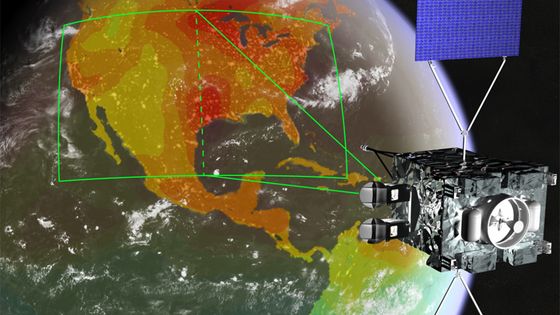
Efforts to monitor methane emissions that cause global warming from satellites have begun with private companies
Which is the main component of natural gas
Private Space Race Targets Greenhouse Gas Emitters-Scientific American
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/private-space-race-targets-greenhouse-gas-emitters/
Companies and regulatory agencies need to know methane emissions accurately, but the sensors installed on the ground have limits to what can be monitored and are not practical. Therefore, an idea was proposed to monitor methane emissions from satellites.
It has been around 2016 that monitoring of methane emissions from satellites has begun to attract attention. The proof-of-concept satellite Claire , launched in 2016 by Montreal-based start-up GHGSat , Canada, succeeded in monitoring methane emissions on the earth with high accuracy. Claire, which orbits the earth about 15 times a day, conducts monitoring at various places such as oil and natural gas purification facilities, power plants, coal mines, landfills, and pastures. I got the data.
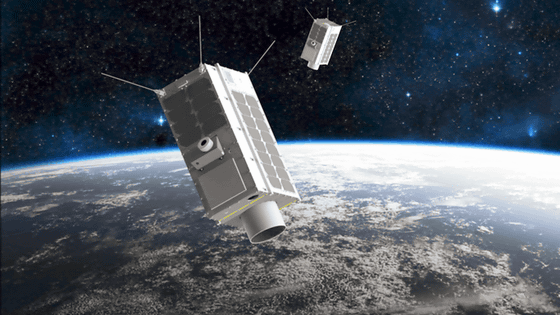
In response to Claire's successful monitoring of methane emissions from satellites, several non-profit environmental groups have set up a satellite 'MethaneSAT' to monitor methane emissions and appealed to various companies Yes. The successful launch and operation of MethaneSAT scheduled for 2021 will enable monitoring of up to 80% of the world's major oil and gas production sites.
Companies and government regulators are impressed with the private satellite monitoring efforts. Based in San Francisco, Planet Labs is working with the California state government on a methane gas monitoring project to identify methane gas from oil and natural gas facilities, landfills and cattle in ranch.
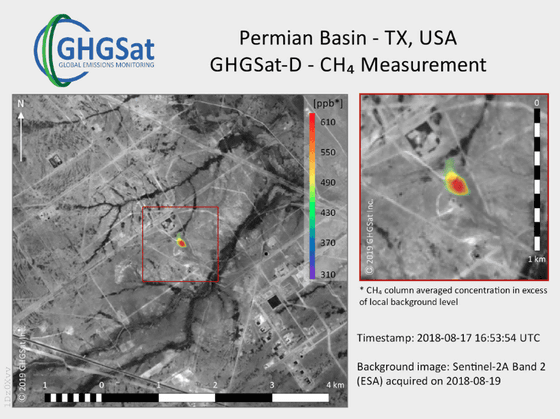
Also, Bluefield , another San Francisco company, has already signed an agreement to measure methane gas emitted by several oil and natural gas companies, even though satellites have not yet been launched. . Bluefield plans to launch an artificial satellite in 2020.
However, Laure Brooker Lizon-Tati of EU's SCARBO (Space Carbon Observatory) does not yet know whether companies like GHGSat and Bluefield can actually put their methane emissions monitoring business on track And. As of 2019, methane emissions are monitored by comparing measurements from satellites with measurements from ground sensors. “The level of accuracy required by sensors under development by private companies to measure methane emissions It is difficult to assess whether the requirements are met, ”said Lizon-Tati.
However, advances in satellite methane emissions monitoring will enable companies to quickly identify methane leaks from plants and pipelines and respond to increased emissions. It also has the benefit of visualizing methane emissions by satellite data from super-altitudes.
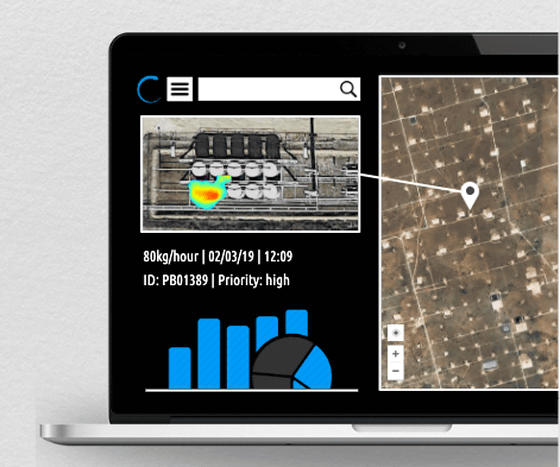
“Climate change is a difficult concept to touch and see humans,” said Thomas Lauvaux, a climatologist at the University of Pittsburgh. However, as methane is being discharged from the tank, it can be seen from satellite images I think many things will become inevitable, 'he said.
Related Posts: