AI successfully analyzes electromagnetic waves leaking from HDMI cables to read video

HDMI is an interface standard for transmitting video and audio digitally, and is mainly used to connect televisions and hard disk recorders, or game consoles and PCs to monitors. A research team from
[2407.09717] Deep-TEMPEST: Using Deep Learning to Eavesdrop on HDMI from its Unintended Electromagnetic Emanations
https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.09717
Security researchers reveal it is possible to eavesdrop on HDMI cables to capture computer screen data
https://techxplore.com/news/2024-07-reveal-eavesdrop-hdmi-cables-capture.html
AI can see what's on your screen by reading HDMI electromagnetic radiation | TechSpot
https://www.techspot.com/news/104015-ai-can-see-what-screen-reading-hdmi-electromagnetic.html
When video and audio were transmitted as analog signals, it was relatively easy for hackers to analyze the electromagnetic waves leaking from video cables and reproduce the screen. With the spread of digital protocols such as HDMI, the difficulty has increased significantly, but a certain amount of electromagnetic waves still leaks out when transmitted through an HDMI cable, which allows hackers to intercept the video.
The team trained their AI system using the electromagnetic waves leaking from the HDMI cable and the image transmitted through the cable. As the AI was trained, it was gradually able to reproduce an accurate image from the electromagnetic waves leaking from the HDMI cable.
To test the accuracy of the AI, the research team applied text recognition software to the image that the AI had reconstructed from the electromagnetic waves leaking from the HDMI cable and compared the extracted text with the original image transmitted by the HDMI cable. As a result, the text was reproduced with about 70% accuracy, 60 points higher than conventional methods. Although this accuracy is not perfect, it is enough to understand the gist of the text displayed on the screen, and the research team claims that it may be possible to intercept passwords and confidential data.
The video below shows this attack technique, named 'Deep-TEMPEST,' in action.
Demo of deep-TEMPEST - YouTube
The monitor in the back shows the footage to be intercepted, and the one in the foreground is the laptop used in the attack.

It uses an antenna and software-defined radio to capture the electromagnetic waves leaking out of the HDMI cable.

Deep-TEMPEST saves time by performing a mathematical analysis of the signal beforehand.

After waiting a few seconds, a screen similar to the one being transmitted over the HDMI cable appeared on the attack laptop.
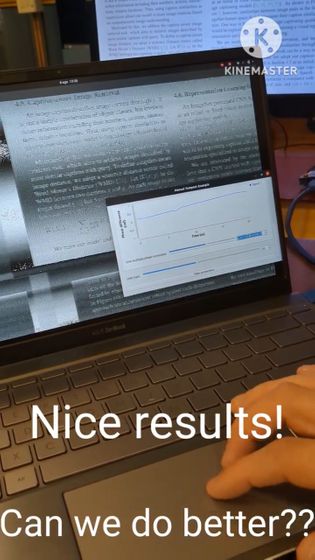
By applying text recognition software to this, it becomes possible to read the text with a fair degree of accuracy.

The researchers note that hackers may already be carrying out similar attacks against government agencies and sensitive industrial facilities, but they say it's unlikely that households are being targeted because of the high hurdles involved in deploying the necessary AI models and signal-capture equipment.
'Governments are concerned about this attack, but it's not something that ordinary users need to worry about,' said Federico Larroca of the University of the Republic of Uruguay, a co-author of the paper. 'But if you're really concerned about security, whatever your reason, this attack method might be a problem.'
Related Posts: