Mechanism that the brain's neuro substance "dopamine" makes people more impulsive
There are various types of human personality, from a patient who is patient, a person who shows a short-tempered impulsive reaction. In particular in the case of impulsive reactions occur in the brainDopamineIt is said that the work of the person has an important meaning.
Why Dopamine Makes People More Impulsive - Knowing Neurons
http://knowingneurons.com/2016/03/10/dopamine-makes-people-impulsive/
So farDopamineIs the brain'sReward systemIt has been known to play an important role in. This is one of the functions of the brain that feels pleasure when desires are satisfied, and this pleasure is thought to play a major role in judging decisions and behaviors.
At the same time, however, understanding is progressing about another influence that dopamine brings. There is a phenomenon that personality is impulsive to people who have increased levels of dopamine, which is one of the features that is common among people suffering from Parkinson's disease. People with Parkinson's disease often show impulsive reactions to behaviors such as gambling, shopping, or eating. Also, this is a symptom also found in addicts such as alcohol and cocaine, has been confirmed to cause impulsive behaviors by releasing a lot of dopamine in the brain.
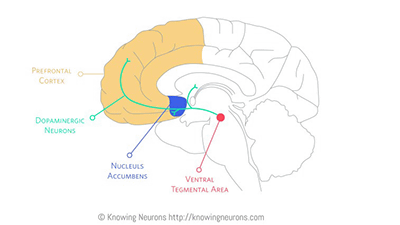
Brain sites important for the function of dopamine,Ventral tegmental areaIt is a part called "congestion hinaga". Neurons related to the function of dopamine are gathered at this site, and it is thought that it is a part forming the brain's compensation system.
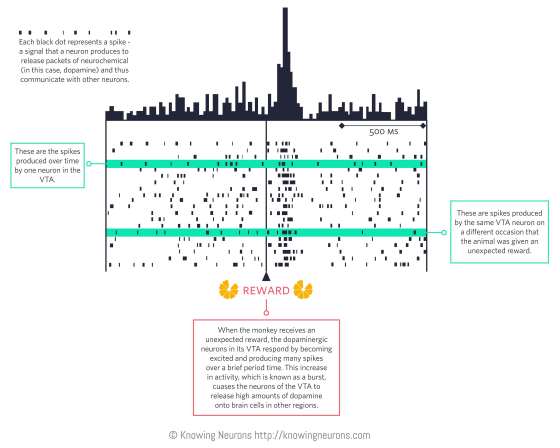
The graph below shows electrical records of monkey's brain activities. In monkeys' brains given fruits at the timing of "REWARD (reward)", dopamine related neurons in the ventral dental cortex are emitting a lot of spikes (sudden electric pulses), and the function of the reward system You can see that it is becoming active.
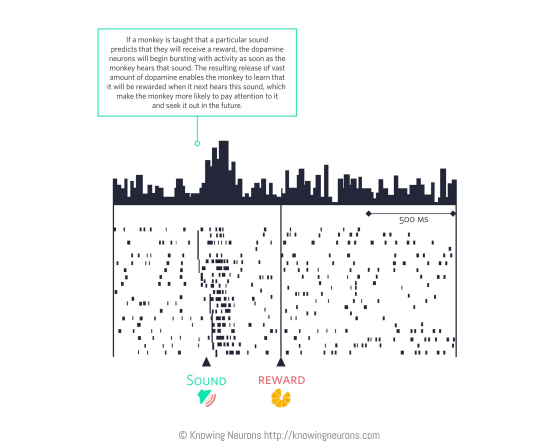
The reaction also occurs when a stimulus related to actual reward is given. The following graph shows the reaction when you let a certain sound related to actual rewards be heard but in the monkey's brain a lot of spikes occurred when hearing the sound, "sound = You get a feeling of pleasure from the reward system that you get fruits "occurs before the actual reward.
It turns out that spikes are caused by the stimulus associated with the reward, but it turns out that when the stimulus and actual reward time are extended for a long time, the reaction becomes weak. The following graph shows the response when giving a reward 2 seconds, 4 seconds, 8 seconds after the stimulation when performing the same experiment, but it got used to the reward after 8 seconds from stimulation In the group of monkeys ("8s delay" below), you can see that it does not show a reaction even if it is stimulated by sound.
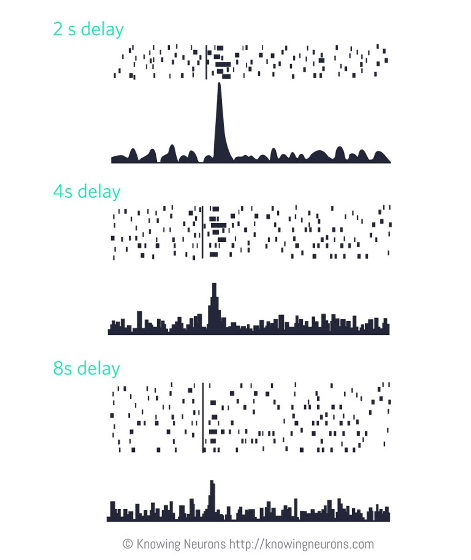

This is called "value discount due to delayed compensation", a phenomenon that pleasure due to reward weakens as the time from stimulation to reward increases. And how to feel this value discount depends on the level of patience strength of each person.
The graph below is a graphical representation of the reaction when we asked the human, "Would you like to earn 20 dollars now or 40 dollars in 6 months? Although it is a simplified graph, here we can see that the reactions differ greatly depending on the three types of personality (Personality Type): Patient (Patient), Average (Average), Impulsive (Impulsive) I will. People who are Patient judge that rewards after a long period of time are of great value, while Impulsive people can not wait, so we can show you the response that we want to get paid now as the amount of money can be small That is why.

And this trend is known to be related to the release of dopamine. The graph below creates dopamine in the bodyL-DOPAI showed how delayed discounts occur between the subjects who received the placebo and the subjects who received the placebo (placebo). However, subjects who were given L-DOPA, that is, a large amount of dopamine released It is known that there are many delayed discounts, that is, subjects being tended to show an impulsive reaction.
It plays an important role in the function of dopamine, it stimulates the brain's reaction by binding with dopamineD2 receptorIt is a neurotransmitter called.
D2 receptor has a function to promote inhibitory action by binding with dopamine. In the impulsive human brain, since the function of the D2 receptor is weaker than that of the normal human's brain, the function of suppressing the impulses of the brain is weakened, resulting in impulsive feelings and actions as a result I will. Also, if the release of dopamine is greater than that of normal people, the same reaction will occur. Also,psychopathPeople say that similar signs can be seen.

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log







