A mummy that may be `` a species in the process of evolution from a wolf to a dog '' is found in permafrost in good condition

DNA analysis of a mummy of a puppy excavated from Siberian permafrost revealed that it died in less than two months after birth in about 18,000 and that it was an animal that could not be identified as a dog or a wolf . Experts say that this puppy may shed new light on the process of dog evolution.
Amazingly preserved puppy with whiskers, eyelashes, hair and velvety nose intact puzzle scientists
18,000-year-old frozen puppy leaves scientists baffled | CNN Travel
https://edition.cnn.com/travel/article/frozen-puppy-intl-scli-scn/index.html
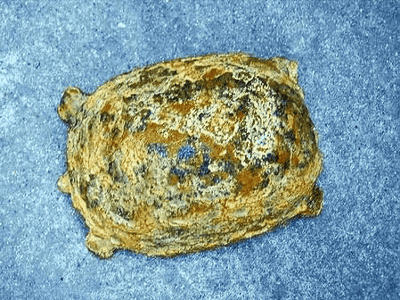
This puppy mummy was found in permafrost near the Indigirka River, northeast of Yakutsk, Russia. The state of preservation was very good and remained not only in the whole body, nose, mouth and teeth, but also in beards and eyelashes. The actual photo is below.


The condition of the head is particularly good, and even if it is limited to the mouth, it appears to be alive.
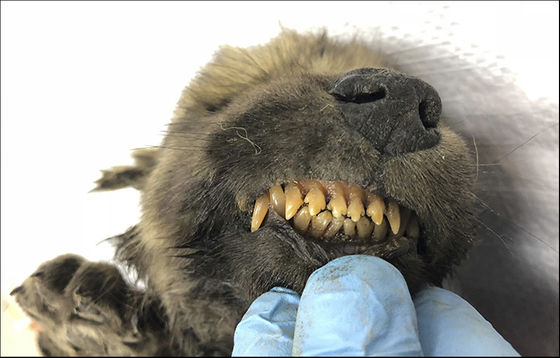
CPG has one of the largest “dog DNA banks” in Europe, and would normally be able to identify the breed of dog in a single trial. Researcher David Stanton, who belongs to CPG, commented that `` I can easily tell if it is a dog or a wolf normally '', but said that it is easy to distinguish between a dog and a wolf, but DNA testing The result overturned the assumption.
Dogs are thought to have been bred from the wolf sub-species, but no specific theory exists regarding which sub-species that lived in which region. A study published in Nature Communications in 2017 advocates the theory that modern dogs are 'species derived from a group of wolves about 20,000 to 40,000 years ago'.
Ancient European dog genomes reveal continuity since the Early Neolithic | Nature Communications
https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms16082

On the other hand, a study published in Science in 2016 has taken the position that “two species of wolves domesticated in Asia and two domesticated species in Europe are the ancestors of modern dogs”. The
Genomic and archaeological evidence suggest a dual origin of domestic dogs | Science
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/352/6290/1228
The research group considers that the puppy discovered this time is a `` species of the process of evolution from wolf to dog '', and continuing research can provide a lot of information about `` when the wolf was domesticated '' Suggests sex.
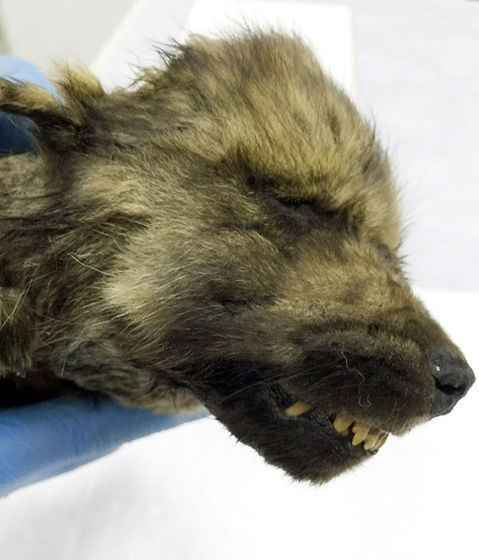
In addition, as a result of genome analysis, we know that the puppy is a male, and as a result of the findings, we know that the cause of death is unknown, but we did not feel pain at the time of death. As a result of the discussion, the researchers have given the puppy the name “Dogor”, which means “friend” in the Yakut language, the local language where the puppy was found.
Related Posts:
in Creature, Posted by darkhorse_log