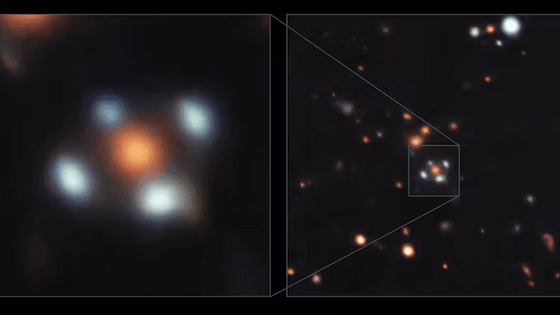
A 'Einstein's Cross' is discovered where a galaxy 20 billion light-years ahead looks four-fold with a gravitational lens

A new example of “
A New Einstein Cross Gravitational Lens of a Lyman-break Galaxy-IOPscience
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ab0aeb/meta
A new Einstein cross is discovered
https://phys.org/news/2019-03-einstein.html
In general relativity, space-time is said to be distorted by the gravity generated from heavy objects, and light is bent along the distorted space. Therefore, if there is another object between the observer and the observation object, the central object plays the role of a convex lens, and the observation object appears to be split apparently. This is the 'gravity lens effect'. In the image below, the path through which light actually travels is indicated by a white arrow, and the apparent path is indicated by an orange arrow.
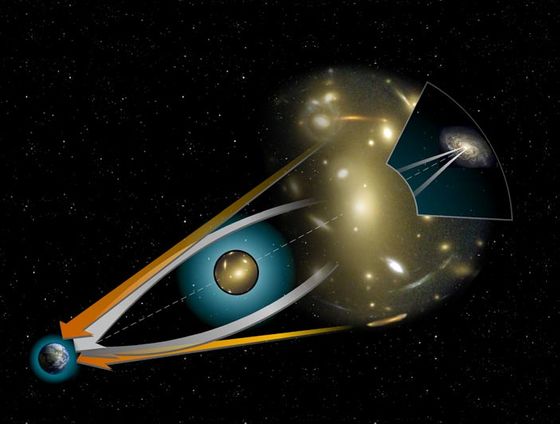
When a celestial body appears to be split due to the gravitational lensing effect, it is difficult to find out that the gravitational lensing effect is occurring because the distance between the divided bodies is very small. Furthermore, even if you discover an astronomical object that appears to have a gravitational lensing effect on the surface, you need to make sure that it is light emitted from the same astronomical object.
A team of scientists from Italy succeeded in breaking down three of the four lights found in the high resolution image of the Hubble Space Telescope into spectra, and the emission line of ionized hydrogen appeared at the same wavelength Confirmed. The presence of the same emission line at the same wavelength indicates that the light is coming from the same object, which indicates that the gravitational lensing effect works.

So far, only one case has been reported for the 'Einstein's Cross', in which the image of the celestial body is divided by the gravitational lens and appears as a cross. The new 'Einstein's Cross', the second case in this case, was named 'J2211-0350' according to galactic coordinates . It also turns out that the object that acts as a gravitational lens is an elliptical galaxy approximately 7 billion light years away, and the light source is another galaxy at least 20 billion light years away. According to the author of the paper Daniela Bettoni, the light source for the gravitational lensing effect is almost always the quasar , and it is very rare for the galaxy to be the light source.
When an astronomical object with a gravitational lensing effect is found, what appeared to be the same light appears to be slightly different, so by analyzing the difference, what substance is in the path that the light traveled You can know what it was. In addition, as it collects light at one point like ordinary glass lenses, it is expected to progress in astronomy, such as observing weaker light.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1d_ts