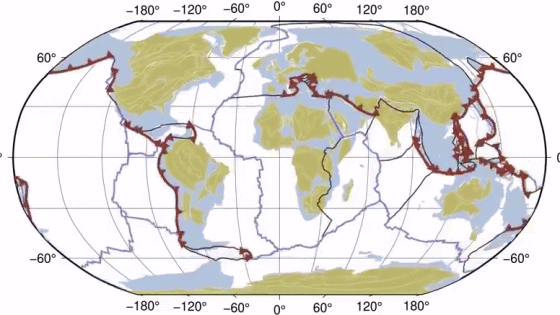
A science video that looks back at the 4.5 billion year history of the Earth

The Earth was born about 4.5 billion years ago, but even though it is said to be 4.5 billion years old, it still doesn't make much sense. Kurzgesagt, who creates many science-related videos, has created and released a video that looks back on the Earth's 4.5 billion years in one hour.
4.5 Billion Years in 1 Hour - YouTube
4.5 billion years ago, the Earth was new and full of lava. The Earth then collided with a Mars-sized object called Theia, which is thought to have formed the modern moon.

It is said that water existed around 90 million years after the Earth's birth. Measuring the oxygen isotope ratio of a mineral called zircon, which is thought to have been formed during this period, reveals the possibility that there was water near the surface at that time.

In any case, the Earth has been hit by numerous asteroids since its birth. Hundreds of millions of years after its birth, the earth's surface was still hot, but it is believed that this is where the primordial cells began to spread across the earth.

The Earth then continues to cool, and over millions of years it begins to rain, covering the still young Earth with water. This began in an era called

At this time, most of the Earth was still underwater and the first supercontinents were forming deep within. Sedimentary rocks called stromatolites , which are thought to have been constructed during this period, have been found even today, and research is being conducted as a clue to estimating the exact moment when life was born on Earth.

Fast forward to about 3.2 billion years ago, when tectonic plates collided with each other, pulled together, and some were pushed deep into the Earth's core and dissolved. This is the foundation of today's continent. This was a time when the ocean was as hot as hot water, exceeding 40°C, and microorganisms began to spread everywhere. There were still no plants consuming greenhouse gases, and it was very hot everywhere. There is also no oxygen in this atmosphere yet.

2.8 billion years ago, the Earth was still in an extremely harsh environment, but more and more chemical substances emerged from within the Earth, and life evolved using them. During this period,

2.5 billion years ago, an event occurred that drastically changed the Earth. Around this time, the atmosphere became saturated with oxygen released by photosynthetic cyanobacteria, and life became even more diverse. Oxygen in the air reacted with methane to form carbon dioxide and water, rapidly cooling the planet. From here on, ice ages will continue for hundreds of millions of years.

About 2.3 billion years ago, volcanic activity increased, heating the Earth and causing the ice to slowly melt. Two billion years ago, a huge asteroid collided with the Earth, creating a huge crater that still remains today. Large mountain ranges were also created due to tectonic movements.

1.6 billion years ago, eukaryotes with cell nuclei began to appear. One of the most important moments in the history of life.

1.4 billion years ago, the Earth's inner core finally formed, and 1 billion years ago, the Earth was filled with oceans.

After that, large eukaryotes were born one after another over hundreds of millions of years, but the earth froze again 720 million years ago. We don't know how life survived during this time.

635 million years ago, the supercontinent

The ancestors of today's major animals appeared during this period, and plants expanded onto land. As plants spread throughout the earth, soil was created on the ground, and the carbon dioxide that covered the earth was converted into oxygen. Trees, forests, and underwater life are born, and the first vertebrates come onto land.

During

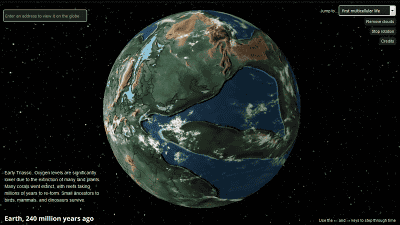
About 252 million years ago,

After that, dinosaurs became extinct. Approximately 66 million years ago, during

Related Posts: