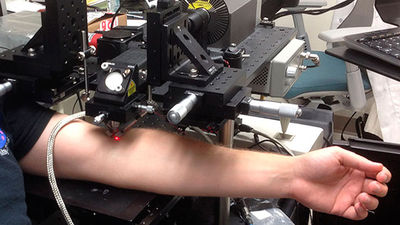
New technology to safely separate cancer cells from blood with sound waves
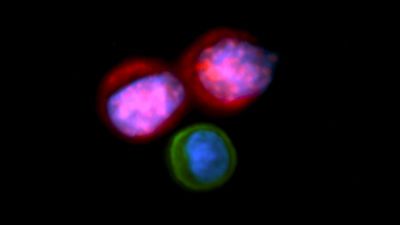
Cancer cells that have been released from cancerous or metastasized tissues and invaded into the blood are called "blood circulating tumor cells (CTC)". In order to safely separate this CTC from the blood without hurting, a new method that had never existed before was invented.
Acoustic separation of circulating tumor cells
http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2015/04/02/1504484112
Sound waves separate rare cancer cells from blood | Ars Technica
http://arstechnica.com/science/2015/04/sound-waves-separate-rare-cancer-cells-from-blood/
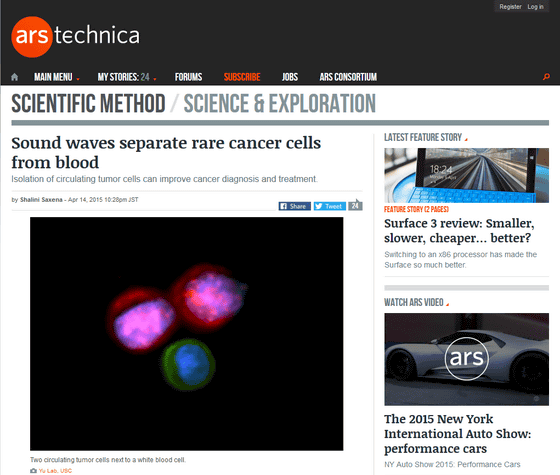
CTC is an unusual type of cancer cell that is found in the blood of patients with localized tumors. If we can isolate only CTC, which is also considered to be the main cause of cancer metastasis, "without destroying" from the blood, we can judge whether the cancer character subtype analysis, therapy monitoring, cancer treatment is effective Great help. However, at the present stage, in order to separate CTCs from the blood, a method of analyzing the difference between CTC and other cells' antibody / cell size / polarizability / electrical properties and separating it is adopted, It seems to be difficult to separate cancer cells "alive".
Meanwhile, researchers at the State University of Pennsylvania are developing a new CTC separation method. That separation method is to separate cancer cells using "sound wave". With this method using a sound wave, it is possible to separate from the blood while retaining CTC viability, cell function, phenotype, genotype etc, and to mutate cells other than CTC There is no such thing. In other words, biocompatibility and safety are greatly improved from the conventional method. And you can collect blood CTC "as it is alive".
ByThe Journal of Cell Biology
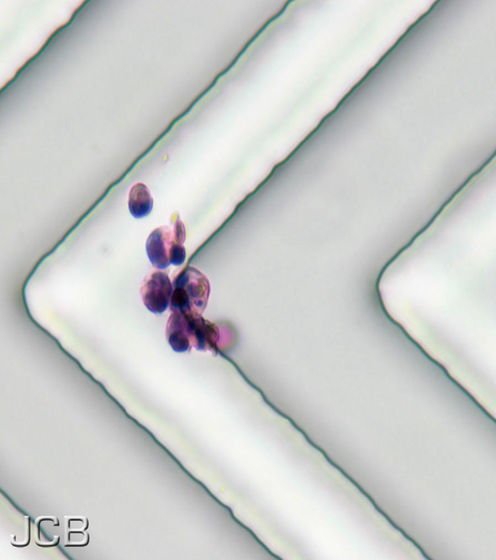
Previously sound-based CTC separation technology could not separate CTCs from the blood of clinical samples. Although it seems that processing capacity was insufficient and instability in long-term use was a problem, high sound processing capacity and stability are expected to be expected for sound wave based CTC separation microfluidic device developed by Penn State University.
The microfluidic device for CTC separation arranges multiple transducers, converts electric power into sound waves, and changes the direction of sound waves with microfluidic channels. In use, when blood flows in the microfluidic device for CTC separation, when blood passes through the sound field generated by the oscillator, the CTC and other cells receive different force due to the acoustic radiation and flow in a slightly different direction Become. And as the number of cells flowing in the device increases, the path difference between CTC and other cells becomes large, and CTC can be separated without damaging the cells.
Although microfluidic devices for CTC separation using sound waves are of great help for cancer diagnosis and treatment, it seems that there is a need to pursue safety by repeating experiments and research, not at the practical stage.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by logu_ii