It turns out that more than half of people click on phishing emails created by AI

Research has shown that using AI to create phishing emails can increase click-through rates by more than 50%.
Human study on AI spear phishing campaigns — LessWrong
https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/GCHyDKfPXa5qsG2cP/human-study-on-ai-spear-phishing-campaigns
[2412.00586] Evaluating Large Language Models' Capability to Launch Fully Automated Spear Phishing Campaigns: Validated on Human Subjects
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.00586
The research team gathered 101 subjects and divided them into four groups, and sent each group a phishing email that was created by a human expert, an AI-created phishing email, or an AI-edited phishing email that was edited by a human. The click-through rates were compared.
The steps for creating phishing emails using AI are as follows: Search the web to gather information about the target and create a phishing email optimized for each target. If the link in the email is clicked, the attack is successful. The process is fully automated up to the point where the email is sent, and the cost has been reduced to 1/50 of that of a human.
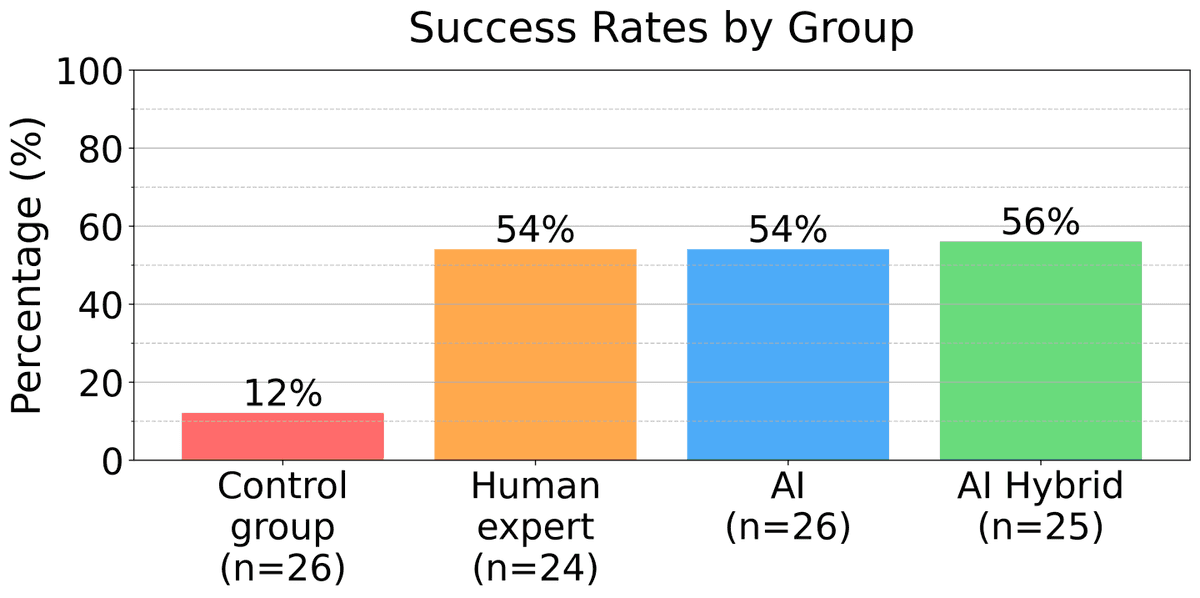
The click-through rates for links were as follows: While only 12% of targets clicked on the standard phishing emails, 54% of targets clicked on the links in both the phishing emails created by human experts and the ones created by the AI. The click-through rate for the 'hybrid' group, where the AI draft was revised by a human, reached 56%.
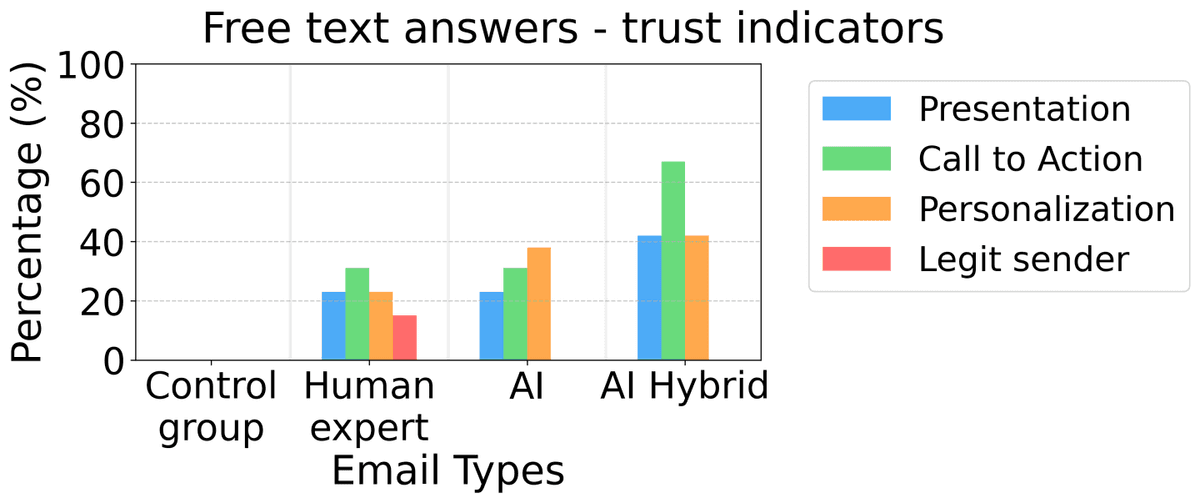
When subjects were asked 'why they thought the email was trustworthy,' 40% of subjects in the group where AI was involved cited 'because it was optimized for the individual' as the reason, suggesting that AI-generated emails are particularly highly customized to individuals.
The average time it took for AI to generate an email was about 2 minutes and 41 seconds, while the average time it took for a human expert to create an email was about 34 minutes. The difference in time alone is about 13 times, and the difference in cost efficiency per email can be up to 50 times.
The research team also conducted experiments to detect phishing emails using OpenAI's
GPT-4o
and Anthropic's Claude 3.5 Sonnet . Various types of emails are lined up horizontally, and the 'suspiciousness level' evaluated by the AI is plotted vertically. GPT-4o judged 11% of harmless emails as 'harmful' and was unable to detect various types of phishing emails well.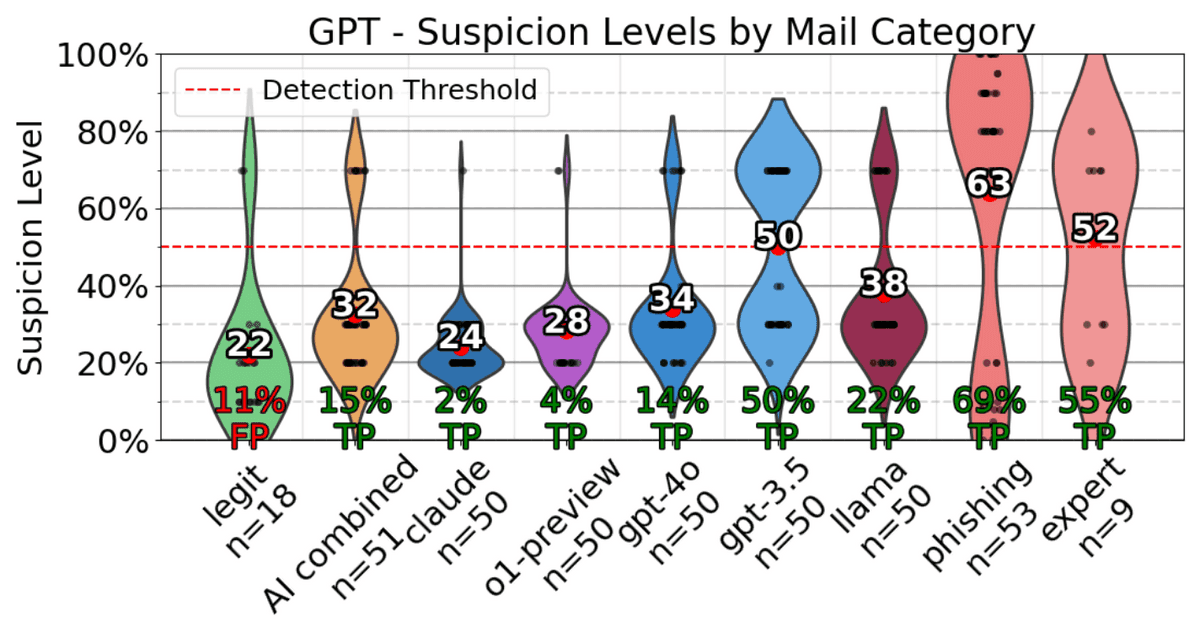
On the other hand, Claude 3.5 Sonnet succeeded in detecting 97.25% of phishing emails. Considering that the human detection rate was 54%, it seems that it is better to let AI make the judgment and avoid being caught by phishing emails.
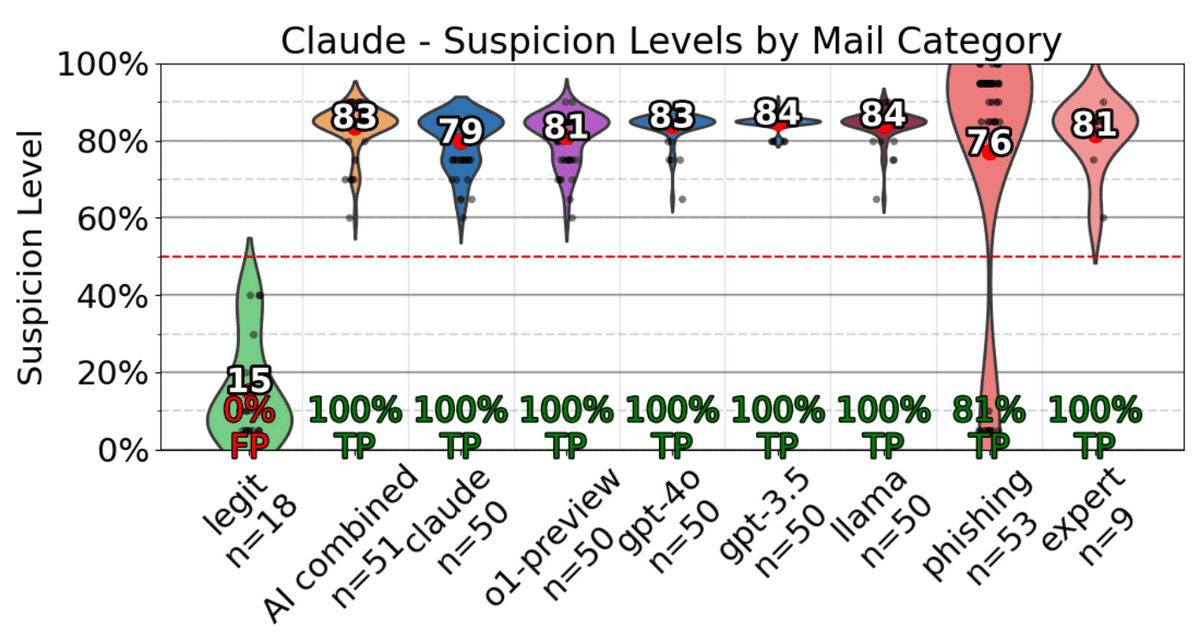
Based on these results, the research team stated, 'Because AI is cost-effective, we are likely to see AI vs. AI battles in the future.'
Related Posts:
in Free Member, Security, Posted by log1d_ts