Succeeded in producing a safe biocompatible plastic from sugar and carbon dioxide

A researcher at Bath University in the UK succeeded in producing biocompatible plastics using carbon dioxide and sugar without using highly toxic raw materials.
Polymers from sugars and CO 2: ring-opening polymerisation and copolymerization of cyclic carbonates derived from 2-deoxy-d -ribose - Polymer Chemistry (RSC Publishing) DOI: 10.1039 / C7PY00236
http://pubs.rsc.org/-/content/articlehtml/2017/py/c7py00236j
Scientists make plastic from sugar and carbon dioxide | University of Bath
http://www.bath.ac.uk/research/news/2017/06/12/scientists-make-plastic-from-sugar-and-carbon-dioxide
"Transparent thermoplastic plastic"Polycarbonate"Is a familiar resin material that is used for water bottles, CDs and DVDs, lenses for eyeglasses, and scratch resistant coatings. Generally, bisphenol A (BPA) or phosgene, which is a highly toxic chemical substance, is used in the production of this polycarbonate. However, in recent years, the risk that plastic products derived from BPA may adversely affect the human body has been pointed out, and its use in baby bottles for infants has been banned worldwide.

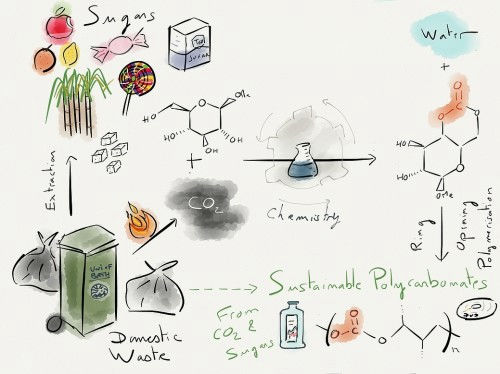
In contrast, the research team of Dr. Antoine Buchard of Bath University et al.ThymidineAnd succeeded in developing a process to produce a new polycarbonate resin by reacting enzymes derived from soil bacteria with carbon dioxide as a raw material. Moreover, synthesis is possible under low pressure and room temperature environment. Biocompatible plastics can be produced by synthesizing polymers from thymidine, which is one of base + sugar-bonded nucleosides.
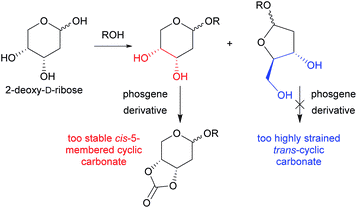
It is not possible to use phosgene in this generation process, emissions of pollutants in the manufacturing process will be suppressed. In addition, this new polycarbonate is because there is biodegradable made from thymidine, there is also an advantage that the disposal problem of not degraded plastic does not occur.
It is said that plastic produced from thymidine is as strong as that made from petroleum, and shows physical properties such as being transparent and resistant to scratching. Because it has biodegradability and in-vivo compatibility, it is expected to be used not only for replacing food containers but also for "medical scaffolds" that support medical implants and transplanted organs.
Researchers in the future,RiboseYaMannoseWe are planning to study the process of synthesizing resin from other sugars such as. Dr. Buchard said, "Chemical technology has been synthesizing plastics from petroleum products over a period of 100 years, but we need to start switching to plastics made from degradable and renewable sugar etc. Although it is still in the early stages, It is promising. "
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log