Arctic found out that scientists are in an unusually abnormal state

ByLwp Kommunikáció
From January to February of 2018, the record cold wave hit the Japanese archipelago, and in the region where snow hardly occurs usually heavy snowfalls and other abnormal weather suffered. However, record warming has occurred in the Arctic Ocean,Bering SeaIt is known that the area of the sea ice is decreasing at an abnormal speed. Zachary Michael Labe, a climate scientist at the University of California, reports the situation where record warming occurring in the North Pole and the sea ice area of the Bering Sea are decreasing using several images on Twitter .
Climate Code Red: What is happening in the Arctic is now beyond words, so here are the pictures
http://www.climatecodered.org/2018/02/what-is-happening-in-arctic-is-now.html
The graph below shows the sea ice area of the Bering Sea observed so far. It is indicated by a red line in 2018, and past observation results are recorded with thin lines. In 2018, we recorded the lowest level in satellite observation history from the beginning of the year, and as of late February 2018, we recorded an incredibly low value from past trends.
"Warm" and strong southerly winds have contributed to this anomalous retreat of ice into the Bering Strait. 2018 is the clear outlier in the satellite era (each thin line = 1979 - 2017,@NSIDCdata)pic.twitter.com/kzEV6yEFmp
- Zack Labe (@ ZLabe)February 24, 2018
Mr. Labe then released an image that summarizes the temperatures of the Arctic Ocean Day graphed. The red line is for 2018, past observation results are indicated by thin lines, white thick lines indicate average temperature. Even with this graph, you can see that the temperatures recorded in the Arctic Ocean in 2018 are prominent unexpectedly due to the previous trends.
The extreme event continues to unfold in the high# Arctictoday in response to a surge of moisture and "warmth"
- Zack Labe (@ ZLabe)February 25, 2018
2018 is well exceeding previous years (thin lines) for a month of February. 2018 is the red line. Average temperature is in white (https://t.co/kO5ufUWrKq)pic.twitter.com/cLeMxSxvWo
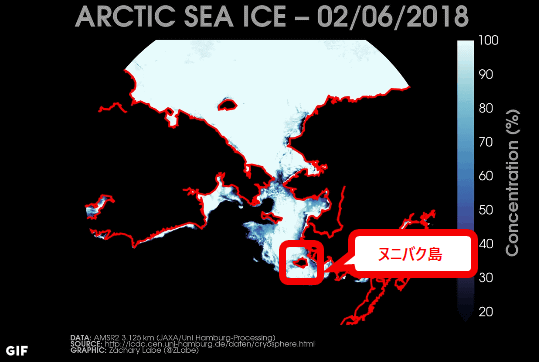
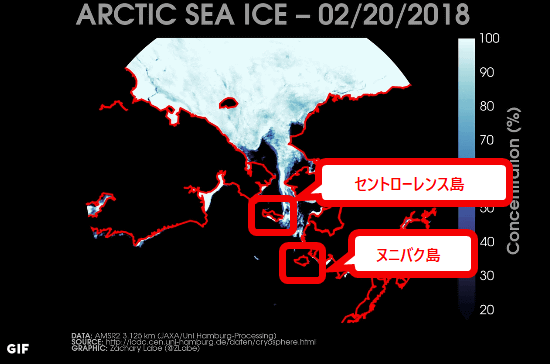
The following shows the trend of sea ice in the Bering Sea in two weeks from February 6, 2018 (Tue) to February 20 (Tue) 2018.
February? This is crazy. Retreat of sea ice in the Bering Sea continues - well below the previous record low in the satellite era.pic.twitter.com/9UoqZvaFr2
- Zack Labe (@ ZLabe)February 21, 2018
As of February 6, 2018Nunibac IslandIt was completely covered with sea ice ... ...
As of February 20, 2018 the ice which covered Nunibaku Island will disappear. Also on the north sideSt. Lawrence IslandSea ice which covered about half of it is only touching a part of the west side in only two weeks.
It is on the northernmost tip of Greenland on Saturday, February 24, 2018Morris Jessup CapeIt seems that we recorded an air temperature of 6.1 degrees at the observatory. According to Labe, it rarely exceeds 0 degrees during winter, but it is quite unusual.
Cape Morris Jesup (# Greenland's northernmost observation station) is now reporting days well above freezing today ... + 6.1 ° C at the latest observation! Crazy!
- Zack Labe (@ ZLabe)February 24, 2018
Station is provided by@ dmidkathttps://t.co/kedfPPAg9q.pic.twitter.com/wEcs4B61mo
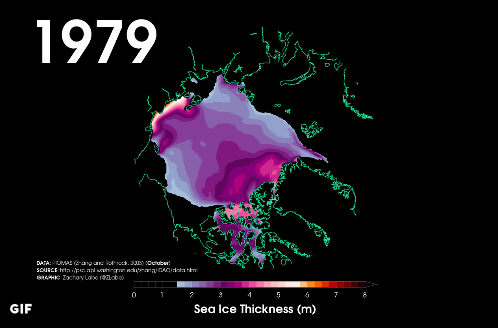
Mr. Labe introduces a movie showing the transition of the sea ice thickness in the Arctic Ocean from 1979 to 2016. The place where the thickness of the sea ice became less than 1.5 m is shown in black, focusing only on the part of "thickness" rather than the actual sea ice area, so the reduction of sea ice becomes easier to understand It is appealing the crisis of the Arctic Ocean.
A look at the loss of thicker (usually older)# Arcticsea ice in Octobers from 1979-2016 (PIOMAS, ice < 1.5 meters masked black)pic.twitter.com/BtHCwVUdKk
- Zack Labe (@ ZLabe)November 14, 2016
As of 1979, most of the sea ice thickness in the Arctic Ocean occupies 2 m or more.
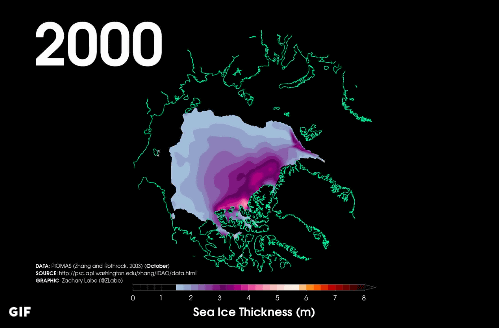
In 2000 after about 20 years, although the area of the thickness of 1.5 m or more has changed little, the thickness of the sea ice is getting thinner overall.
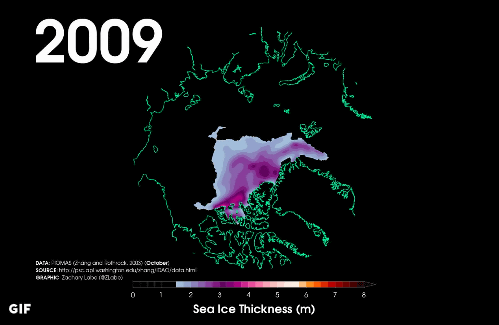
In 2009, there is almost no ice with a thickness of 1.5 m or more ... ...
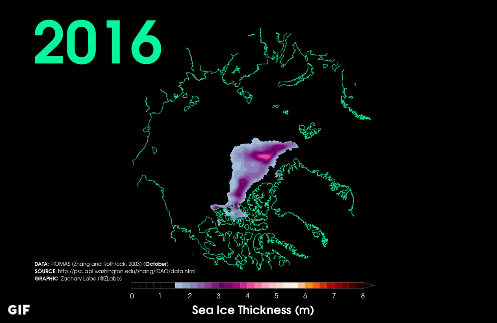
In 2016 the range is narrowed further.
Related Posts: