How is the cloud drive of 'ProtonMail' boasting super strong security built up?

The ProtonDrive security model --ProtonMail Blog
https://protonmail.com/blog/protondrive-security/
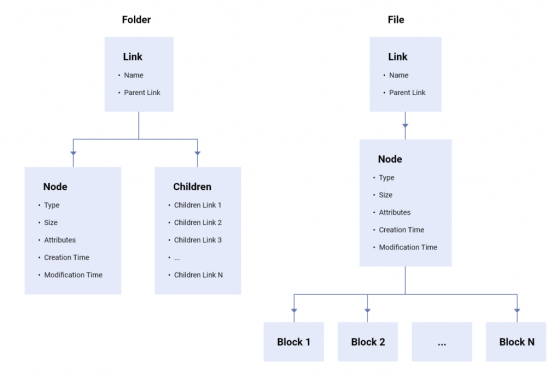
Proton Drive holds data by three elements called 'volume', 'node', and 'link'. Volume is the storage capacity allocated to each user, and the data uploaded to Proton Drive is stored in the volume according to the tree structure . The saved data is divided into blocks, linked to the node along with the data type, capacity, modification date, etc., and the position of the data in the tree structure in the volume is recorded in the link.
When users access data, they will use 'share' which regulates access authority for one link. For example, when accessing 'File 3' in the figure below, the user must follow the access privileges of Share 1 and Share 2.
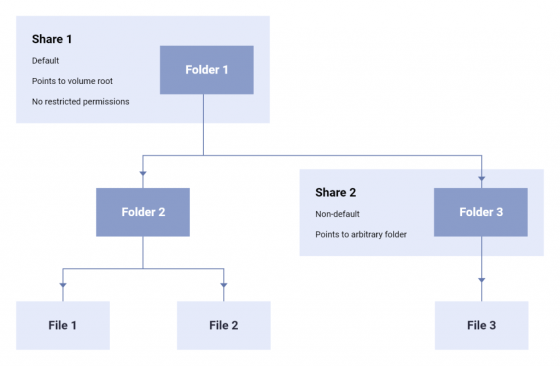
Since permissions can be set for each user in a share, it is possible to give different permissions to each user with one share.
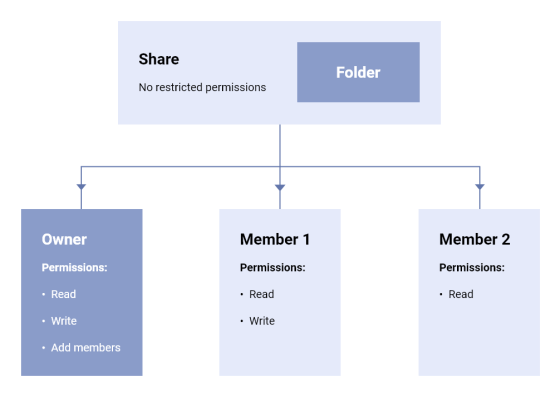
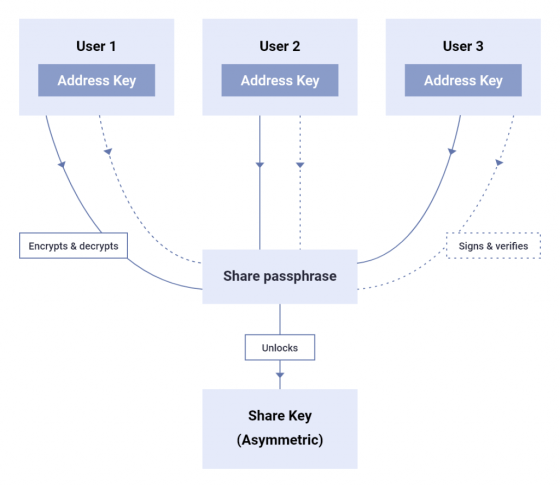
Since it is possible to manipulate the access authority if the share is tampered with, the share is naturally encrypted. When the share is generated, the encryption system will generate a 32-byte share passphrase and a paired
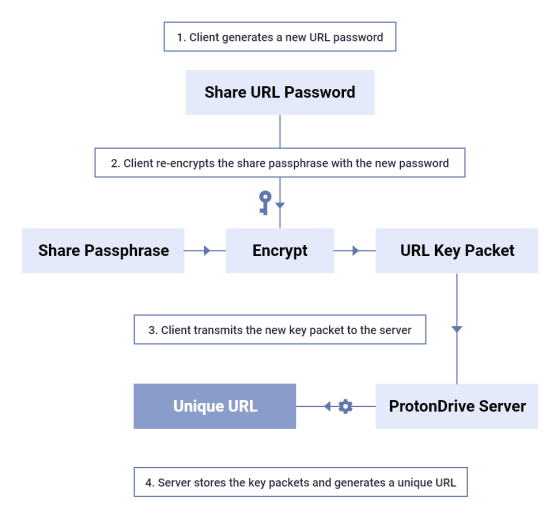
Data sharing to non-ProtonDrive users is done by encrypting the share passphrase and generating a dedicated URL. Next, the share passphrase is encrypted based on the password generated at the same time as the URL is generated. The encrypted passphrase will be shared with the other party as a URL via the Proton Drive server. Since the password information set in the URL is not stored on the ProtonDrive server, the password will not be leaked from the server to a third party.
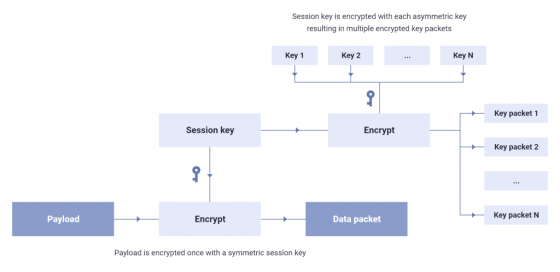
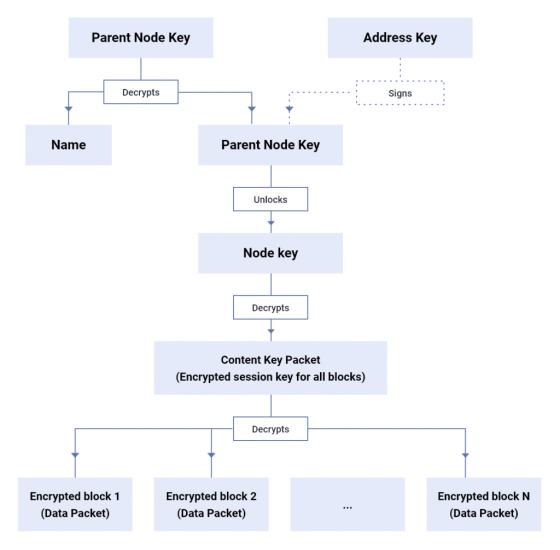
Packets at the time of data upload and download are encrypted by a common key called 'session key', and the session key is encrypted into different packets by each user's asymmetric key. Since ProtonDrive has a tree structure, the lower layer share passphrase has a chain structure that is encrypted by the upper layer key.
As with share encryption, passphrases and 'node keys' are used for node encryption that indicates the attributes of files and folders. Node encryption also has a hierarchical structure in which the node key of the parent node encrypts the node key of the child node.
ProtonDrive is under development at the time of writing and is expected to be in beta within 2020.
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Security, Posted by darkhorse_log