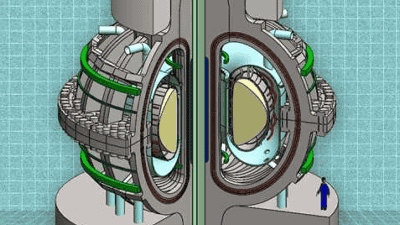
A project is underway to store surplus energy from wind and solar power generation as heat with a huge 13m-tall 'sand battery'

In order to stop the progress of global warming, it is essential to generate electricity using renewable energies such as wind and solar power. However, these power generation methods that rely on nature have the disadvantage that it is difficult to always generate electricity at a constant output, so in order to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy, storage batteries that store the generated electricity in the form of energy are needed. (battery) is required. In a new move, Finnish energy storage startup Polar Night Energy has announced that it will build a giant 13m-tall 'sand battery' that will store excess energy in the form of heat.
Loviisan Lämpö Invests in Polar Night Energy's Sand Battery in Pornainen – Towards Non-Combustion Heat Production — Polar Night Energy

'A very Finnish thing': Big sand battery to store wind and solar energy using crushed soapstone | Euronews
https://www.euronews.com/green/2024/03/10/sand-batteries-could-be-key-breakthrough-in-storing-solar-and-wind-energy-year-round
Giant 'sand battery' holds a week's heat for a whole town
https://newatlas.com/energy/sand-battery-finland/
What Is a Sand Battery? Polar Night Energy's Sand-based Thermal Energy Storage Explained - YouTube
Polar Night Energy is a startup founded in Finland in 2018. Founder Markku Ylönen says, ``We were talking about how if we had the freedom to design communities for ourselves, how could we solve energy problems in a limited environment? Especially in Finland. 'In northern countries like this, if you try to produce as clean energy as possible, you quickly run into problems with energy storage.'
While considering ways to store surplus electricity generated with renewable energy, Ylönen and his colleagues discovered that it is efficient to store energy as heat in ``sand grains''. Based on this idea, Polar Night Energy has developed a 'sand battery' that can store energy for long periods of time and release it on demand.
Polar Night Energy's sand batteries consist of large quantities of sand or similar solid material packed into a steel thermal silo with an embedded heat exchanger. Surplus electricity generated from renewable energy is converted into thermal energy using electrical resistance, which is then circulated through a heat exchanger in the form of hot air to heat the sand, allowing the sand to retain heat of around 500 degrees Celsius for several months. He says he will save it.

Ylönen says, 'There's nothing fancy about sand batteries. The complicated part happens on the computer. How the energy, or heat, moves inside the storage, how much heat is available, how much 'You can always know if it is possible to release and fill at the same rate.'
Theoretically, it is possible to convert the stored thermal energy back into electrical energy and supply it, but it is more efficient to use the thermal energy as is. Polar Night Energy has developed a system that connects sand batteries to the heating network of a community or facility, releasing thermal energy to be used for space heating or hot water supply as needed.

In 2022, a sand battery prototype measuring 7m high and 4m wide, capable of storing up to 8MWh of thermal energy, began operation in Kankanpaa , western Finland.
World's first commercial ``sand battery'' begins energy storage in Finland - GIGAZINE

On March 7, 2024, Polar Night Energy announced that it had signed a contract with Loviisan Lämpö, a district heating company, to build a new gigantic sand battery measuring 13 m high and 15 m wide in Pornainen , southern Finland. did. The sand batteries in Polnainen can store up to 100 MWh of thermal energy and will be connected to Loviisan Lämpö's district heating network.
Once Polniainen's sand battery is in operation, it will be possible to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 160 tons per year, equivalent to 70% of the total emissions of district heating networks. It is also expected that not only will the use of oil in district heating networks be completely cut, but the amount of wood chips burned will also be reduced by around 60%. According to Polar Night Energy, the heat storage capacity of the sand battery in Polniainen is equivalent to the heat demand for about one month in summer and one week in winter across the entire Polniainen area.
The Polunainen sand battery is estimated to take approximately 13 months to construct and test, and is scheduled to be operational from winter 2025.
Related Posts: