Research results that ``muscle training'' may be effective against Alzheimer's disease

Muscle training is known to have various positive effects on the mind and body, and it has been pointed out that it is useful not only for increasing muscle size but also for
Frontiers | Neuroprotective effects of resistance physical exercise on the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1132825
Study suggests resistance training can prevent or delay Alzheimer's disease | AGÊNCIA FAPESP
https://agencia.fapesp.br/study-suggests-resistance-training-can-prevent-or-delay-alzheimers-disease/41795/
One Type of Exercise Could Alleviate And Even Delay Alzheimer's Symptoms : ScienceAlert
https://www.sciencealert.com/one-type-of-exercise-could-alleviate-and-even-delay-alzheimers-symptoms
Previous studies have shown that physical exercise is beneficial in improving Alzheimer's disease by eliciting neuroprotection and anti-inflammatory responses. However, most of them focus on aerobic exercise, and there are cases where it is difficult for elderly people who are prone to Alzheimer's disease to perform long-term aerobic exercise.
Therefore, research teams at the Federal University of Sao Paulo and the University of Sao Paulo in Brazil conducted research on the neuroprotective effects of `` resistance exercise '', which repeats resistance to muscles. Examples of resistance exercises include squats, push-ups, and dumbbell exercises, and even elderly people can do them if the intensity is light.
In addition, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends resistance exercise as the best option for training balance, improving posture, and preventing falls, which are important to prevent injuries in the elderly. Resistance exercise is effective in increasing bone density and muscle mass, which tend to decline with age, and in preventing sarcopenia (muscle atrophy) . I have.

The research team divided mice with genetic mutations that accumulate a protein called
At the end of the program, a field test was conducted in which stress was applied to the mice by placing them in a narrow cylindrical tube, and anxiety levels were measured from the walking tendencies of the mice. As a result, it was shown that mice with genetic mutations that underwent resistance exercise had lower levels of anxiety when stressed compared to mice that did not undergo resistance exercise. Restless gait is one of the early symptoms of Alzheimer's disease, and this result suggests that resistance exercise may have prevented or alleviated Alzheimer's disease in mice.
The research team also analyzed blood samples taken from the mice. As a result, it was found that the amount of corticosterone , which is a type of stress hormone and corresponds to human cortisol , was suppressed in mice that underwent resistance exercise to the same extent as mice without genetic mutations.
The graph below shows 'CTRL' mice without gene mutation, 'APP/PS1' mice with gene mutation that did not perform resistance exercise, and 'APP/PS1 RE' mice with gene mutation that performed resistance exercise. The vertical axis indicates the blood corticosterone concentration. Mutated mice that underwent resistance exercise produced less stress hormones to the same extent as mice without the mutation.
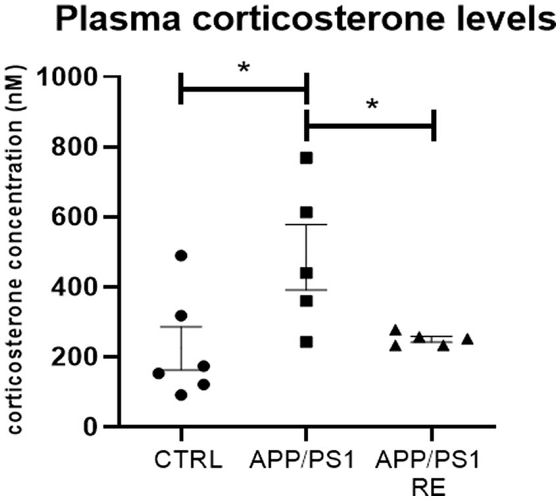
Previous research has shown that ``the risk of Alzheimer's disease increases when a large amount of cortisol is secreted due to daily stress,'' and that the blood of mice that performed resistance exercise has less stress hormones. That suggests that resistance exercise may reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
In addition, as a result of analyzing mouse brain tissue, it was found that the amount of amyloid-β accumulated in the hippocampus of mice with genetic mutations was lower in mice that underwent resistance exercise than in mice that did not exercise.
It should be noted that this research was conducted on mice rather than humans, and the role that amyloid β plays in Alzheimer's disease has not been clarified. We cannot say with certainty that exercise prevents Alzheimer's disease.
Still, lead author Enrique Correia Campos of the Federal University of São Paulo said: 'Our results show that physical activity can reverse the neuropathological changes that drive the clinical manifestations of Alzheimer's disease. I back it up,' he said.
In addition, another research team has also reported research results that taking a 'muscle strengthening supplement' may stop the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Possibility of stopping the progression of Alzheimer's disease by taking supplements for muscle strengthening - GIGAZINE

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik