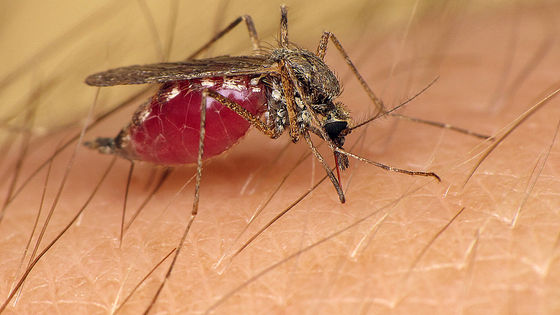
The medicine 'Ivermectin' which kills mosquitoes with blood loss reduces malaria by as much as 20%

By
According to a study led by a team at the Colorado State University, blood taken by ivermectin medicines is deadly poisonous to mosquitoes, causing more than half a million victims annually It has been able to control malaria, which is There are almost no fatal side effects on people from the intake of ivermectin, and may be effective for malaria control.
Efficacy and risk of harms of repeat ivermectin mass drug administration for control of malaria (RIMDAMAL): a cluster-randomised trial-The Lancet
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736 (18) 32321-3 / fulltext

Drug which makes human blood 'lethal' to mosquitoes can reduce malaria spread, study shows | The Independent
Dr. Satoshi Omura, known for receiving the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 2015, has been researching a microbe that produces substances that can be used in medicine as a director of the Kitasato Institute Antibiotics Laboratory since 1973. The In that study, we discovered a new species of actinomycetes 'Streptomyces avermectin Cu Chi Fresenius' from Ito, Shizuoka Prefecture Kawana golf of soil. When I checked with MSD (Merck & Co.) who is collaborating, I found that the chemical substance “ Avermectin ” released by this bacterium is effective against parasites.
Then, repeated research and improvement, kill the parasite that causes ' onchocerciasis ' that causes blindness or ' lymphatic filariasis ' that causes chronic inflammation or swelling, and kills mites that cause itch in close proximity ' Ivermectin ' was born.
Ibermectin is known not only to be effective against parasites, but also has the effect of causing human blood to be toxic to mosquitoes and to kill mosquitoes that have taken blood.

By primastock
Ivermectin has been commonly used for treatment of parasites and scabies, but it is still in the stage of testing for malaria, and this is the first large-scale experiment. The experiment was conducted in eight villages of Burkina Faso in West Africa.
A total of 2,700 people, including 590 children, live in eight villages. One half received ivermectin once every three weeks, and the other half did not receive ivermectin as a control group , and observed 18 weeks. According to the diagnosis and blood tests of malaria in each group, children who did not receive ivermectin had been infected with malaria on average 2.49 times during the experimental period, but the number of infections of children who received ivermectin was It was found that ivermectin reduced the number of malaria infections by about 20% on average twice. Also, no adverse side effects were observed with the administration of ivermectin through this experiment.
Dr. Chris Drakeley, who has been studying malaria for over 25 years at the University of London's Department of Hygienics and Tropical Medicine , said, “This is the first community-scale research to have demonstrated the effects of ivermectin. So, they have shown new possibilities for malaria control. '
Related Posts: