Algorithms for placing sound effects according to images in deep learning have appeared, and when sound is added to images, this is

If you are a human being, it is not too difficult to imagine the sound of grass "Gasagasa" or the sound of a wooden desk "Con" based on the image you saw, but evolution is remarkableDeep learningTechnology, it is becoming possible to make such a sensory prediction also for computer algorithms. At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's (MIT) Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Lab (CSAIL), research has been conducted to show the video to a computer that had previously learned the relation between video and sound and predict the sound that sounds to be actually heard It seems that it is now possible to put sound effects on images with high precision.
Visually-Indicated Sounds - YouTube
Sounds that hit "trembling" with wooden bars with wooden sticks ... ...

The sound of hitting a steel rack "gon"

Puddle as a "pasha" ...

The glass bowl is "Chin"

A thick reference book is "Bakku"

In the case of mugs, in addition to the visual information entering from the eyes, like "chin", the information of the hearing coming into the ear plays a very important role in recognizing the situation the person is currently in.

CSAIL develops an algorithm that learns and predicts the sounds that can be heard from the video in this way. This algorithm learns the relation between video and sound based on the sound of 46,000 patterns included in 1,000 movies given as a material and then predicts sound from silent video given as a task Then, it is possible to give the sound that will be closest. Analysis of sounds includes subjective elements, not frequency and volumepitchWhenloudnessIt is said that the scale of is used.

In the algorithm, regression analysis is performed on images given by a "neural network" that imitates the structure of the human brain, and collated with pre-stored databases to find the one that seems to be the closest.

By fitting the sound to individual places, the image as if a real sound is coming out is completed.

Initially it is silent video showing what kind of sound was actually synthesized. In this example, the sound is applied to the image to be implanted with drum sticks, but in the case where the sound of striking the ground of dead leaves as in the right screen is synthesized ... ....

There are cases where almost the same kind of tapping tapes are selected.

If I think about it, why is the sound hitting the table or why ... ...

A tree stump ...

There are cases where something like a plastic bag is chosen. In this way, there seems to be room for improvement in terms of accuracy, but when I actually look at the picture, I am surprised that it is in a state with less discomfort. Also note that the difference between when you hit the object and when you stroke the surface is reproduced.

For the image hitting a rail of a tree, sounds hit by a cold water machine were synthesized ......

The sound of the tree table was synthesized.

Somehow, scenes synthesizing the floor of the elevator hall as well. It may be said that the characteristic of the algorithm that searches for near sound by judging only the sound itself unlike human beings is well represented in this area.

Furthermore, using this algorithm, it is also possible to synthesize sound effects based on the analysis result of video. This means that it will be possible not only to synthesize sound but also to understand what elements were extracted from the image.

The sound of striking the chair back ... ...

It seems that sounds such as beating fallen leaves are synthesized. If there is some sound that seems to be due to the original sound, it is expected in the future that there is also a sound that "thinks"?

It seems that we are not good at making sounds on the surface of the water.

Also, since it produces sound based on video, it sounds at the timing that should not be due to misrecognition. In this video, the hit sound is attached even when you stick up the stick.

The research team showed the subjects both the image of the original sound and the image the sound of which the sound was given to the subjects to see how realistic the sound is attached, and conducted a survey to have the subject judge which sound is right. Then, it is said that the result that humans makes 2 times wrong judgment than algorithm. In particular, it was said that many mistakes were seen in cases like falling leaves and it was said that the correct answer rate was high for "simple" sounds like striking the table with a stick.

What is noteworthy in this technology is that AI (artificial intelligence) caused by deep learning makes judgments judging across two senses, "image" and "sound", that is, visual sense and auditory sense. Abhinav Gupta, Associate Professor of Carnegie Mellon University Robotics Engineering says, "While current AI technology targets only one sensation from among the five senses that human beings have, it is important that both auditory and visual It can be said that this research to deal with the correct direction in mimicking the process by which humans learn sensory learning, "he says the results of the research.
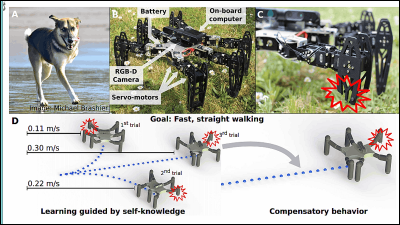
As this technology develops, it is thought that it not only adds sound to images, but also judges the state of the ground from the captured images and sounds, and leads to development of AI to determine how the robot walks It is done.
Along with predictive judgment, algorithmic techniques have also been developed to predict behaviors after 1 second, including predicting human behavior from images as follows, "shaking hands after this" and "hugging after this" .
Action-Prediction Algorithms - YouTube
Related Posts: