Succeeded in creating artificial placenta using 3D printer

The belly that is always in the human body is a proof that it was physically connected with the mother when he was a fetus. The fetus receives oxygen and nutrients from the " placenta " in the uterus of the mother through the umbilicus. Vienna Technical University reports that this placenta was successfully created "3D placenta " reproduced with 3D nanoprinter and biopolymer.
Technische Universität Wien: Die künstliche Plazenta im Labor
https://www.tuwien.ac.at/en/news/news_detail/article/126119/
The placenta is an organ that connects the mother and the fetus and exchanges oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and waste products. Since direct investigation of the human placenta is involved in the fetal life, what kind of process is being exchanged between mother and child, and the permeability of the human placenta is still completely obvious It has not become.
For example, when a mother carries a disease such as diabetes or hypertension, it may affect the substance transport to the fetus. However, because the process of mass exchange in the placenta has not been clarified, research on how it has specific effects has not progressed quite a bit.
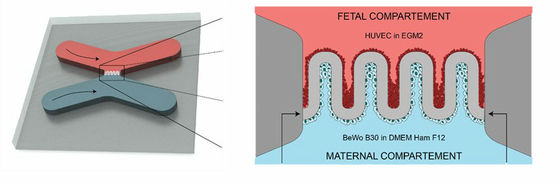
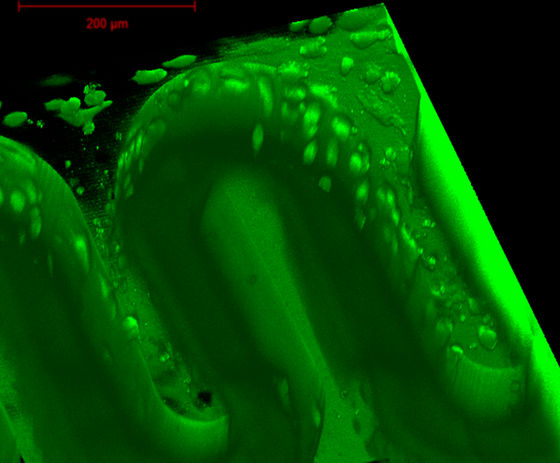
The Vienna University of Technology used a specially developed femtosecond laser 3D nanoprinter to mold a biopolymer membrane with a villus like the real placenta into a microfluidic chip . In the illustration below, the gray boundary portion waving between the red "fetus" and the blue "maternal body" corresponds to the biopolymer membrane formed by 3D nanoprinter.
The biological chip for research which actually reproduced artificial placenta is the image below.
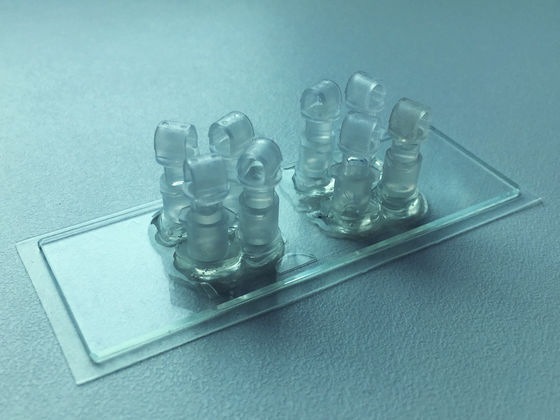
The umbilical cord and placenta-derived cells were injected into the chip together with the culture medium and observed, and as a result, the substance exchange was confirmed between the fetus part and the maternal part in the same way as in the real placenta. By using this artificial placenta, research team says that we can study the mechanism that glucose as nutrient is exchanged between mother and fetus, and the influence of blood pressure, blood glucose level, drug, etc on placenta.
Professor Alexandre Ovesianikov of the Institute of Materials Science and Technology, Vienna Institute of Technology said, "Besides the nutrient permeation through the placenta, the transport of substances via biological membranes such as the stomach, intestines, blood brain barrier, etc. plays an important role in various fields We are commenting that 3D nanoprinter technology is expected to be applicable not only to artificial placenta but to other organizations.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1i_yk