Even if you hate exercise, you can get the benefits of exercise by taking a hot bath, why?

It is a well-known fact that exercise is important for good health, but many people cannot exercise on a daily basis due to lifestyle and physical reasons. As a solution to these people's problems, research is being conducted focusing on the benefits of exercise through 'warm bathing' rather than exercise.
Can't face running? Have a hot bath or a sauna – research shows they offer some similar benefits
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 'moderate exercise of 150 minutes or more per week or high intensity exercise of 75 minutes or more' as the amount of exercise required for adults, but 4 One in a person does not meet this criterion . Especially in the United States, it is said that 40% of the adult population is under-exercised.
A research team at Coventry University focused on 'bathing' as a way to improve the health hazards caused by lack of exercise. In recent years, research has progressed on the benefits of bathing, and studies have shown that regular saunas and hot water baths reduce the risk of heart disease. The review article published in 2020, that the leak aerobic exercise as well as of the advantages of the medium strength from low-intensity regular sauna and hot bath is such as walking, jogging, cycling has been shown .

The long-term research conducted in Finland is particularly famous for the effects of saunas and hot baths. The study showed that the frequency of saunas was associated with a reduced risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in middle-aged Finnish men. Originally in Finland, it is said that 'sauna is a poor pharmacy', but in fact, in research, people who enter the sauna 4 to 7 times a week are more deadly than those who enter once a week. The risk of cardiovascular disease was
Similarly, in Japan, studies have shown that the more frequent bathing in hot water, the greater the protective effect against the risk of cardiovascular disease (PDF file). The results of these studies show that regular exposure to heat reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
When a person's body is exposed to heat, the body temperature begins to rise, and 'a method of releasing excess heat' is taken to regulate the body temperature. One of these methods is 'increasing blood flow to the skin'. Arteries and capillaries dilate as blood flow to the skin increases. For this reason, as blood flow increases, various molecules that promote cells and repair and protect blood vessels are manufactured and sent to blood vessels.
The difference between a sauna and a hot bath is that the hot bath is accompanied by water pressure. Water pressure is thought to help blood return to the heart, and although there is no scientific evidence at the time of writing, it could be one reason why hyperthermia is recommended for improving cardiovascular health in the future. ... apparently ...

Against this background, a research team at Coventry University, who speculated that 'the effects of exercise may also be obtained by warm bathing,' asked the subjects to 'warm bath' and 'moderate cycling,' and physiology. He said he observed the reaction. As a result, although the difference is that 'exercise consumes a lot of energy', the
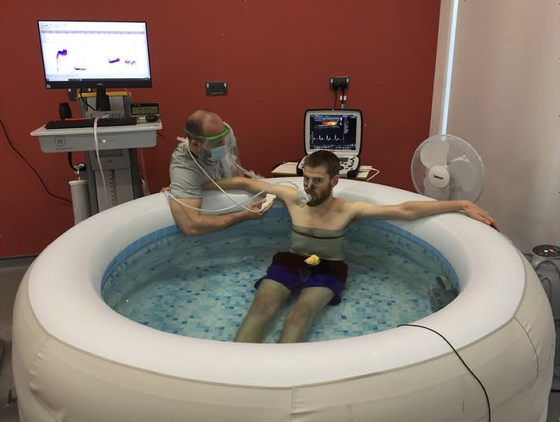
However, when the experiments were conducted in the laboratory, the temperature of the hot water was kept constant by careful monitoring to maintain the core temperature and comfort of the subjects. When bathing in a general household, the temperature of the hot water decreases over time, so it is not possible to reproduce exactly the same content as in the experiment. In addition, if you continue to take a hot bath or sauna for a long time,
In addition, experiments have shown that 'the core temperature rises by 1.5 degrees by soaking in hot water of 40.5 degrees for 60 minutes', but even if the body temperature is not raised so far, a sufficient effect can be obtained within the range of general bathing. Is believed to be. For example, researchers at Liverpool John Moores University have taken a bath that raises core temperature by 0.6 degrees three times a week for six weeks, creating new blood vessels, increasing insulin sensitivity to control blood sugar, and exercising. It shows that the effect has been improved (PDF file) .
Recent studies have also shown that both exercise and hot baths promote cardiovascular health over either single exercise, as shown by the fact that hot baths improve the effects of exercise. On the other hand, since weight loss is basically achieved by 'increasing calories burned more than calories consumed', it is difficult to achieve weight loss by using a sauna or a hot bath that consumes less calories. In addition, saunas and hot baths do not contract muscles or stress bones, so they do not affect muscle mass or bone density. Still, researchers think that hot baths and saunas increase athletic ability and functional ability by heat, so people who have difficulty exercising will be the 'entrance' for exercising in the future.

Researchers are paying particular attention to the possibility that 'a warm bath after exercise maximizes health benefits.' Although it is still in the preliminary research stage, when the subjects took a hot bath after cycling, it was shown that the core temperature and heart rate increased, and the health benefits could be increased.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log







