Detects the largest gravitational wave in the history of observation generated when two black holes collide and merge to form an 'intermediate mass black hole'

The largest gravitational wave that was thought to have occurred when a black hole with a mass 85 times that of the sun and a black hole with a mass 66 times that of the sun collided and merged was detected. Most of the black holes that have been observed so far can be classified into
GW190521
https://www.ligo.org/detections/GW190521.php
A'bang' in LIGO and Virgo detectors signals most massive gravitational-wave source yet-ScienceDaily
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/09/200902082341.htm
On May 21, 2019, we succeeded in detecting a signal named ' GW190521 ' with LIGO , a laser interferometer gravitational wave observatory in Louisiana, USA. The signals it detected were four short, short-duration signals with a very short duration of less than a tenth of a second.
The results of the analysis based on the state-of-the-art calculation tools and modeling tools, GW190521 is about 5 Gigapaseku it was found (about 16.3 billion light-years) is a gravity wave generated at a remote location. This will be 'the farthest gravitational wave detected so far,'. Researchers also think that this gravitational wave is likely to be generated when black holes collide and coalesce.
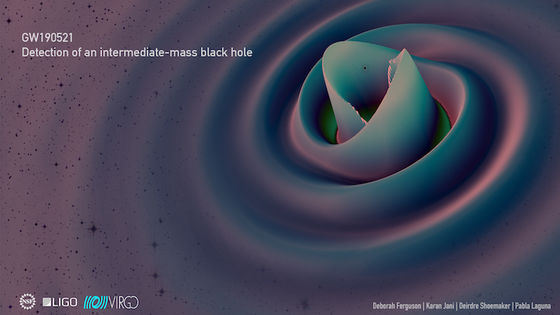
Almost all gravitational wave signals detected so far have been generated when two black holes or two
The newly detected gravitational waves have also been analyzed to have occurred when a black hole of approximately 85 solar masses and a black hole of approximately 66 solar masses collided and merged. It is thought that the mid-mass black hole of 142 solar mass was born as a result of the merging of the two black holes.
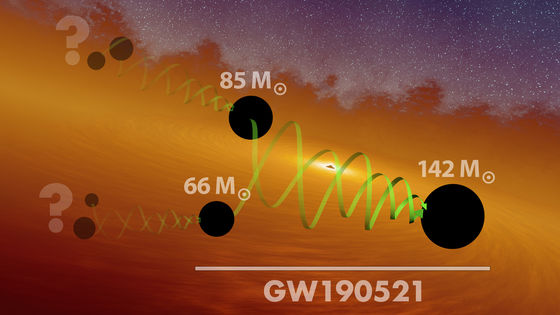
In addition, as a result of measuring the rotation of the two detected black holes, the research team found that the black holes may orbit while approaching each other and may rotate at an angle offset from the orbit axis. It has been pointed out that the reason why the rotation axis of the black hole is offset is that the two black holes may have caused a precession when they swirl toward each other.
As a result of the birth of an intermediate mass black hole with a mass of 142 times the mass of the sun, the research team claims that a huge amount of energy equivalent to 8 solar masses was diffused throughout the universe in the form of gravity waves.
Nelson Christensen, a member of the research team and a researcher at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), said, ``The gravitational waves detected this time are extremely intense, the most detected by LIGO and Virgo. It's a big signal.'
The following is a visual image of a numerical simulation up to the moment when two black holes collide and merge to form an intermediate-mass black hole.
Numerical simulation of a heavy black-hole merger (GW190521)-YouTube
The two black holes that created the final formed intermediate-mass black hole are also characterized by their size.
In the physics of stellar evolution, it is thought that the outward pressure caused by photons and gas in the stellar nucleus supports the star against the gravity that inwards, and maintains a stable state like the sun. I am. In the case of massive star nuclei, the fusion of heavy nuclei, such as iron, does not produce enough pressure to support the outer layers. When such an 'outward pressure falls below gravity', the star collapses under its own weight, causing an explosion called a supernova explosion, forming a black hole. The mass of this black hole is less than half that of the original star.
So, for example, if a star with 130 solar mass exploded in a supernova, the maximum number of black holes left behind would be 65 solar mass. However, in the case of a star with 130 to 250 solar mass, a phenomenon called anti-unstable supernova that emits more energy than supernova explosion occurs, so it seems that a black hole with 120 solar mass or more will be formed. In other words, it has been thought that a black hole with a solar mass of 65 to 125 will not be formed as long as the phenomenon of anti-unstable supernova exists.
However, since the two black holes that formed the intermediate-mass black hole in this discovery were 'black holes with masses that should not be formed,' 66 solar mass and 85 solar mass, respectively. Many astrophysicists will struggle to understand if a black hole has been formed,' said Christensen, a researcher.
Related Posts: