Website 'Bicycle' that you can intuitively understand 'mechanism of bicycle running' just by operating with a mouse

There should be many people who ride bicycles on a daily basis as a means of transportation. However, it is difficult to imagine how the bicycle works. A web page where you can learn such a 'mechanism of bicycle running' while operating a slider with a mouse ' Bicycle 'Has been published by Mr. Bartosz Ciechanowski, an engineer who has explained
Bicycle – Bartosz Ciechanowski
https://ciechanow.ski/bicycle/
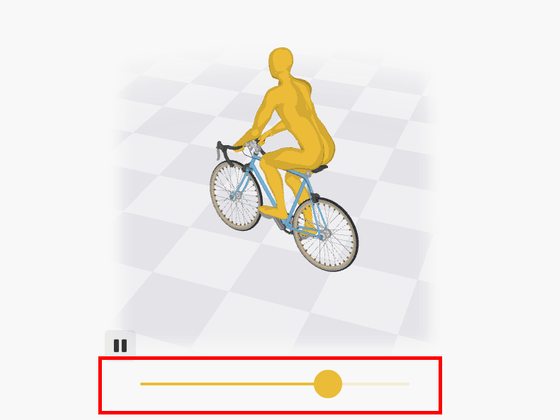
Compared to complex power such as an engine, a bicycle is a fairly simple machine, and you can visually check how the parts are moving. But the 'power' that allows you to ride and control your bike is invisible. In the figure below, you can bend the running direction of the bicycle left and right by moving the yellow slider.
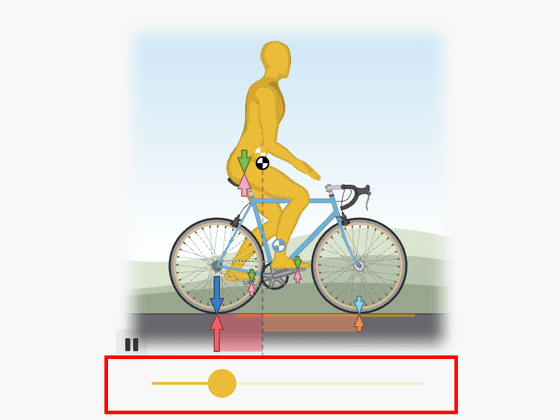
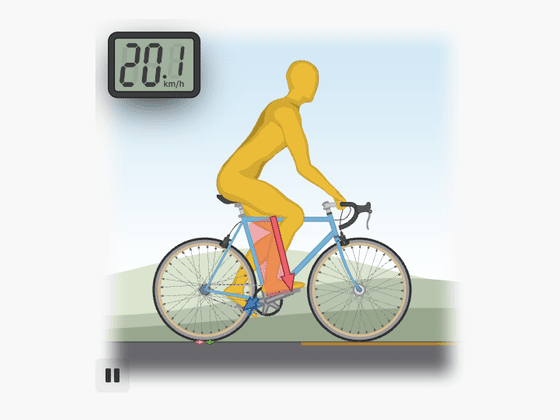
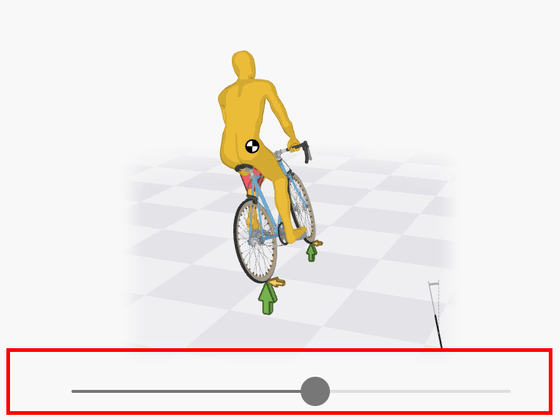
Since various forces are intricately intertwined in the mechanism of bicycle running, it is important to know the vertical force first. In the figure below, by moving the yellow slider left and right, it is possible to change the posture of the model riding the bicycle, and you can check the magnitude of the force that changes at that time. When you raise your upper body and stretch your spine, the weight of your upper body and the reaction force that
Avoiding exercises that cause imbalance

The above model was a model during coasting without stepping on the pedal of the bicycle. In fact, when riding a bicycle, you have to keep pedaling to move forward. When you pedal a bicycle, it creates a torque that acts on the sprocket . Furthermore, by pulling the chain to which the sprocket is connected, it acts on the sprocket of the rear wheel, creating a force that tries to kick the ground and push it back.
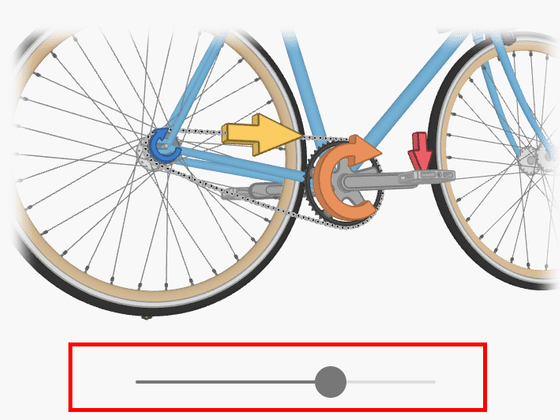
Friction between the tire and the road keeps the bottom of the tire wheel in contact with the ground. At that time, when the tire rotates, the wheel pushes the ground to the left, and the reaction pushes the ground back to the right, allowing the bicycle to move forward.
On the other hand, when the brakes are applied while driving, the brake lever pulls the cable, and the arm connected to the cable presses the brake pad against the tire wheel.
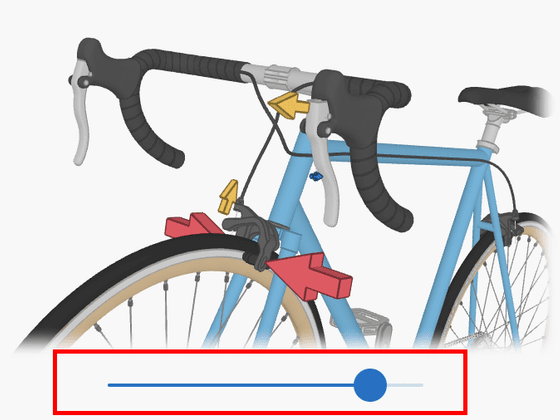
The brake pads pressed against the tires generate friction, and the tire pushes the ground forward, the tire pushes the ground forward, and at the same time, the tire and the entire bicycle are pushed backward.
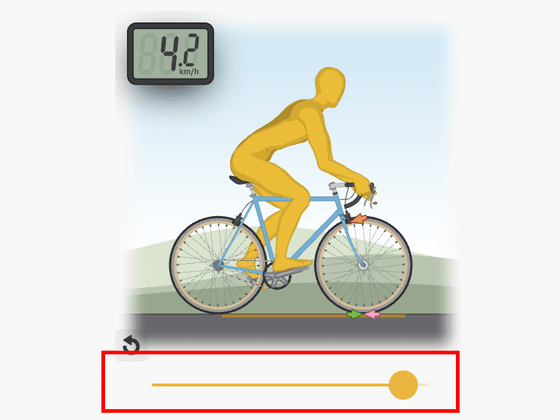
If you apply the brakes while riding, the bike will try to turn clockwise, increasing the load on the front wheel. At that time, if the front wheel brake is applied strongly, the load on the rear wheel will be lost and the car will fall. If you move the gray slider to the right, you can see that the rear wheel is floating as a result of applying the front wheel brake hard. Therefore, when slowing down the bicycle, it is recommended to use the rear wheel brake or the front wheel brake together. In addition to braking, air resistance and uphill are cited as the force that slows down the bicycle.
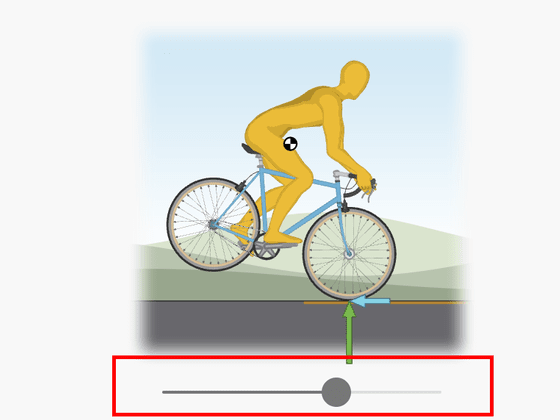
If you hold the handle straight, the bike will topple over if you lose your balance. In the figure below, if you leave the yellow slider without moving it, the bicycle will fall over on its own.
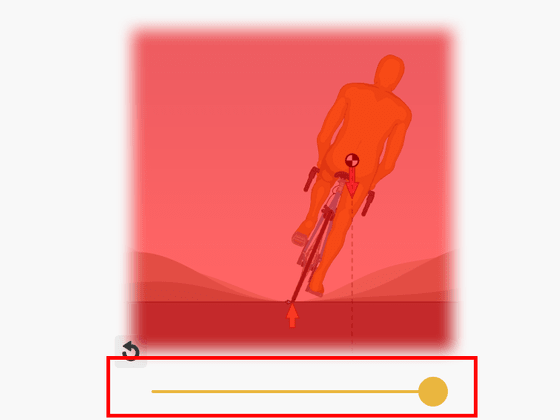
Also, it is difficult to balance by tilting the upper body while the bicycle is falling down, and in the figure below you can confirm that even if you tilt the body by moving the yellow slider, it will eventually fall down.
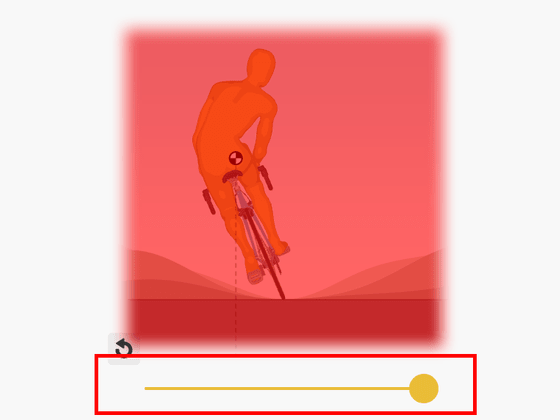
Therefore, when the bicycle is about to fall over, you can avoid falling by tilting the handle left and right.
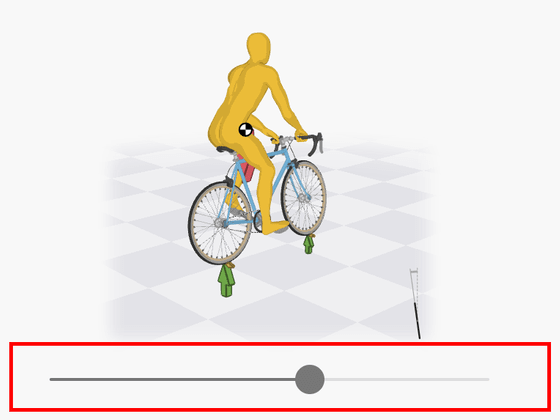
If you tilt the steering wheel to the left or right, a lateral force is applied to the tires, making it possible to turn. In the figure below, you can check the force applied to the tire and the direction of the tire by moving the gray slider.
In order for the bicycle to run stably, the property called '
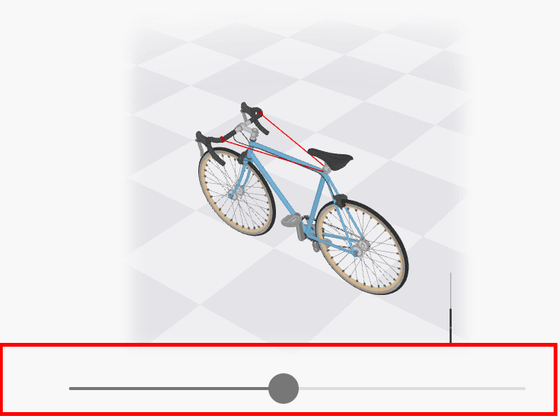
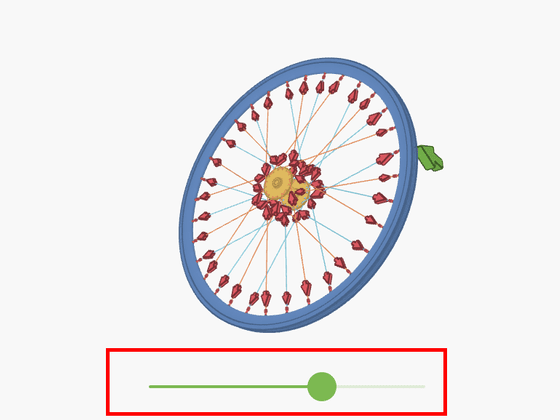
There are other forces on the bicycle that are applied to
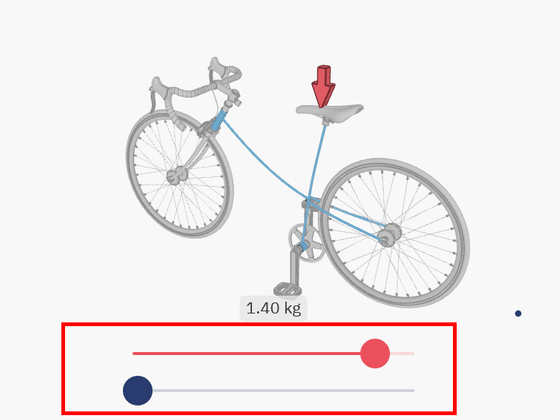
Since the bicycle frame bears the weight of the human body, a thin frame cannot withstand the load and bends greatly. In the figure below, you can adjust the load on the bicycle by moving the red slider and adjust the stiffness of the frame by moving the blue slider.
The above demos are part of the demos included in Bicycle, and if you access Bicycle, you can understand how bicycles work while touching a large number of demos. If you are interested, please access it.
Related Posts: