A revolutionary electrolyzer is devised to efficiently convert carbon dioxide to propane fuel, with great potential for greenhouse gas reduction and renewable chemical production

A research team at
Imidazolium-functionalized Mo3P nanoparticles with an ionomer coating for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to propane |
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01314-8

Illinois Tech Engineer Spearheads Research Leading to Groundbreaking Green Propane Production Method | Illinois Institute of Technology
https://www.iit.edu/news/illinois-tech-engineer-spearheads-research-leading-groundbreaking-green-propane-production-method
Revolutionary Electrolyzer Efficiently Converts CO2 into Renewable Propane Fuel – ScienceSwitch
https://scienceswitch.com/2023/08/22/revolutionary-electrolyzer-efficiently-converts-co2-into-renewable-propane-fuel/
Carbon dioxide is one of the main greenhouse gases, and has contributed about 76% to global warming since the industrial revolution. Carbon dioxide accounts for about 90% of greenhouse gas emissions in Japan. . The US government also has a goal of net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, calling for innovative ways to reduce carbon dioxide emissions from the power and industrial sectors.
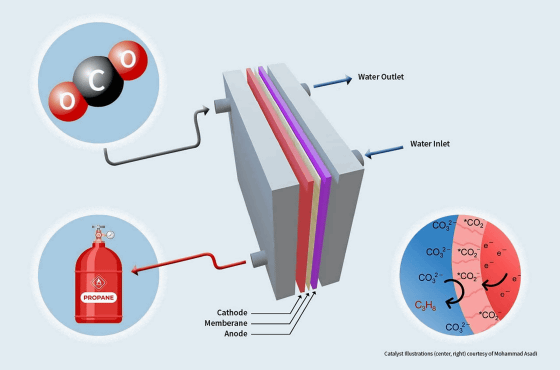
Therefore, a research team led by Mohammad Asadi , an assistant professor of chemical engineering at the Illinois Institute of Technology, conducted research on an electrolytic device that converts carbon dioxide to propane using inexpensively available materials. Propane is a component of natural gas and is used as a fuel not only in daily life but also in a wide range of industrial fields.

In recent years, research on electrode catalysts that convert carbon dioxide into various chemical substances has progressed, but it was difficult to directly produce molecules consisting of three or more carbon atoms from carbon dioxide. Since propane is also
To solve this problem, the research team devised a new catalyst system using nanoparticles of molybdenum phosphide (Mo3P), which is a combination of molybdenum and phosphorus . A combination of computer modeling and experiments was used to analyze the activity and selectivity of this catalytic system.
The research team has implemented an electrolyser design that allows propane production by continuous flow rather than batchwise processing, so they claim that propane can be produced continuously and on a large scale. According to the research team, this catalytic system can efficiently convert carbon dioxide to propane in an electrolytic cell for 100 hours, and the Faraday efficiency, which indicates the proportion that contributes to the product, reaches 91%.
``Renewable chemical production is really important. This is the best way to close the carbon cycle without losing the chemicals we use on a daily basis today,'' Asadi commented. I'm here.
Illinois Institute of Technology is partnering with SHV Energy , a global propane company, to optimize and disseminate this innovation. Keith Simmons, Head of Sustainable Fuels Development at SHV Energy, said: 'This is an exciting development that paves the way for purpose-built propane production and benefits propane fuel users around the world. It's something,' he said.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







