NASA detects a ``super emitter'' that emits a large amount of powerful greenhouse gases from the space station

As a
Methane 'Super-Emitters' Mapped by NASA's New Earth Space Mission | NASA
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/jpl/methane-super-emitters-mapped-by-nasa-s-new-earth-space-mission
Methane 'super-emitters' on Earth spotted by space station experiment | Space
https://www.space.com/emit-instrument-international-space-station-methane-super-emitters
NASA Finds More Than 50 Super-Emitters of Methane | Smart News|
Smithsonian Magazine
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/nasa-finds-more-than-50-super-emitters-of-methane-180981045/
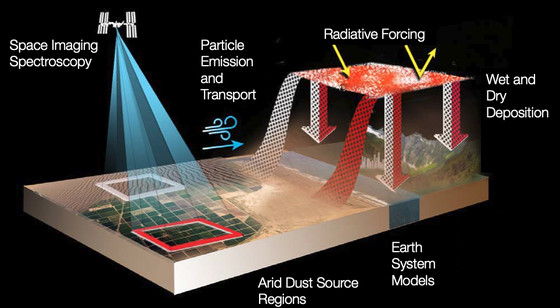
NASA's Surface Mineral Dust Source Survey (EMIT) mission is to improve our understanding of the impact of dust on humans by using satellites to detect mineral dust in the air. However, it was also demonstrated that EMIT has the function of detecting not only the dust of minerals but also the presence of methane, a powerful greenhouse gas. NASA announced on October 26, 2022 that it was able to map the
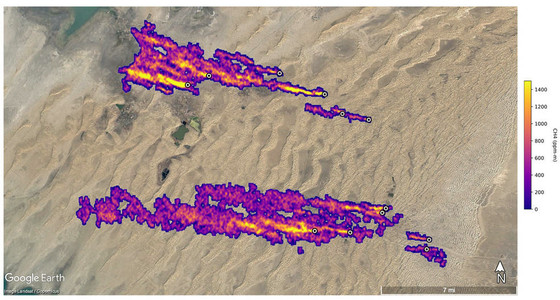
Facilities, equipment, and other infrastructure that emit large amounts of methane in fossil fuels, industrial waste, or the agricultural sector are collectively referred to by NASA as 'superemitters.' A total of more than 50 areas of superemitters have been identified in Central Asia, the Middle East, and the southwestern United States, according to data collected by EMIT since its installation on the International Space Station in July 2022. The following image shows the methane detected in the Caspian Sea coast of Turkmenistan in purple or yellow depending on the concentration, and it is said that the wide one spreads over 32 kilometers.
Methane is estimated to be 80 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere for 20 years after release than carbon dioxide per tonne. Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, is thought to persist in the atmosphere for centuries, while methane is believed to persist for only about ten years. In other words, if methane emissions are reduced, the impact on the atmosphere will be easier to see in the short term, making it possible to clearly curb the progress of global warming.
“Reducing methane emissions is key to reducing global warming,” said Bill Nelson, project manager. 'Not only does it help us more accurately identify who is at risk, but it also quickly provides insight into how it can be addressed.' In addition, Mr. Andrew Thorpe, a researcher at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) , which conducts research and development of unmanned spacecraft at NASA, said at a press conference, 'The results of mapping greenhouse gases are the EMIT We are really excited about EMIT's potential to reduce emissions from human activity by identifying sources of methane emissions.' .
EMIT is expected to identify hundreds more superemitters by repeatedly observing large areas from the space station's vantage point. “As we continue to explore the planet, EMIT has observed places that no one had previously thought were sources of greenhouse gas emissions, and no one expected them,” said EMIT principal investigator Robert Green. We will discover the emitter,' he says of the significance of the project.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1e_dh