Intel publishes comparative benchmark results of 56 core 112 thread processor `` Intel Xeon Platinum 9282 '' and `` AMD EPYC 7742 ''

Chipmaker Intel says that 56-core, 112-threaded server processor ``
[Updated] HPC Leadership Where it Matters — Real-World Performance
https://medium.com/performance-at-intel/hpc-leadership-where-it-matters-real-world-performance-b16c47b11a01
EPYC 7742, a processor for servers developed by AMD, is manufactured on a 7nm process, with 64 cores and 128 threads, a base frequency of 2.25GHz, a boost frequency of 3.4GHz, and an L3 cache of 256MB. A review comparing such EPYC 7742 and Xeon Platinum 8180M , a processor for Intel servers, was released in September 2019.
AMD core processor `` AMD EPYC 7742 '' with 64 cores / 128 threads achieved amazing benchmark results-gigazine

Intel announced in April 2019 Xeon Platinum 9282 is a 2nd generation Xeon scalable processor designed with 14nm manufacturing process, 56 cores 112 threads, base frequency 2.60GHz, boost frequency 3.80GHz, smart cash 77MB spec.
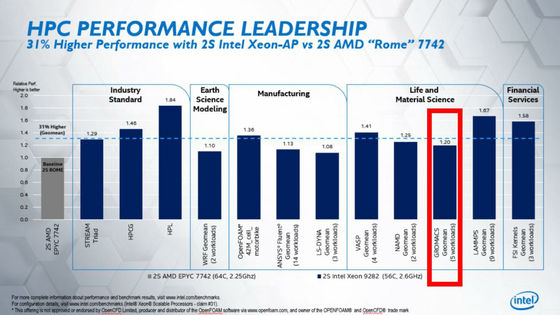
And Intel released its Xeon Platinum 9282 and AMD's EPYC 7742 in a high performance computing (HPC) benchmark comparison. The result is the following graph. The gray bar graph on the left is the EPYC 7742 benchmark result. The blue bar graph lined up to the right represents the result of Xeon Platinum 9282 when the result of EPYC 7742 is 1.0. Looking at the graph, all Xeon Platinum 9282 results exceed 1.0, and Intel argues that 'Xeon Platinum 9282 is 31% higher than the EPYC 7742 result in geometric mean '.
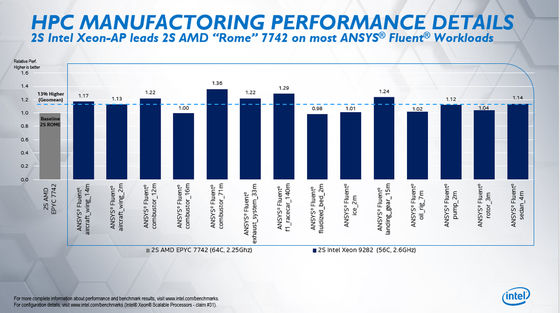
The following graph shows the results of performance comparison using ANSYS Fluent, a thermal fluid analysis software. Compared to the leftmost EPYC 7742 (gray bar graph), the Xeon Platinum 9282 (blue bar graph) on the right is 2% to 36% higher.
However, technical media ServeTheHome points out that there are problems with the high-performance calculations used in comparative benchmarks conducted by Intel.
Intel Performance Strategy Team Publishing Intentionally Misleading Benchmarks
Intel's comparative review initially used molecular dynamics simulation software called GROMACS . The version used in the comparative review was GROMACS 2019.3, which was released on June 14, 2019, but GROMACS 2019.4 was released on October 2, 2019.
ServeTheHome noted that some of the updates made in GROMACS 2019.4 included fixes for errors that occurred when using AMD Zen2 architecture CPUs, and Intel's comparative review was a disadvantage to EPYC 7742 I argued that “The Xeon Platinum 8280 should be compared to the EPYC 7742 in terms of power consumption and supported platforms,” ServeTheHome claims.
In response to ServeTheHome's criticism, Intel updated to GROMACS 2019.4 data. The following graph is the result of the comparative review after the update, but as Intel said, `` No substantial difference was found from the previous data posted in the 2019.3 version '', the result was unchanged. .
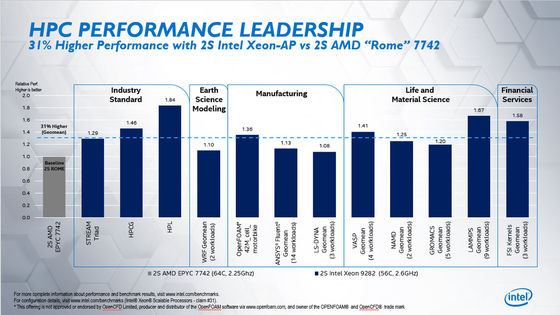
In response to this update, ServeTheHome said, “The Intel product that is most often compared to the AMD EPYC 7742 is the Xeon Platinum 8280. Although comparing EPYC 7742 and Xeon Platinum 9282 is probably not a very useful comparison. I think Intel is pushing forward, Intel is very active in supporting the Xeon Platinum 9282, and I think there are cases that outperform low-power chips. Is a conviction to the comparison between EPYC 7742 and Xeon Platinum 9282. '
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by log1i_yk






