Why are deep-sea creatures so huge?

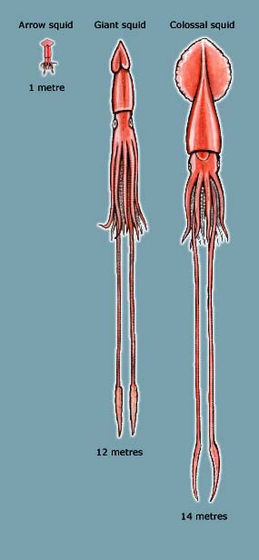
Deep-sea creatures, such as squids that are 14 times longer than normal size and
Why are there so many giants in the deep sea? | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/why-deep-sea-animals-are-giants
According to the New Zealand Encyclopedia, an online encyclopedia established by the Ministry of Cultural Heritage of New Zealand, the giant squid 'Colossal squid ' that lives in the sub-Antarctic waters is about 14 of the common squid 'Squid' in New Zealand. It is twice as long. The Colossal squid is known as one of the largest invertebrates in the world along with the giant squid , and both are deep-sea squids.
Most of the food that exists in the sea is located in shallow waters, so the deepest part of the sea is scarce in resources compared to other waters. According to Alicia Bitondo, who works at the Monterey Bay Aquarium in California, organisms that live in such food-poor areas can benefit greatly from being larger.
'Large creatures will find it easier to find food and companions, and will be able to move faster and farther, and larger creatures will be more efficient,' said Bitondo. Due to its high metabolism, it is possible to work for a long time with less food. Therefore, when the dead organisms reach the deep sea in shallow water, the larger organisms eat more dead organisms than other organisms. Is possible, and 'more energy can be stored in the body for a longer period of time.'
In addition, low water temperatures in the deep sea may significantly slow down the metabolism of organisms, thus contributing to the 'growth of deep-sea organisms.' The

by NOAA Ocean Explorer
Cases in which organisms grow enormously in low-temperature environments have been confirmed outside the deep sea. Huge slugs, worms, sea spiders, etc. have been confirmed in Antarctica, and even in shallow water of about 30 feet (about 9.1 meters), larger creatures than usual have been confirmed.
Professor Art Woods, a biophysiologist at the University of Montana, who studies the phenomenon of giant organisms in cold environments, said, 'There is something in the Antarctic continent that allows giant organisms to live near the surface. It may be, 'he said, pointing out that low temperatures and oxygen supply may be the reason for the large number of giant organisms in the Antarctic continent.
According to the

However, there seems to be a limit to the growth of organisms that live in the deep sea. A study published in 2017 revealed that Arctic sea spiders can grow to as long as 12 inches (about 30.5 cm) in length, and giant sea spiders have low oxygen levels in their bodies. increase. So, Professor Woods said, 'I think the Arctic giant sea spider has grown to a size that is too big to take in enough oxygen. That is, the giant sea spider is already reaching its size limit. That's why. '
In addition, 'cold seawater' and 'poor food' are cited as the reasons why deep-sea organisms become huge, but since various other factors can be considered, the mechanism for changes in physique is 'organisms'. I can't say anything scientifically certain, 'says Professor Woods.
Related Posts: