What is 'purchasing power parity' that sets out indicators such as 'How much can you buy Big Mac for 5000 yen?'

In order to compare differences in living standards and productivity between countries, it is necessary to consider various factors such as price differences. Economist Michael Boyle explains the macroeconomic analysis indicator ``
What Is Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), and How Is It Calculated?
https://www.investopedia.com/updates/purchasing-power-parity-ppp/
Purchasing power parity is an economic theory that compares the currencies of different countries using a combination (basket) of goods and services purchased by consumers. There are two types of purchasing power parity: absolute purchasing power parity and relative purchasing power parity. The former is determined by the purchasing power of currencies between two countries. This is the idea that if a basket that can be bought for 1 dollar in the United States can be bought for 100 yen in Japan, the appropriate exchange rate is 1 dollar = 100 yen. The latter is based on the exchange rate at the time when trade with normal competitiveness was taking place between the two countries, and the rate is determined by calculating the subsequent change in the inflation rate.
Using this PPP, attempts are also being made to evaluate the exchange rate by changing the basket to a Big Mac and launching an index 'How much can you buy a Big Mac for 5000 yen?'

In order to compare prices in different countries, it is necessary to compare various goods and services, but this amount is enormous and unrealistic. To facilitate this comparison, the University of Pennsylvania and the United Nations worked together to launch the International Comparative Program (ICP) in 1968.
The program bases its calculations on global price surveys that compare the prices of hundreds of different goods and services to help macroeconomists estimate global productivity and growth rates. I'm here.
Some forex traders also use PPPs to spot potentially overvalued and undervalued currencies. Investors holding stocks and bonds of foreign companies may use PPP figures to predict the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the country's economy.
In modern macroeconomics, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) can be divided into 'nominal GDP' and 'real GDP' in consideration of price fluctuations, but GDP can also be considered by adjusting PPP. that's right. Below is a chart created by Mr. Boyle of economic media based on the data of the International Monetary Fund, the left is GDP with PPP added, and the right is nominal GDP.
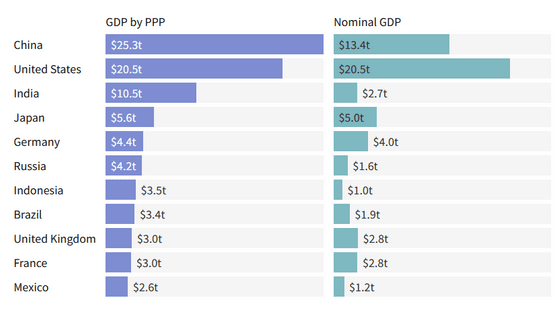
In presenting the above chart, Boyle said, 'Nominal GDP comparisons may be inaccurate due to possible currency manipulation. PPP-weighted GDP based on a basket of commodities is more It could be a fairer cross-country comparison.'
However, PPP is not a perfect metric because it cannot accurately take into account the cost of shipping goods, customs duties, labor costs and utility costs in each country, Boyle said.
Related Posts:
in Posted by log1p_kr







