OpenAI announces it has blocked accounts using ChatGPT to generate disinformation on multiple topics, including the presidential election.

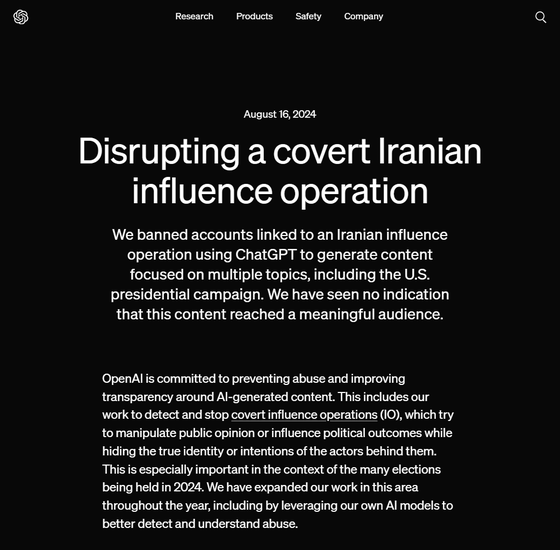
On Friday, August 16, 2024 (local time), OpenAI announced that it had detected and blocked accounts using ChatGPT to generate false information about multiple topics, including the US presidential election. However, there is no indication that the content generated by ChatGPT has been posted in public view of the general internet user base.
Disrupting a covert Iranian influence operation | OpenAI
OpenAI disrupts Iranian operation that used ChatGPT to for disinformation
https://www.axios.com/2024/08/16/openai-iran-disinformation-chatgpt
OpenAI is committed to preventing the misuse of AI-generated content and improving transparency. This includes efforts to detect and disrupt influence operations that attempt to manipulate public opinion or influence political outcomes while concealing the true identities and intentions of those behind them. With elections scheduled for 2024 around the world, disrupting influence operations will be particularly important. Therefore, OpenAI has been working to properly detect misuse using its proprietary AI models.
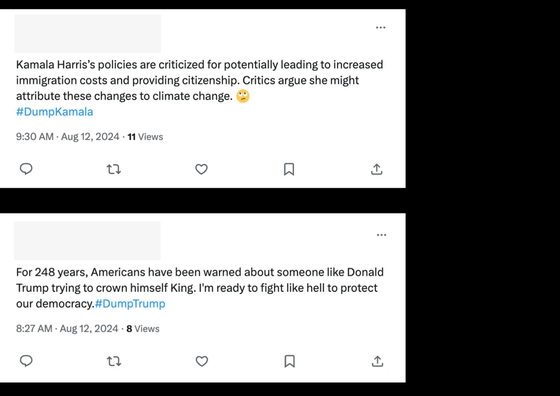
The company announced that it had blocked the account's access to ChatGPT after its fraud detection AI model detected an influence operation known as ' Storm-203 ,' which was generating disinformation aimed at influencing the US presidential election. Storm-203 reportedly used ChatGPT to generate disinformation focused on a variety of topics, including comments about candidates on both sides of the US presidential election, and shared it via social media and websites.
However, OpenAI found that the majority of social media posts containing disinformation created by Storm-203 using ChatGPT were 'posts with little impact,' with few likes, shares, or comments. OpenAI uses '
In Storm-203, ChatGPT was found to be used for 'creating long-form articles' and 'creating short social media comments.' In the 'creating long-form articles' segment, articles were created primarily about American politics and world affairs, and disinformation articles were published on five websites posing as both progressive and conservative news organizations. In the 'creating short social media comments' segment, short comments were created in English and Spanish and posted on social media. Storm-203 was found to have used 12 X accounts and one Instagram account, and some of the comments posted by these accounts were apparently rewritten by ChatGPT from actual social media users.
Storm-203 primarily generated content related to the Gaza conflict, Israel's presence in the Olympics, and the US presidential election. Other topics included Venezuelan politics, Latino rights in the US, and Scottish independence. OpenAI noted that the political content was interspersed with commentary on fashion and beauty, likely a ploy to disguise the AI-generated content or to gain followers.
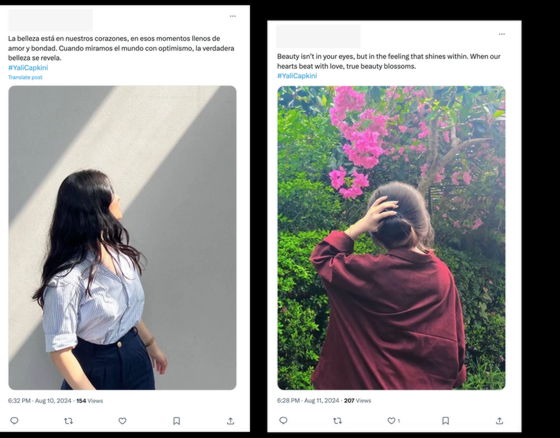
When news media Axios inquired about this incident, Meta responded that the Instagram account in question was disabled and that the attack was related to an Iranian disinformation campaign carried out in 2021 targeting Scottish users.
Axios has also reached out to X for comment, but has not received a response at the time of writing. However, OpenAI noted that all of the social media accounts in question were 'inactive' at the time of writing.
Related Posts:
in AI, Web Service, Posted by logu_ii