What is a `` quasar '' that is considered one of the brightest objects in the universe?

A '
The Black Hole That Kills Galaxies-YouTube
A quasar is a relatively small celestial body, but it basically exists in the center of the galaxy.

Quasars are also known to be the brightest and most powerful objects in existence, suggesting that they could completely remake the universe around them.

The discovery of such quasars began in the 1950s, when astronomers noticed that mysterious powerful radio waves were being emitted from various parts of the universe. The source of the radio waves was found to be a celestial body whose internal structure could not be confirmed with an astronomical telescope, and which could only be observed using a radio telescope.

This object was named a ``quasi-stellar radio source'' because the light source looked like a fixed star.

It is also called 'Quasar' as an abbreviation for 'quasi-stellar radio source'.

It is known that quasars include objects that blink, emit radio waves, and emit X-rays and visible light.

The quasar's spectrum has a strong

Being billions of light-years away and appearing bright and large, quasars are believed to be thousands of times brighter than
Astronomers have so far discovered more than one million quasars, all of which have been found to be far from Earth.

Also, since many quasars are far away, it is estimated that they peaked in the early stages of the universe's formation, 3 billion years after the Big Bang.
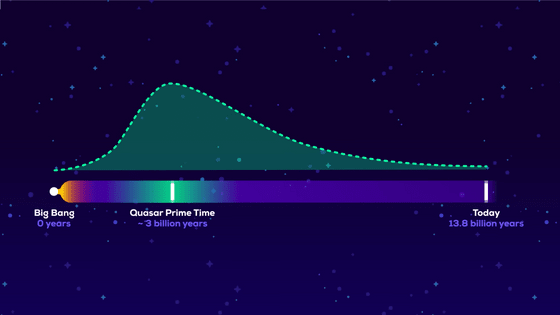
A ``supermassive black hole'' is the reason why quasars are able to produce intensely bright energy in the early stages of the immature universe, three billion years after the Big Bang.
When the surrounding gas and dust are sucked into the supermassive black hole, which is thought to exist at the center of every galaxy, these gas and dust form a disk while rotating around the black hole. This disk is called the '

Matter sucked into the black hole moves at a speed close to the speed of light before it crosses
In the accretion disk, the temperature rises to several hundred thousand degrees Celsius or more due to friction between substances, and the substance turns into

The central part of such an active galaxy is called an '

In the early days of the universe, which is about one-third the size of the current universe, gas and dust collided more violently than they do today, generating strong frictional heat. Therefore, it is thought that many active quasars were formed.

Particularly active quasars are known to emit huge beams of matter called ``jets'' that grow to sizes of hundreds of thousands of light years.
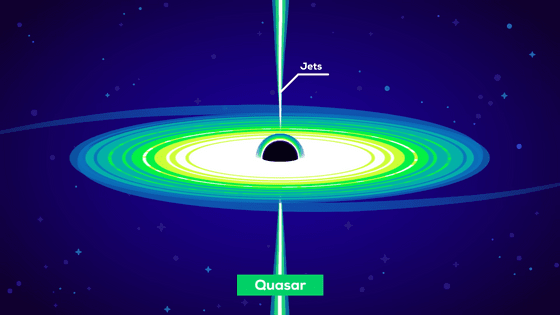
But the violent jets overheat the gas needed for star formation, and star formation stops.

Not only that, but if the jet pushes gas out of the galaxy, not only the quasar but also the galaxy will starve and lose the raw material for new stars.

On the other hand, the gas is compressed by the shock waves and jets from the quasar, and it is possible to form new stars for a short period of time. Also, the gas pushed out by the jet is mixed with the gas entering the galaxy and recycled.

However, it is thought that once a quasar has fallen into a starvation state, it will disappear, leaving only a supermassive black hole.

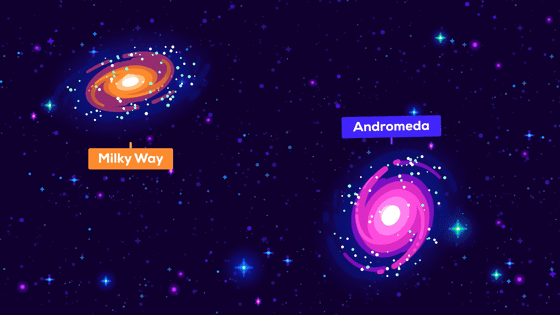
Also, it has not been clarified whether quasars once existed in the Milky Way galaxy to which the earth belongs.

However, since

Billions of years from now, when the Milky Way and
Related Posts:







