain had hidden power
by
Glial cells are a general term for cells that are not nerve cells (neurons) among the cells that make up the nervous system. Although glial cells have long been considered to play a major role in retaining neurons, much research has shown that glial cells themselves also play an important role.
Glial Brain Cells, Long in Neurons' Shadow, Reveal Hidden Powers | Quanta Magazine
https://www.quantamagazine.org/glial-brain-cells-long-in-neurons-shadow-reveal-hidden-powers-20200127/
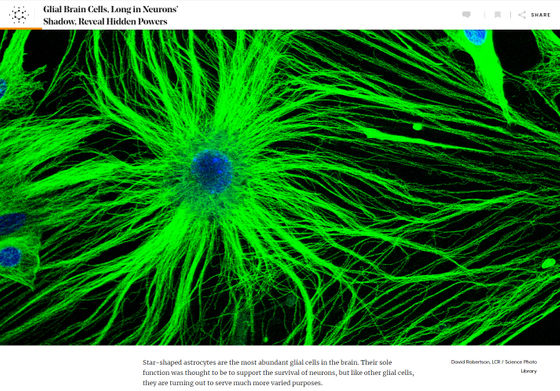
Glial cells are intricately intertwined with numerous projections protruding from the cell surface, and at first glance they are invisible to cells. Therefore, when it was first discovered, it was considered not simply a cell, but simply a body tissue to support neurons. In a medical book written in 1856, a 19th-century German physician
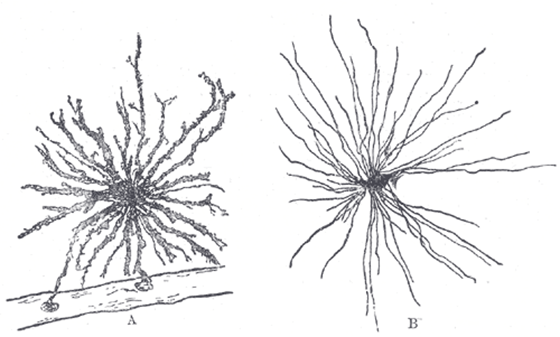
One of the major reasons that glial cells have not received much attention compared to neurons, which have been regarded as important in the early stages of neuroscience, is the inability to observe the structure of nerve tissue in detail. Early neurologists discovered that neurons form a complex, intertwined network by staining and sketching nerve tissue with drugs.
On the other hand, glial cells often look like mere clumps, so Santiago Ramon y Cajal, known as a giant in neuroscience and neuroanatomy, was able to discover a type of glial cell at the same time as neurons. , But overlooked most other glial cells as 'third elements that are neither neurons nor another type of cell.' However, as technological advances have made it possible to observe nervous tissue in detail, glial cells have become increasingly focused.
by
There are various types of cells, such as oligodendrocytes , which function as an insulator that protects neurons, and Schwann cells , even if they say glial cells. Among them, microglia has a particularly hot gaze.
'Microglia research has exponentially increased in recent years,' said Amanda Sierra, a researcher specializing in microglia at the Achucaro Basque Neuroscience Center in Spain. According to Sierra, microglia has been shown to play an important role in dealing with brain damage and controlling inflammation.
Guy Brown, a professor of biochemistry at Cambridge University, has found that microglia prey on bacteria and cell debris that damage the brain, much like macrophages , which are immune cells. 'If you look at microglia moving with the latest technology, you can see how microglia eats neurons that are old and no longer needed,' Brown said.
by NIH Image Gallery
In addition to the microglia, astrocytes a kind and of glial cells that, Schwann cells also have also been identified to remove the synaptic connection. However, according to Brown, 'it is rare to study these glial cells in groups.' Because glial cells are so diverse, in 2017 there were papers advocating that `` you shouldn't call them 'glial cells' anymore '', and many people refrain from using the term glial cells .
`` We know that neurons and glial cells can't survive without each other, and the interactions between neurons and glial cells are essential to the thoughts and emotions that the nervous system produces, '' said Stacy Bilbo, a neurologist at Duke University. However, the cooperation between them is still a mystery. '
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks