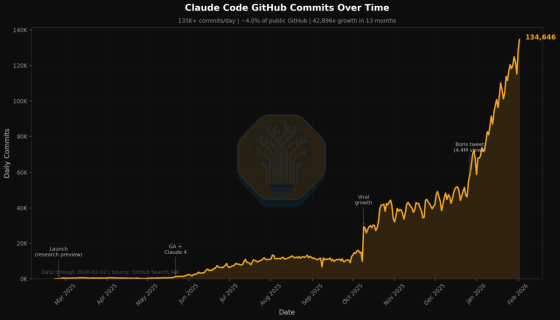
Claude Code accounts for 4% of GitHub's public commits and is expected to exceed 20% of daily commits by the end of 2026

With the advent of
Claude Code is the Inflection Point - SemiAnalysis
https://newsletter.semianalysis.com/p/claude-code-is-the-inflection-point
SemiAnalysis emphasizes that 'the main role in development is changing.' Instead of sitting next to the person writing the code and providing advice, Claude Code can handle the entire project from a terminal, proposing multiple changes at once and implementing them if necessary. In other words, with Claude Code, instead of a human writing code line by line by hand, Claude Code advances the entire process, and the human spends more of their time communicating the objectives and inspecting and correcting the results.
To illustrate this shift, SemiAnalysis estimates that as of February 2026, 4% of public GitHub commits will be created by Claude Code.
Furthermore, if the rate of increase from the introduction of Claude Code to February 2026 continues at this rate, it is possible that 'more than 20% of daily commits will be from Claude Code' by the end of 2026. The graph below shows how the percentage of commits from Claude Code has increased over time and its future outlook.
This change will mean that human engineers will have to do less 'writing' and more 'verifying.' The more AI can generate large amounts of code, the more humans will be required to 'communicate requirements in a way that cannot be misunderstood,' 'find and specifically point out any deviations from the intention,' and 'verify operation and safety.'
SemiAnalysis also expects these changes to extend beyond coding to a wider range of information-handling jobs. The process of 'reading documents, making judgments, summarizing them in text or tables, and then confirming the content and finalizing' is common not only in development, but also in research, clerical work, analysis, report writing, and more. If AI types like Claude Code, which 'are given a goal and can assemble and proceed with the steps along the way,' become more common, there is a possibility that we will see an increase in situations where AI will be entrusted with comprehensive tasks rather than just answering one-off questions.
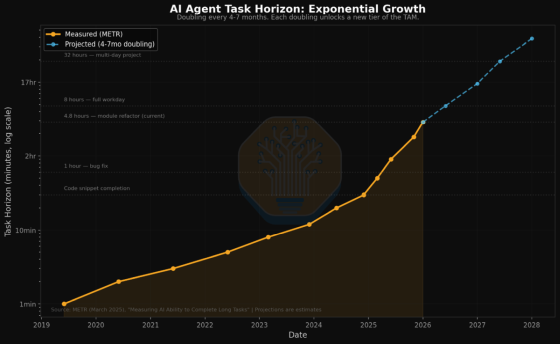
Another important aspect that SemiAnalysis considers important is how long an AI can continue a task without breaking down. SemiAnalysis calls this the 'task horizon,' and believes that the longer an AI can operate autonomously, the more work it can be entrusted with, expanding from small 'assistance' tasks to larger 'processes.'
If it can only complete short tasks, it will be considered a secondary tool, but once tasks lasting several hours to several days become a reality, the range of work that can be replaced by AI will expand dramatically. The graph below shows how this is expected to continue for an extended period of time.
If AI, available for a monthly fee, can reduce work time compared to manual methods, it will be easier for companies to adopt AI. Conversely, SemiAnalysis concludes that if AI can create deliverables without relying on traditional work flows that require people to operate a screen, it could change the very design of work and the value of software.
Related Posts:
in AI, Posted by log1b_ok