How long does it take to connect to a website depending on the top-level domain, such as '.com' or '.net'?

by
The URL required to access the website contains a name that identifies the server, called a ' domain name ', and is resolved to an IP address by a system called DNS . Domain names have a hierarchical structure, and the last part is called a top-level domain (TLD) , which is famous for '.com' and '.net'. Dejan Grofelnik Pelzel , founder of BunnyCDN, a content delivery network (CDN) company, has published a survey of the time it takes to resolve names by TLD.
Is your fancy new domain hurting your performance? Benchmarking the top-level domain names-BunnyCDN Blog
https://bunnycdn.com/blog/is-your-fancy-new-domain-hurting-your-performance-gtld-benchmark/
To resolve a domain name to an IP address, the DNS cache server first connects to the root server . The DNS cache server connects to the TLD DNS server such as '.com' based on the response from the root server and then connects to the lower DNS server, but if the response from the TLD DNS server is slow, The name resolution of the domain itself may be delayed, and in rare cases it may cause a stop response. For CDNs that need to reduce the speed of 1 millisecond, the response speed of TLD becomes a major issue.
So BunnyCDN monitored its network of 50 locations worldwide and surveyed the performance of 42 major TLDs. The surveyed data is aggregated in two ways, the median and the 85th percentile , and the graph is as follows.
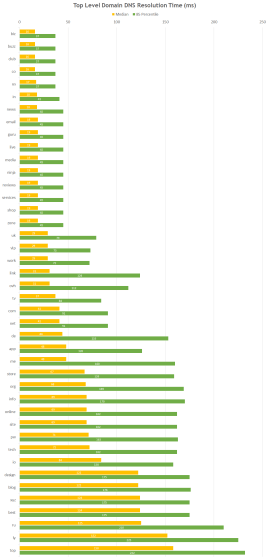
Looking at the graph, you can see that the results at the 85th percentile of the old and widely used '.info' and '.org' domains are very poor. According to additional research, the performance of DNS servers used in these domains is low. If newer domains like '.live' and '.email' are performing well, '.co' and '.biz' are performing very well and you want to get the best performance , These domains are said to be worth considering.
Research has shown that the performance of name resolution varies depending on the TLD, but websites that are frequently accessed are cached in the DNS cache server, and it is often unnecessary to access the TLD DNS server itself, so the performance is Pelzel says that you don't have to worry about using bad domains.
Related Posts:
in Note, Web Service, Posted by darkhorse_log