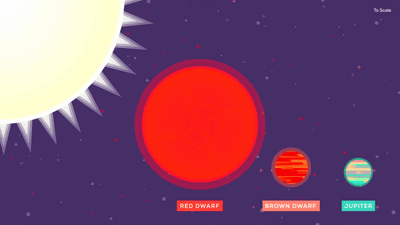
Which star is the 'largest star in the universe'?

The universe is wide and full of mysteries for modern humankind.
The Largest Star in the Universe – Size Comparison --YouTube
The most familiar example of a giant star is Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system. Jupiter is about 11 times larger than Earth and weighs 317 times.

Even larger than Jupiter is the

The next largest star category after brown dwarfs is

When a gas such as hydrogen or helium collects in excess of a certain mass, the central part reaches a high temperature that causes combustion.
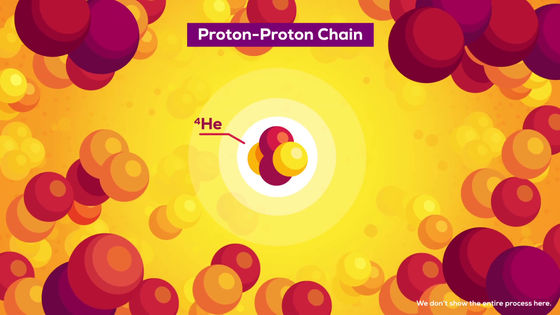
As a result, a proton-proton chain reaction, which is a type of fusion reaction in which hydrogen is converted to helium, occurs in the central part. It emits a huge amount of energy. The heavier the mass of a main sequence star, the higher the temperature and the stronger the light, but the shorter its lifespan.
When the central hydrogen is depleted by the proton-proton chain reaction, the main sequence stars suddenly grow to hundreds of thousands of times larger and then die.

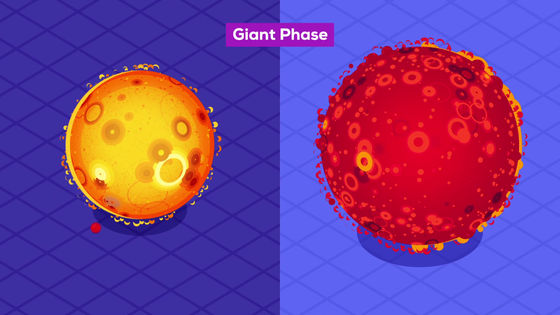
Even if you say 'compare the size of stars' in this way, you should keep in mind that the size of stars changes during their lifetime, so it is possible to compare 'adults and children'.
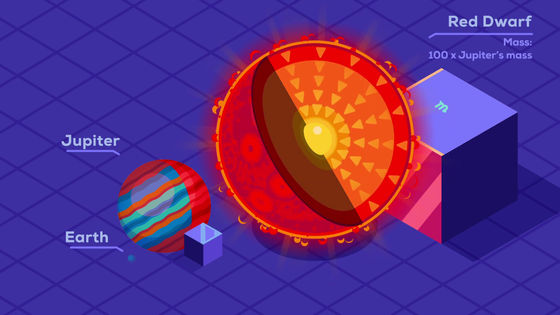
The smallest
Due to the small mass of red dwarfs, large fusion reactions do not occur. Therefore, the emitted light is very weak and never becomes huge by the time it dies.
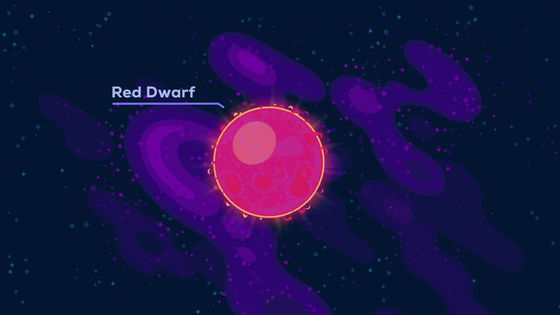
Red dwarfs have a lifespan of 10 trillion years, making them the most abundant stars in the universe.
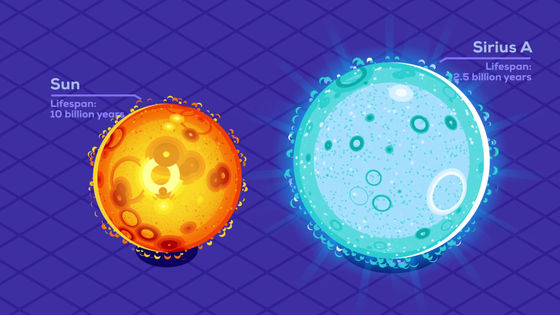
The second largest star in the main sequence after the red dwarf is the sun-like star. The surface temperature of the sun is as high as about 6000 degrees Celsius, and although the light emitted is strong, it has a lifespan of only about 10 billion years.

Let's move on to stars that are larger than the sun. Sirius A, which constitutes
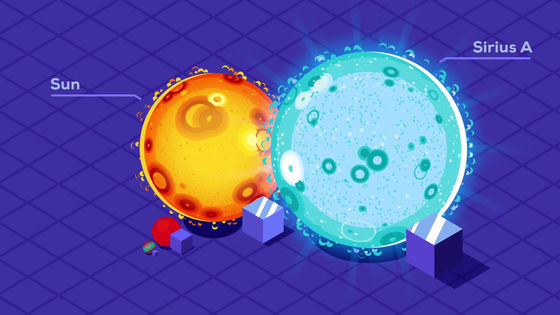
However, on the other hand, the life of Sirius A has dropped sharply to about 2.5 billion years.

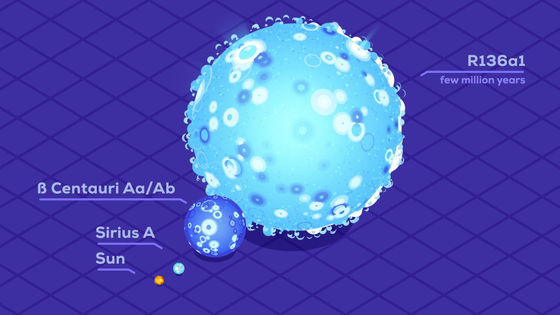
As you can see from the examples so far, the larger the mass, the larger the size.

The heaviest star ever discovered is

However, the size difference is small compared to the mass and brightness, and the R136a1 is about 30 times larger than the sun. The life is about several million years.
A large amount of mass is escaping from R136a1 due to the

R136a1 is believed to have been formed by the coalescence of supermassive planets, and hydrogen in the nucleus is expected to run out in millions of years.
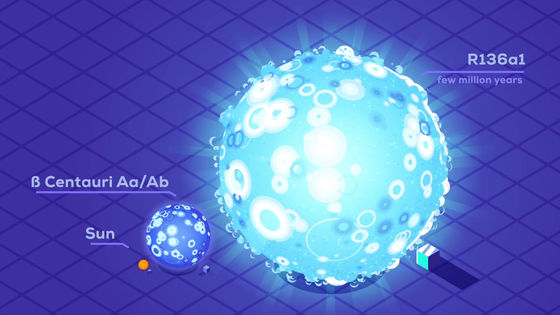
The above stars have been consistently proportional in mass and size. However, when considering stars larger than this, 'expansion' is an important factor.

When a main sequence star runs out of hydrogen in the nucleus, the nucleus is compressed and the temperature and pressure rise as the fusion efficiency in the nucleus decreases. As a result, the outer layer of the star expands over time due to the increased outward energy.
For example,
On the other hand, the radius is thought to expand 200 times just before the sun dies.
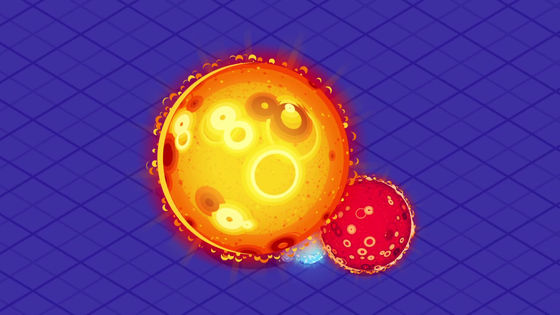
If it expands to a radius of 200 times, Mercury and Venus are expected to be swallowed.
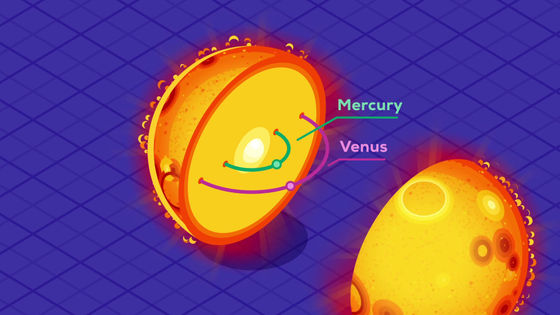
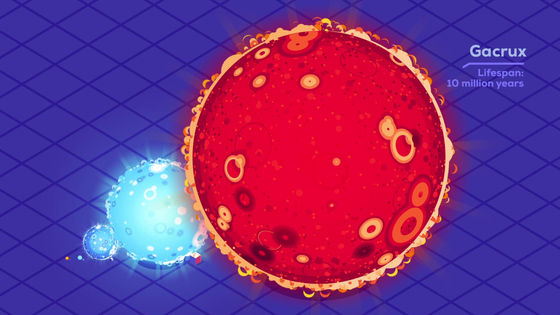
And it is

Hypergiants are very bright, but the surface gravity is weak, and it is thought that a large amount of mass is flowing out from the surface.


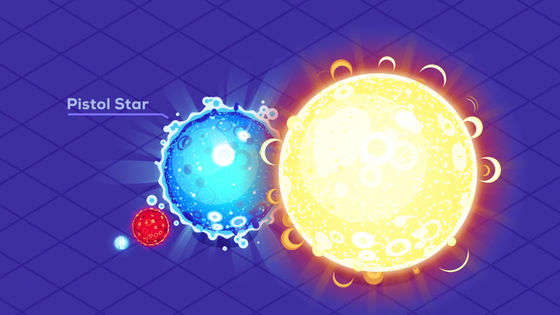
The most studied yellow hypergiant,

Rho Cassiopeia has 40 times the mass of the Sun and its radius is 500 times. The brightness is about 500,000 times higher.
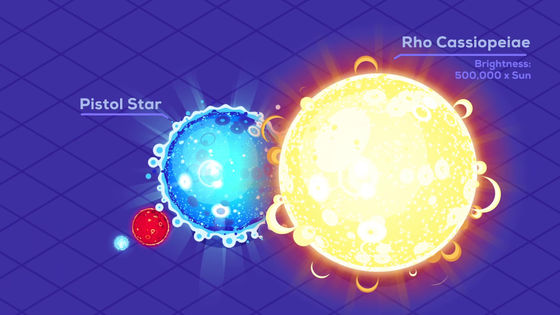
If Rho Cassiopeia was in the same position as the Sun, humanity would burn out and die.

Yellow hypergiants are rare, and only 15 have been discovered so far. This means that the Yellow Hypergiant has a short lifespan.

Larger than this yellow hypergiant is the

Then, after all, which star will be the 'largest star in the universe' ...

The exact answer is 'I don't know.' This is because the stars classified as yellow hypergiants are too bright and far from the earth, and even a small measurement error can cause a large error in the measurement result.
In addition, the red hypergiant is comparable in size to the solar system and emits a large amount of mass, making it difficult to measure. Therefore, as science and technology progress and the measuring instruments themselves improve, the answer to the question 'the largest star in the universe' will change.


Stephenson 2-18 had several times the mass of the Sun at birth, but is believed to have lost half of its total mass.

The average yellow hypergiant is thought to have a radius about 1500 times that of the Sun, while Stevenson 2-18 has a radius of 2150 times that of the Sun and is expected to be as bright as 500,000 times that of the Sun. I am.

Compared to Stephenson 2-18, the sun is about the size of Chile. For humankind, the hugeness of Stephenson 2-18 is unimaginable.

It takes about 8.7 hours to go around Stephenson 2-18 at the speed of light. In the case of the
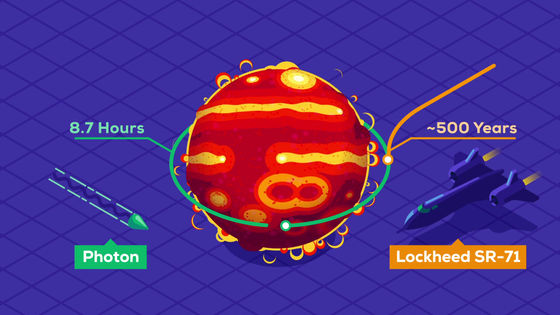
If Stephenson 2-18 was present at the position of the Sun, its surface would reach Saturn.

As Stevenson 2-18 continues to emit mass, its temperature continues to rise and heavy metals continue to accumulate in its core. And Stevenson 2-18 is thought to eventually cause a supernova explosion, sprinkling gas containing heavy metals into the universe.

The gas that is scattered starts a new cycle in which stars are born and die.

Related Posts: