Scientists propose that Saturn's moon Enceladus has all the building blocks for life

by
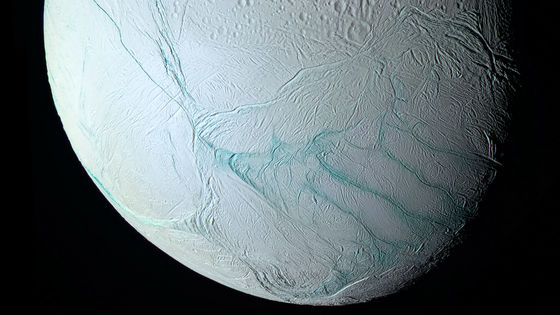
Enceladus , a satellite of Saturn, has been found to contain water , organic compounds , and hydrogen , which are important for life, and is considered a promising star with the possibility of extraterrestrial life. A new study finds that Enceladus may have an environment suitable for life.
Observations of Elemental Composition of Enceladus Consistent with Generalized Models of Theoretical Ecosystems | bioRxiv
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.10.29.564608v1.full
Enceladus has All the Raw Materials for Life - Universe Today
https://www.universetoday.com/164050/enceladus-has-all-the-raw-materials-for-life/
Enceladus: Uncovering the Potential for Life in Saturn's Ocean Moon
https://ts2.space/en/enceladus-uncovering-the-potential-for-life-in-saturns-ocean-moon/
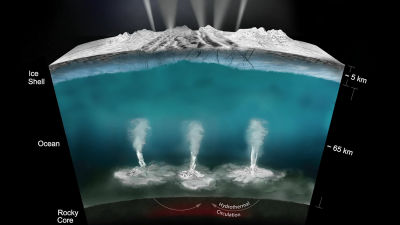
Much of what we know about Enceladus so far came from the Saturn probe Cassini, which was launched in 1997. Cassini entered Saturn's atmosphere in 2017 and completed its mission, but scientists are still busy analyzing the huge amount of data left behind by Cassini.
In a study published on the preprint server bioRxiv on October 29, 2023, Daniel Mulatore of the Santa Fe Institute in the United States and his colleagues revealed the ratio of chemicals and elements present in Enceladus and the possibility of their presence in Enceladus. We modeled the metabolism of substances by a certain life form.

by
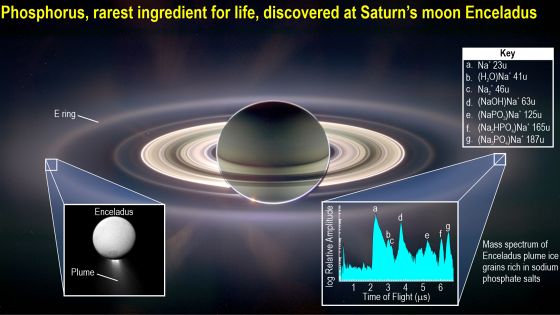
The focus of this study is the discovery of ammonia and inorganic phosphorus in Enceladus' oceans. Analysis of Cassini data from observations of geysers spewing out of Enceladus' ice shows that the ocean beneath the ice contains high levels of inorganic phosphate. 'This report of the presence of phosphorus follows previous work that identified carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen, the elemental constituents of many of Earth's life forms, in Enceladus's ejecta,' the researchers said. I'm explaining. Furthermore, subsequent research found many chemical substances common to living things, such as amino acid precursors, ammonium, and hydrocarbons, in Enceladus' ocean.
In further analysis, Muratore and his colleagues used the Redfield ratio , which is the ratio of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus found in Earth's oceans, to explore the possibility that life could live in Enceladus' ocean.
The Redfield ratio is a term named after American oceanographer Alfred Redfield. Redfield published in 1934 that the carbon:nitrogen:phosphorus ratio in total marine biomass was consistently 106:16:1. Subsequent research revealed that this ratio varies slightly depending on region and phytoplankton, and that the exact ratio is 166:22:1.
The important point here is that the Redfield ratio of elements has universality and can be applied to all living things on Earth, so it is also an important indicator in the search for extraterrestrial life. Regarding this, Muratore et al. explain, ``Because of this universality, the Redfield ratio is considered a signature that can be targeted for astrobiological life detection, especially on oceanic worlds like Europa and Enceladus.'' doing.

by blueforce4116
Mr. Muratore and his colleagues developed a model for whether methanogenic archaea could reproduce on Enceladus using the Redfield ratio, and applied it to Cassini data to verify it. They found that Enceladus' oceans have high concentrations of phosphorus, and that the overall proportion may be restricted to life-like cells on Earth.
Based on the results of this study, which show that ammonia and phosphorus exist in Enceladus' oceans, and that their ratios match the Redfield ratio of Earth's oceans, researchers believe that the Redfield ratio could support life on celestial bodies such as Enceladus and Europa. He highlighted the importance of signatures to look for and the need for further research to fully understand the chemical composition of these objects.
Related Posts: