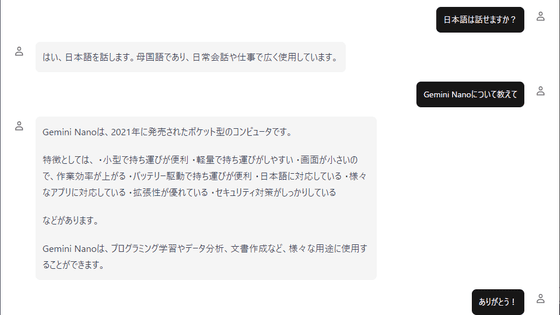
'On-device AI browser' is an AI browser automation tool that uses WebLLM and does not require a cloud or API key.
The trend toward using AI technology to automate tasks previously performed manually is accelerating, and tools that automate operations on web browsers appear to be particularly useful for many users. However, most AI automation tools are cloud-based, requiring cumbersome procedures such as obtaining API keys and raising privacy concerns. 'On-device AI browser' is an AI browser automation tool that loads LLM locally, eliminating the need for a cloud or API key.
GitHub - RunanywhereAI/on-device-browser-agent: On-device AI browser automation using WebLLM. No cloud, no API keys, fully private.
◆Features
According to the official repository, the 'On-device AI browser' has the following features:
On-device AI : Perform LLM inference locally by combining WebLLM with WebGPU acceleration.
Multi-agent systems : Planner and navigator agents perform intelligent tasks
Browser automation : Automate navigation, clicking, typing, and data extraction from web pages.
Privacy first : All AI runs locally, so data stays on the device
- Offline support : Works offline after initial model download
◆Environment settings
To use the 'On-device AI browser', the following environment is required.
Chrome 124 and later : for WebGPU support for service workers
Node.js 18 or later : for building and npm package management
git : For cloning repositories and using Git Bash on Windows
・WebGPU compatible GPU : Any recent GPU should be fine.
First, clone the code from the official repository. This assumes you are using 'Git Bash' on Windows, so please adjust accordingly if you are using a different environment.
[code]
git clone https://github.com/RunanywhereAI/on-device-browser-agent.git
[/code]
An “on-device-browser-agent” folder will be created under the current folder, so move there and install the packages required for building.
[code]
cd on-device-browser-agent
npm install
[/code]
After confirming that the installation is complete, execute the following command to build.
[code]
npm run build
[/code]
If any problems are reported during this process, you must take appropriate action according to the output.
If the build is successful, a dist folder and extension will be generated under the on-device-browser-agent folder.
Finally, load the extension you built in Chrome. First, enter 'chrome://extensions/' in the Chrome address bar to open the extensions management screen, and turn on the 'Developer mode' switch in the upper right corner.
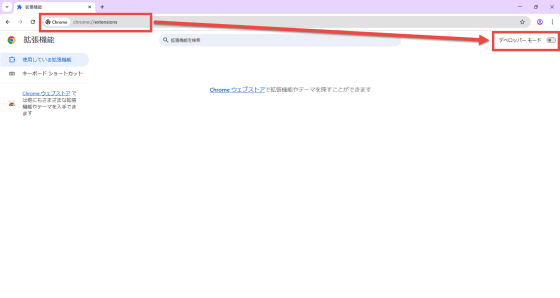
Click the 'Load unpackaged extension' button that appears.
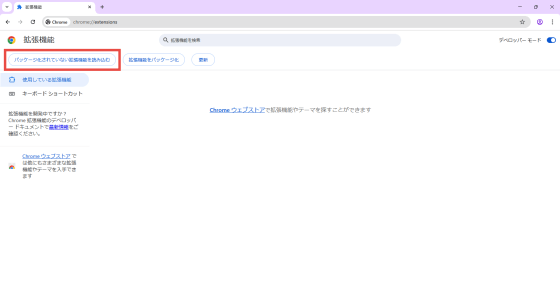
A dialog titled 'Select extension directory' will appear, so select the dist folder under the on-device-browser-agent folder where you built the extension.
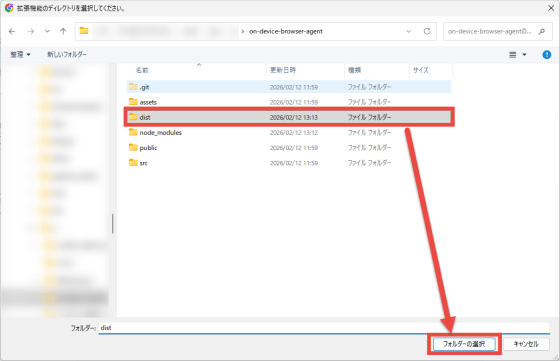
Make sure that the extension named 'Local Browser - AI Web Agent' has been added to the extension management screen, and click the 'Details' button.
The extension details screen will appear, so scroll down.
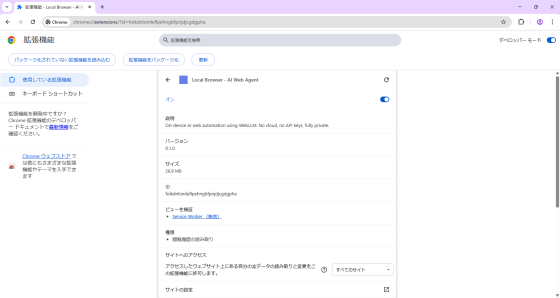
There is a switch called 'Lock to toolbar.' If you turn it on, the extension icon will appear on the toolbar. Note that the first time you click the icon, it will download a model of up to 1GB in size, which may take some time depending on your environment.
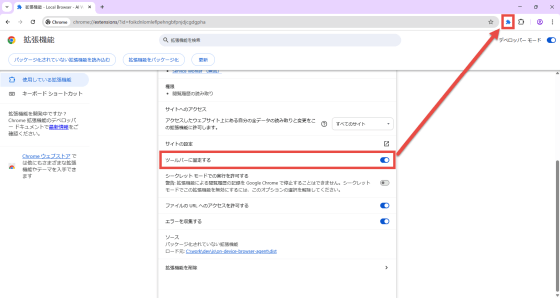
◆How to use
Clicking on the extension icon will display the following popup:
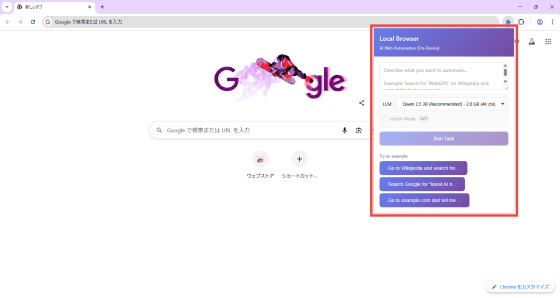
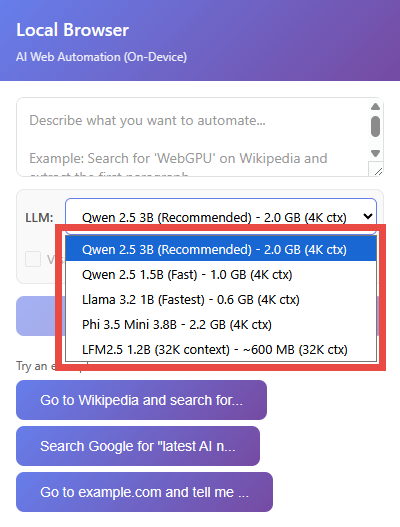
This time we will use the default LLM, but you can choose from the following five options in the drop-down list.
・Qwen 2.5 3B : Recommended (default)
・Qwen 2.5 1.5B : High speed
・Llama 3.2 1B : Fastest
・Phi 3.5 Mini 3.8B
LFM2.5 1.2B : 32K
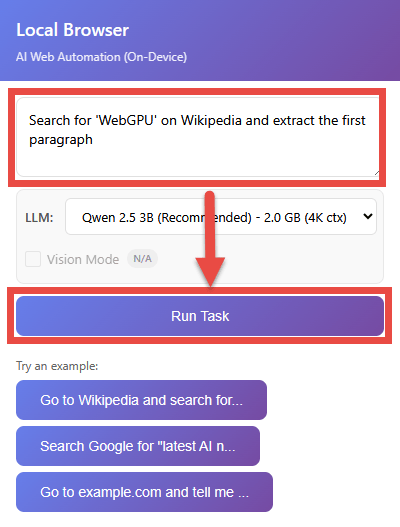
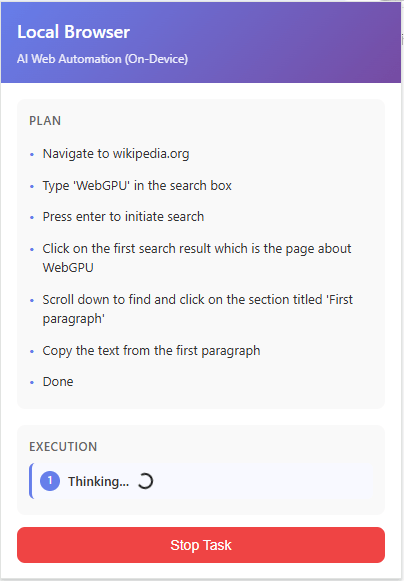
Enter the task you want to run in the task input field and press the 'Run Task' button to start the task. As a test, try running the sample 'Search for 'WebGPU' on Wikipedia and extract the first paragraph' written in the README.
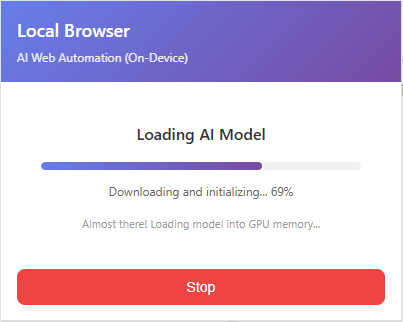
Once started, the progress of the task will be displayed in real time in a popup. First, the AI model is loaded. Loading only occurs the first time the task is run or immediately after switching to LLM.
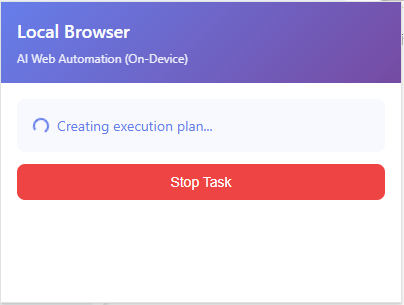
Creating an execution plan.
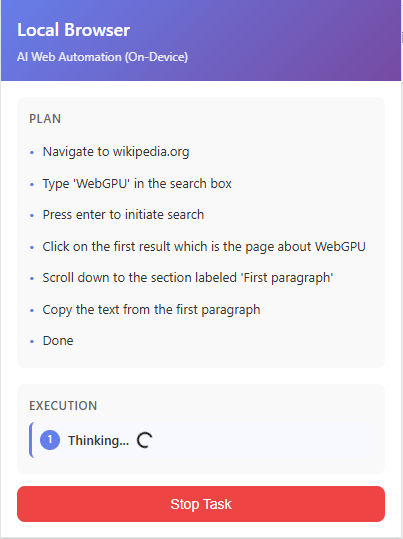
The execution status of the plan is updated in real time.
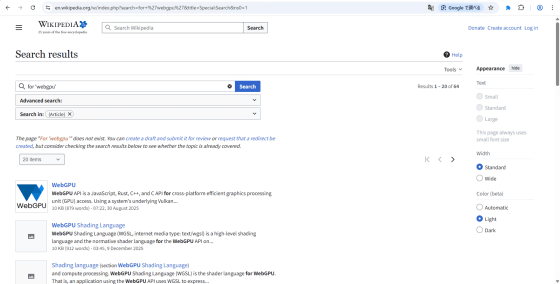
The execution results are as follows.
When we tried giving instructions in Japanese, the first part, 'Search Wikipedia for WebGPU,' was processed successfully, but the second part, 'Extract the first paragraph,' could not be processed correctly and resulted in an error.
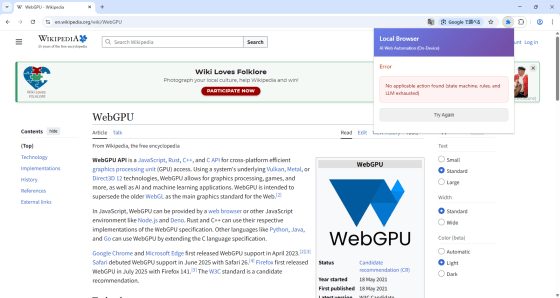
After checking the execution plan, it seems that they are not unable to understand Japanese, but there are some small differences compared to when instructions were given in English, so at least for now, it may be that instructions given in English are more likely to be carried out as expected.
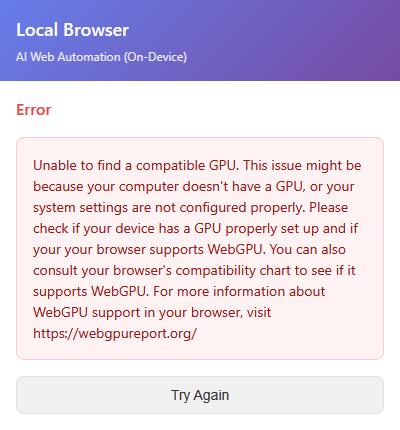
If the GPU does not meet the requirements, the following error message will be displayed.
Summary
At the time of writing, the 'On-device AI browser' is still in development, at version 0.1.0, but it's a very interesting project as a locally-running AI browser automation tool. Future updates are expected to add more features and improve stability, making it a viable option for users who want to use AI automation but don't want to use cloud services.
Related Posts: