Does the speed reduction caused by '2DPC', which inserts two memory modules to increase memory capacity, affect content creation performance?
When configuring a workstation with a consumer-class CPU, striking a balance between memory (RAM) capacity and speed is a key consideration. It's known that when operating in ' 2 DIMM per Channel (2DPC) ' mode, where two memory modules are installed in each of two channels to increase memory capacity, the maximum supported memory frequency decreases.
Does 2 DIMM per Channel RAM Impact Content Creation Performance? | Puget Systems
https://www.pugetsystems.com/labs/articles/does-2-dimm-per-channel-ram-impact-content-creation-performance/
Many consumer PCs have four dual inline memory module (DIMM) slots, but the CPU itself only has two memory channels. When two DIMMs are connected to each memory channel to accommodate more than three DIMMs, the system enters '2DPC mode,' which reduces the maximum supported memory frequency.
Below is a table showing the difference in memory speed between 1DPC frequency (one memory card per channel) and 2DPC frequency (two memory cards per channel) for a PC equipped with Intel's Core Ultra 200 (left) and AMD's Ryzen 9000 (right). In both cases, we can see that the maximum frequency drops significantly when switching to 2DPC frequency.
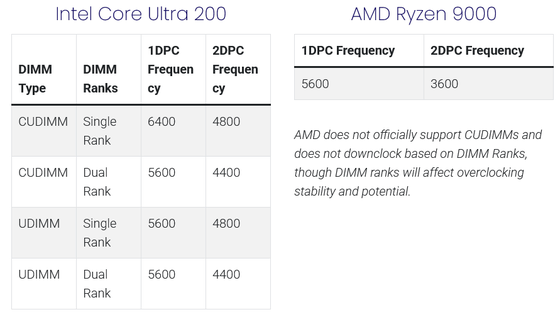
In short, memory capacity is important even in environments with consumer CPUs, but if you increase the RAM capacity by inserting two memory modules per channel to ensure sufficient memory, there is a trade-off: the electrical load increases and speed may decrease.
To determine the extent to which the memory speed reduction caused by this 2DPC configuration affects work, Puget Systems conducted tests using the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K and AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D with several creative applications. These applications included media editing software such as
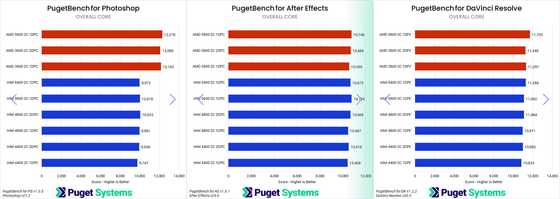
The results of the study showed that for media editing software, the performance impact of 2DPC was negligible. Below are the results for Adobe Photoshop (left), Adobe After Effects (center), and DaVinci Resolve (right). For Intel, the average performance degradation was only about 2% when switching from a 1DPC memory frequency of 6400MT/s to a 2DPC frequency of 4400MT/s. Puget Systems concluded, 'We believe these results are accurate to within 1% accuracy, but from a user experience perspective, a 1% difference is not significant. Users of applications in these media editing software categories should not be concerned about a reduction in RAM speed due to increased DIMMs.'
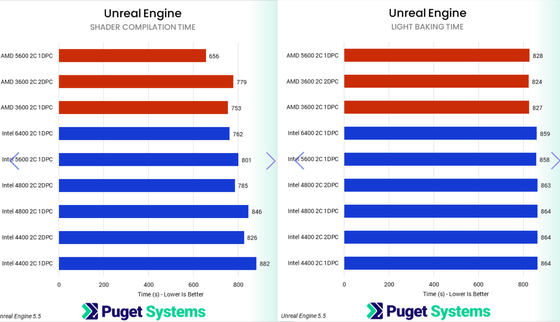
Next, the graph for Unreal Engine is below. Because Unreal Engine involves real-time processing, AMD is particularly dependent on memory speed, with a 2DPC configuration impacting performance by up to 13%. For Intel, a 2DPC configuration can be up to 8% slower than a 1DPC configuration, Puget Systems points out, 'This should be taken into consideration when determining system configuration for real-time processing.'
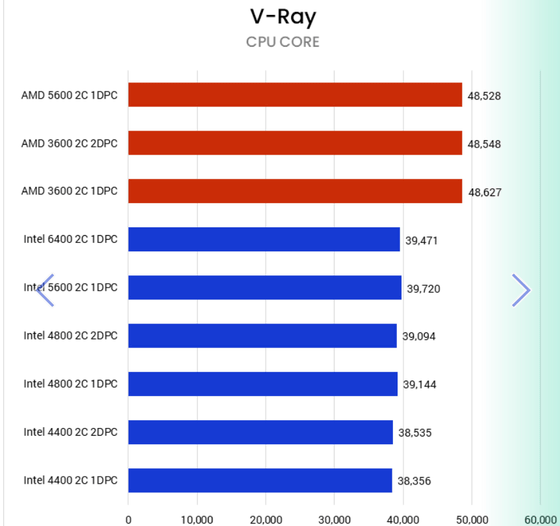
For CAD and renderer applications that place a significant load on the CPU, the maximum performance degradation when switching from a 1DPC to a 2DPC configuration was about 5%. For these applications, maximizing RAM capacity is more important than RAM speed, so switching to a 2DPC configuration is not likely to be an issue for most users.
In addition, when benchmarking large-scale language models, the difference in performance between RAM configurations was limited for AI running natively on the CPU. For AI primarily using the GPU, the CPU still provided data, which impacted memory bandwidth. However, the 2DPC configuration slowed token generation by up to 25% on Intel and 12% on AMD.
Below is a table showing the speed scores for each memory configuration, with the officially supported maximum speeds of Intel's 5600MT/s and AMD's 5200MT/s set to 100. As a general trend, we found that Intel Core Ultra is more susceptible to performance impact from RAM frequency than AMD Ryzen.
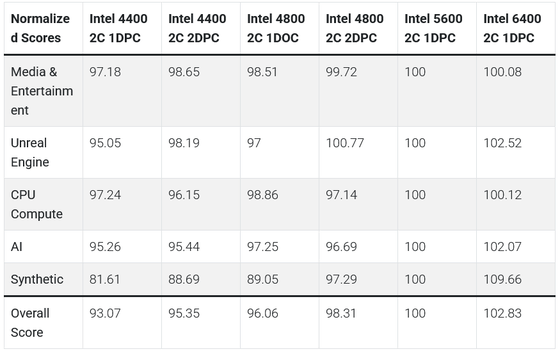
Puget Systems advises, 'The magnitude of the performance impact will vary depending on the CPU and the workload, but the basic premise is that insufficient memory capacity will significantly degrade performance. Users should first evaluate the memory capacity required for their workload, and then, if larger memory capacities are required, consider migrating to 2DPC while taking into account the performance degradation rate. It is also important to note that, in general, using two larger-capacity DIMMs is more effective than using four smaller-capacity DIMMs.'
Related Posts: