Newly discovered eye cells may help restore vision

Researchers in China have reported that they have discovered a new type of cell that was previously unknown to exist in human fetal retina samples, and when they grew the newly discovered cells in a petri dish and transplanted them into mice with eye disease, they were able to restore the mice's vision.
Identification and characterization of human retinal stem cells capable of retinal regeneration | Science Translational Medicine
New cells discovered in eye could help restore vision, scientists say | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/health/anatomy/new-cells-discovered-in-eye-could-help-restore-vision-scientists-say
The retina, located at the back of the eye, plays an important role in detecting light and converting it into signals for the brain. If the retina deteriorates or becomes damaged due to aging, diabetes, injury, etc., it can lead to diseases such as macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa , or even blindness.
Current treatments for these diseases are based on preserving surviving cells as much as possible, and no fundamental treatment has been established to regenerate lost retinal function.
In a study published in Science Translational Medicine, a medical journal published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science on March 26, 2025, a research team led by Hui Liu of the Hospital of Ophthalmology and Optometry, Wenzhou Medical University, China, announced that they had found two types of cells in fetal retinal samples: 'human neural retinal stem cell-like cells (hNRSCs)' and 'retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) stem cell-like cells.'
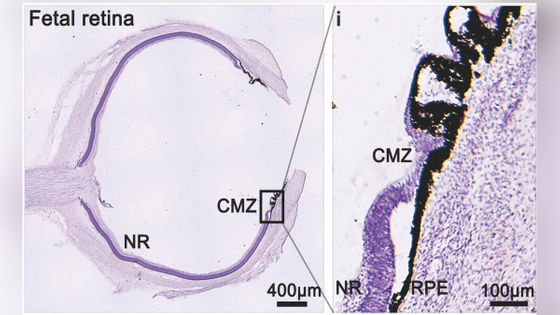
by Jianzhong Su, State Key Laboratory of Eye Health, Eye Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University
Stem cells are cells that can grow into any type of cell in the human body under the right conditions. It is hoped that the retina can be regenerated by replacing deteriorated cells with stem cells, but suitable human retinal stem cells for this purpose have not yet been found.
After confirming that these cells, located at the outer edge of the retina, could self-renew and that under the right conditions, hNRSCs could transform into other retinal cells, the team next grew human stem cells in a petri dish to create a replica of the retina.
' Organoids ,' which are miniature versions of human organs cultured as three-dimensional tissues, are more accurate at replicating human organs than conventional animal models, and another study in the past has even shown that human brain organoids can develop eyes.
Lab-grown human 'mini brain' grows eyes, reacts to light - GIGAZINE
By Elke Gabriel
When the team analyzed the resulting 'retinal organoids,' they found that they contained hNRSCs similar to those found in the fetal samples, and they also identified a series of genetic mechanisms that control the repair process by transforming the stem cells into other retinal cells.
When the organoid-derived stem cells were transplanted into mice with retinitis pigmentosa, the cells differentiated into the mouse's retinal cells and significantly restored the mice's vision.
Although more research is needed to see if the same treatment can be applied to humans, the technique of regenerating the human retina using cells found in the human retina is seen as a promising new approach in regenerative medicine.
'This study not only deepens our understanding of retinal cell biology, but also has great potential for advancing therapeutic interventions for retinal degenerative diseases,' the team wrote in their paper.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks