YouTube and Twitter point out that Ukraine is ignoring Russia's request to remove propaganda

Russia's invasion of Ukraine began on February 24, 2022, and fierce battles are fought online.
Twitter, YouTube ignore takedown requests by the Ukrainian Government
(PDF file https://www.reset.tech/documents/twitter-youtube-ignore-takedown-requests-by-ukrainian-government.pdf

Ukraine struggles for Big Tech's attention as Russian propaganda evolves --The Washington Post
Russian propaganda: Big Tech firms fail to take down Russian propaganda posts, says Ukraine --The Economic Times
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/technology/big-tech-firms-fail-to-take-down-russian-propaganda-posts-says-ukraine/articleshow/92918675.cms
The report was conducted by the Ukrainian government, dissatisfied with Big Tech's response, in partnership with independent researchers at the Disinformation Situation Center, a coalition of European-based nonprofits.
Content requested by the Ukrainian government to be deleted is '1: Account to spread war propaganda and hate speech by Kremlin (Russian government)' '2: Spoofing account on Instagram and Facebook' '3: War by Kremlin on Linked In' It is classified into 5 categories, 'Propaganda', '4: Hate speech on Facebook, YouTube, Twitter' and '5: Advertisement corresponding to war propaganda in Meta products and services', and how much Big Tech responded to each. I am analyzing.
As a result, although Meta has taken a fairly effective response to content flagged by the Ukrainian authorities, the account itself often remains on the platform, and YouTube, Twitter, and LinkedIn are flagged in the first place. It turned out that the response rate itself to the set up content is low.
According to government officials, the platformer's response to flagged content can take weeks and is often completely unresponsive.
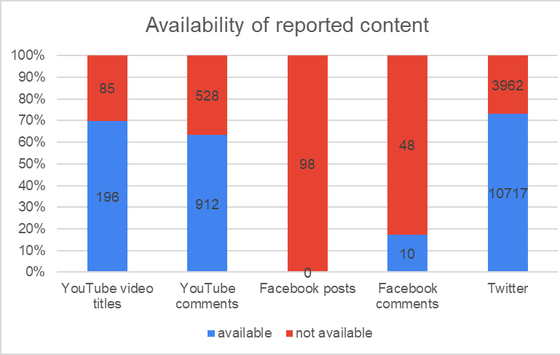
Specifically, the graph below shows the response to hate speech. The vertical axis is the corresponding percentage, red shows the number of cases that were unavailable at the time of analysis, and blue shows the number of cases that were still available at the time of analysis. The bar graph is arranged in the order of YouTube video, YouTube comment, Facebook post, Facebook comment, Twitter tweet from the left, and all 98 confirmed hate speeches are deleted and can not be seen. You can see that it was like this. Forty-eight comments were deleted from Facebook, leaving only ten. On the other hand, about 30% of videos and comments including hate speech were deleted on YouTube, and less than 30% of tweets that reported hate speech were deleted on Twitter as well. On Twitter, the number of tweets that became a problem in the first place is higher than the total of YouTube and Facebook.
Peer Lamberti, co-CEO of German think tank CeMAS, said Russia's propaganda isn't just aimed at Ukrainians, but is costly due to oil sanctions against Russia and military support for Ukraine. By touching it, he points out that he is trying to weaken the support of the people of the countries standing on the Ukrainian side.
While it is important for Big Tech to respond to removal requests, Mr. Lumberty said that what is most needed is to take a proactive and systematic approach to monitoring Russia's propaganda network across the platform. 'If you need fact checking, it's too late,' he warns.
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Posted by logc_nt