A wireless device that can control the mouse brain with a smartphone will be developed
by
The research team at the University of Washington School of Medicine and Korea Daejeon University of Science and Technology succeeded in controlling the behavior of the mouse by controlling the wireless device embedded in the brain with the wireless communication standard Bluetooth .
Wireless optofluidic brain probes for chronic neuropharmacology and photostimulation | Nature Biomedical Engineering
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-019-0432-1
Scientists can now manipulate brain cells using smartphone-ScienceDaily
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/08/190805143525.htm
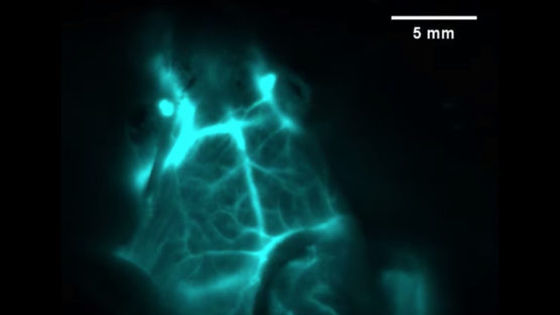
The following image shows a wireless device developed by a research team by Adrian Gomez and others at the University of Washington School of Medicine. The part that is actually embedded in the brain is the part surrounded by a red frame, and if it is limited only to this part, it is the smallest size of hair.
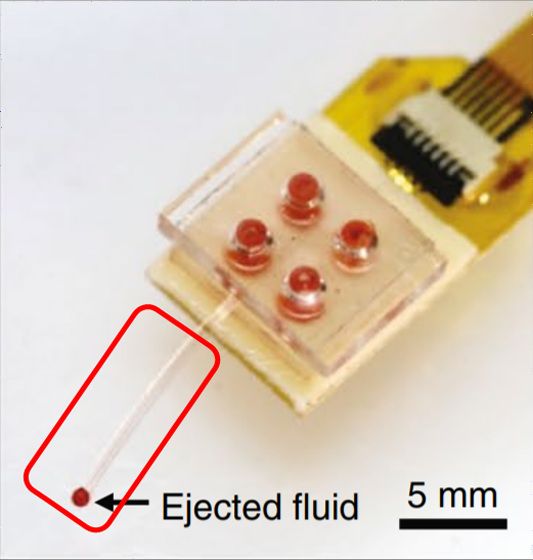
The main body of the wireless device is fixed to the mouse head. By connecting this terminal and an electronic device such as a smartphone via Bluetooth, the wireless device can be operated from a remote location, and the drug installed in the main unit can be administered to the mouse.

A very small LED is embedded at the tip of the part that will be embedded in the brain, and can emit red and blue light.
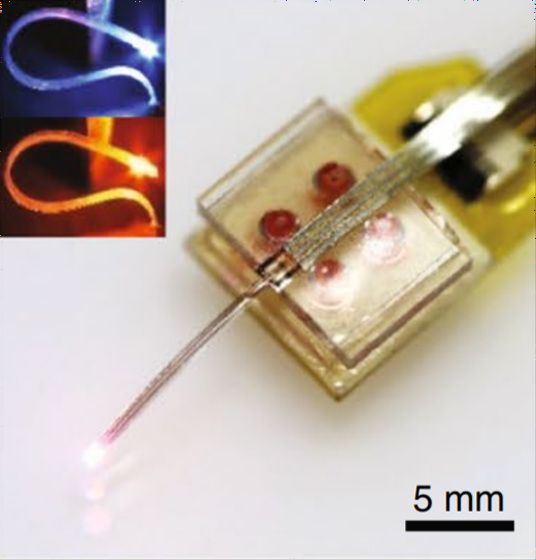
The wireless device emits light because it uses optogenetic technology that stimulates the cranial nerves with
Using optogenetics technology, proteins that respond to light can be introduced into specific cells using genetic techniques, which makes it possible to control the nervous system with high accuracy. However, optogenetic technology has until now had to leave the cable connected, which could hinder the movement of the target mouse or damage the brain with a metal wireless device. was.
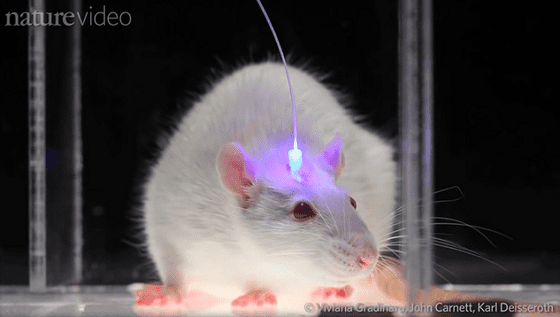
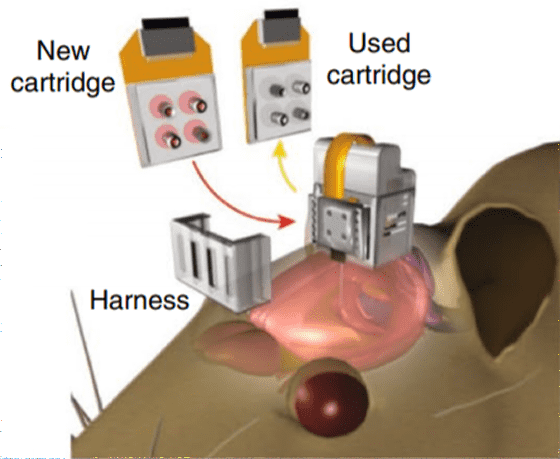
The wireless device developed by the research team is characterized by the fact that it can be controlled via Bluetooth, so no cable is required, and because it is made of a soft material, there is little damage to the brain. In addition, since the chip containing the drug can be replaced with a cartridge, there is no need to remove the wireless device to replenish the drug. This means that it can be used continuously for a much longer period of time than conventional wireless devices.
The research team attached this device to a mouse and conducted an experiment that stimulated by light while administering a GABA-A receptor blocker . As a result, he succeeded in an experiment to keep rotating in a certain direction in a 50cm square room.
The following figure shows the mouse behavior as a heat map, and the closer the color is to red, the longer it was in that place. The left end is in a state where no operation is performed, and since the corner other than the corner of the room is blue and the center of the room is also colored, you can see how it moves around in the room at random. On the other hand, in four experiments conducted every other week after the operation, the red pattern draws a square, indicating that the mouse that received the operation continued to rotate along the wall.
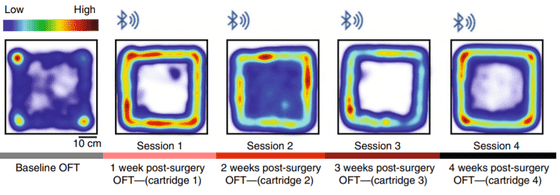
“This experiment has confirmed how neurotransmitters in the brain control behavior,” said Jae-Woong Jeong, co-author of the Daejeon Science and Technology Graduate School of Korea. We are focusing on the development of brain wireless devices that apply knowledge and nano-scale engineering technology, 'he said, and expressed his view that it could be used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer 's disease in the future.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks