The state of the state-of-the-art technology development competition carried out at the factory of F1 team making the world's fastest machine

Motorsports 'history with more than 60 years'Formula 1(F1) "is a place for competition between drivers, and it is also a place for technology competition to make the world's fastest car. Technology-related news siteArs Technica, "Renault Sport Formula One Team" (Renault F1) Factory, I touch the development site aiming for the world's fastest speed.
Formula 1: A technical deep dive into building the world's fastest cars | Ars Technica
https://arstechnica.com/cars/2017/04/formula-1-technology/
The F1 machine which reaches 190 mph (310 kilometers per hour) in a quiescent state and can decelerate to 60 mph (100 kilometers per hour) in only 0.7 seconds is designed as a complete new car from scratch every year. There are only 10 teams in the world that develop F1 machines, most of them have base in the UK, and for more than 60 years, many teams have participated in the fighting to develop the fastest machines .

For F1 machine development, importance was attached to "driver", "tire" and "powertrain (engine)" for about 30 years from the start of F1-GP, but in 1977 Lotus "DownforceAfter adopting the wing by bringing in the concept of aerodynamics such as "The competition for development of machines intensified. Since excellent technical ideas are quickly adopted by other teams, it is necessary to incorporate ideas that can not be easily thought out in order to overcome other teams and develop fast machines. Moreover, there are competing competition to survive the eye of live horse, like pushing the gap of regulation that changes like every year.
This is the so-called "realized by Brabham BT 46Fun car". It was designed to create a powerful downforce by forcing the air under the floor to the rear, but it was too strong so it was banned with just 1 race.

In 1982Jill · VilleneuveAnd in 1994Ayrton SennaAfter the accident death of a genius driver such as a genius driver, the regulation was steered in a direction to emphasize safety more and as a result, by applying restrictions on power train, tire, aerodynamics etc., "Fast improvement" will be added to the F1 machine Often being forced. However, among the machines that got late overall, the development competition aiming to surpass other teams is never over, and the battle making full use of computers is getting more intense.
Although the F1 team will develop machines according to the regulations established by FIA, there are many aspects where revision of regulation can not catch up with advances in technology. For example, the performance of a computer used for simulation to improve aerodynamic performance is said to be "under 25 teraflops in floating point calculation". This figure is based on NVIDIA's Maxwell architectureGeForce GTX TITAN XIt is a computing performance of about a degree and it can not help being said that it is low performance as a computer to develop the world's fastest machine.
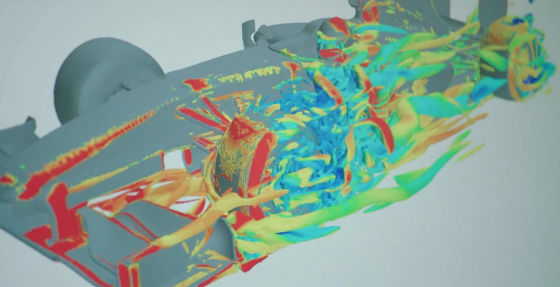
Moreover, according to FIA rules, it is not allowed to use the GPU for simulation, it means that only the CPU can be used. For this reason, Renault F1 has introduced a computer cluster of 18,000 cores with 2000 Intel Xeon CPUs. According to Mark Everest, infrastructure manager for Renault F1, each team has all the hardware setups in the factory, and there are no teams yet to move to the cloud supercomputer. This is impossible due to the above-mentioned CPU tying. However, it seems that details of aerodynamic data are kept in cloud storage.
Renault F1 aero dynamics simulator is made collaborating with aircraft manufacturer Boeing.

In addition, wind tunnel tests to raise "aerodynamic performance", which is one of the most important items for modern F1, also have severe restrictions. The time for the F1 team to conduct the wind tunnel test to examine the aerodynamic characteristics is limited to 25 hours per week. According to Mr. Everest, the restraint bounds are different in 2007, and there were no restrictions on the teraflops of the simulator and time limit of the wind tunnel examination. "We were doing the wind tunnel test without a 24-hour break in 3 shift system, of which we started teams to consider constructing the second wind tunnel to test further, indeed Williams was the second We built a wind tunnel, "Everest said. FIA has severe restrictions concerned about the fact that the disparity between wealthy teams and small teams that can input huge amounts of funds for computer performance and wind tunnel tests spreads and that it can not be realized as a technology development competition.

In the Renault F1 wind tunnel test, aerodynamics are being investigated on a machine that is 60% of the size of the actual machine.

The period and distance of the test run on the circuit for machine development are also severely restricted. Therefore, each team introduces a dedicated simulator to compensate for the lack of testing.

The driver learns the new course layout,ERSWe will run with a simulator to get used to the new technology that will emerge in new regulations such as. Of course, the running data is gathered by engineers and fed back to the development of the actual car.

Although it is the development site of the F1 machine which has strict restrictions on the development of the chassis (car body), there are no surprising regulations for the other parts. For example, there are no restrictions on software CAD and CAM that design parts of a machine, each team can freely use any software you like, and can run it not only locally but also in the cloud. Those software, the results of the wind tunnel testRapid prototypingIt seems that it is used as a group of original software combined.
The factory that the new machine will be developed every two weeks is well organized and beautiful.
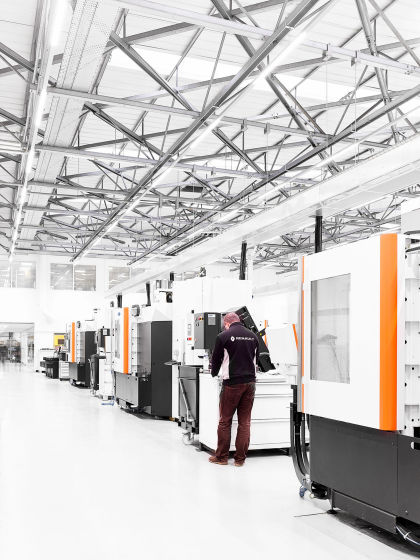

The process using carbon fiber such as monocoque production seems to be located in a relatively slow process.

In F1 which fights the cities around the world, the team will spend about 230 days out of the year in a place away from the home of the UK. Machines are disassembled into pieces every race and it takes about 36 hours to transport about 50 tons of equipment such as spare parts, fuel, tools, computers, food to another city. For example, during the movement of Belgian GP and Italian GP moving in Europe, we will move with a track that we formulated together, but all else will be packed in a container and moved by jet aircraft.

Parts brought in according to the characteristics of the circuit are different. For example, in Monaco where there are many narrow corners and downforce and tire grip power is required, in Monza where the straight is long it can be said that the machine is a completely different thing, the machine will be reassembled per circuit perfectly. Mr. Jeff Simmons of Renault F1 says "The machine is different in every race."
For V6 turbo engineExhaust manifold

Improvement of the machine is done during the season, and the running data of the circuit is fed back. The factory of the team is equipped with CNC milling machine and sintering machine, and the newly designed carbon fiber wing can be manufactured in about 10 days.
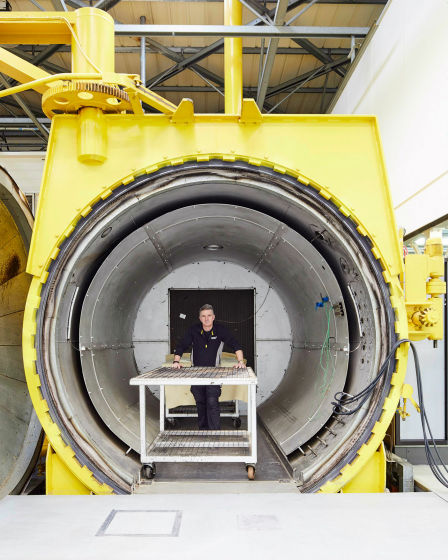
"Autoclave" to burn carbon fiber at high temperature and high pressure

Each part will be airlifted to a team that fights all over the world from the UK in the base. In an extreme case, "The crew who returned to Britain from Barcelona at the last flight packs new parts as a suitcase and leaves the airport at 9:25 am the next morning." By the way, it seems that mobile apps prepared by airlines are used instead of dedicated tools to arrange this airway. Also, "Although it took 20 hours to travel from Enstone (from the base of Renault F1) to Barcelona in the past, now it has been reduced to 18 hours thanks to road information, such as moving apps We are benefiting, "says Geoff Simmons of the race team coordinator.
Approximately 1000 employees are working at the F1 team, but the number of people directly involved in each race is limited to 60 people. To avoid this limitation, each team uses high-speed net lines. The speed of the net line at the pit is about 80 Mbps. Several decisions are made by engineers at the circuit, but most of the calculations, such as course strategy, are handled by remote engineers and delivered to the pit through high-speed lines.
In addition, the real time telemetry from the F1 machine which runs the course is strictly regulated by the FIA. The line speed with the pit is limited to 2 Mbps, and high precision data from the machine with about 200 sensors is stored in the engine control unit (ECU) of the machine and touches the data until the end of the race It is not allowed. In the current regulation, it is only talking with the driver wirelessly that the pit crew can do.

Nonetheless, obtaining meaningful information from raw data from 200 sensors is totally an area of data science. The information gained on weekends from two machines is as much as 35 billion data points, it is indispensable for data analysis professionals to analyze, and in Renault F1 we collaborate with Microsoft to analyze the data through Azure machine learning . It seems that each team contracts with a different cloud computing provider and conducts huge data analysis with different modeling. In addition, Ars Technica told the mechanics of Renault F1 that he was not taught as a top secret when he asked "Are you sure you want to strengthen by machine learning?" This information seems to be a sensitive area that could bring about improvements in machine performance and reliability over the next few years.
The F1 team, which develops the fastest machine in the world, is full of what is regarded as a trade secret, but in reality it is impossible to completely keep it secret. The cause is that most teams are based in the UK based on the geographical proximity, as well as F1 officials such as mechanics and drivers are aware of each other and information exchange is flourishing. In addition, it is difficult to keep important information for a long time secret since the transfer among excellent engineers team is also active. As Mr. Simmons said, "The important thing is" time "anyway," the F1 development team is that each engineer works hard on their own timeline to develop technologies that outstrip other teams, In order to do it we have to keep improving, "Simmons said.

Related Posts: