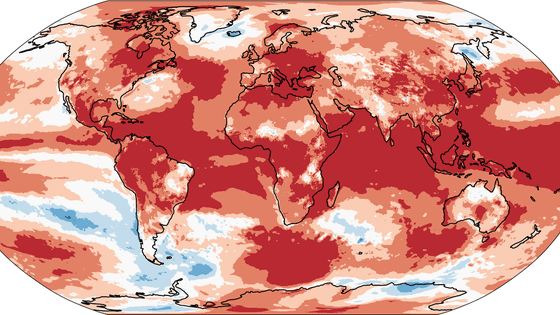
The Antarctic sea ice area has shrunk to a record low, and has continued to update the record minimum area since April 2023

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has reported that Antarctic sea ice extent will be a record low in 2023. NOAA suggests that Antarctic sea ice shrinkage may be linked to long-term ocean and climate changes.
Antarctic sea ice reaches an early winter record low in June 2023 | NOAA Climate.gov

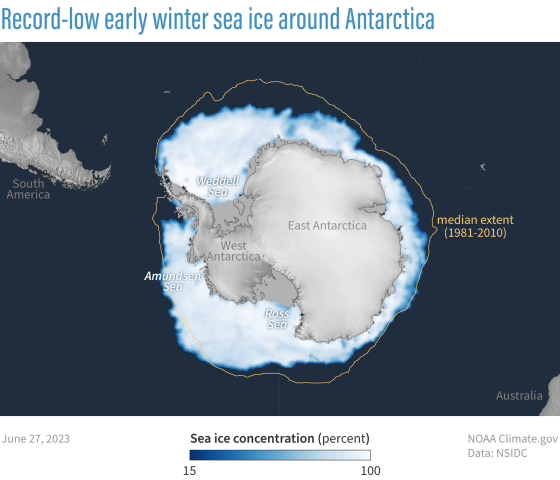
In the figure below, the white part shows the sea ice extent on June 27, 2023, and the yellow line shows the median sea ice extent from 1981 to 2010. Looking at the figure, we can see that the sea ice extent in 2023 is mostly smaller than the median.
The graph below summarizes the `` Antarctic sea ice area with a sea ice density of 15% or more '' by analyzing satellite images. Antarctic sea ice repeats the cycle of ``shrinking in summer and expanding in winter'', but in 2023 (blue line), the expansion of sea ice area will be slow even in winter, and it will be ``record'' 2022 (red line), which recorded the narrowest sea ice area.
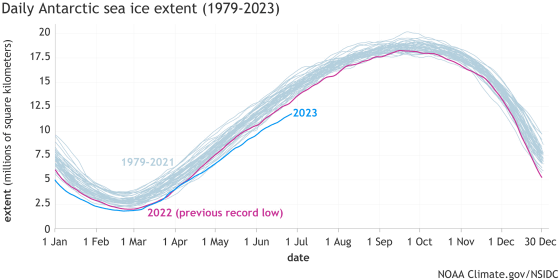
NOAA said on its official Twitter account, ``Antarctic sea ice is in the middle of the winter growing season, but it is record narrow for this time of year,'' emphasizing the narrowness of the sea ice. .
In the midst of its winter growth phase, Antarctic sea ice has reached a record smashing-low extent for this time of year. Sea ice extent is approaching a half a million square miles below the previous lowest extent, observed in 2022. https:/ /t.co/d3Ud8xxy05 pic.twitter.com/GN2YVEMO6K
— NOAA Climate.gov (@NOAAClimate) June 28, 2023
According to NOAA, although a shrinking trend in sea ice area was observed for decades in the Arctic, a long-term shrinking trend was not observed in Antarctica. However, since 2016, it has fallen significantly below the average from 1981 to 2010, and since April 2023, the minimum area for the same period in the past has been updated every day. 'Anomalous changes in Antarctic sea ice extent may signal the onset of long-term changes in the ocean and climate,' said NOAA. It is.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1o_hf