Google DeepMind researchers open-source 'AlphaGenome,' an AI model that predicts 11 types of genome processes, including genetic recombination

The Google DeepMind research team is developing a new AI model called ' AlphaGenome ,' which can analyze long DNA sequences up to one million characters long at a time and predict 11 major genomic processes, such as gene expression and splicing, with high accuracy. The results of this research were published in the scientific journal Nature on January 28, 2026, and the source code and model weights were made publicly available to the research community. AlphaGenome is capable of processing contexts of one million bases (1Mb), double the 500,000 bases that the previous model,
Our breakthrough AI model AlphaGenome is helping scientists understand our DNA, predict the molecular impact of genetic changes, and drive new biological discoveries. ????
— Google DeepMind (@GoogleDeepMind) January 28, 2026
Find out more in @Nature ↓ https://t.co/jvBLRXYzdj pic.twitter.com/WEL4Ptdv06
Advancing regulatory variant effect prediction with AlphaGenome | Nature
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-10014-0
The greatest feature of AlphaGenome is that it can make predictions at an extremely high resolution of single base units, even while handling huge amounts of DNA sequences.
Google launches 'AlphaGenome,' an AI that can analyze the effects of genetic mutations, capable of inputting 1 million base pairs at once, potentially helping to establish treatments for genetic diseases - GIGAZINE
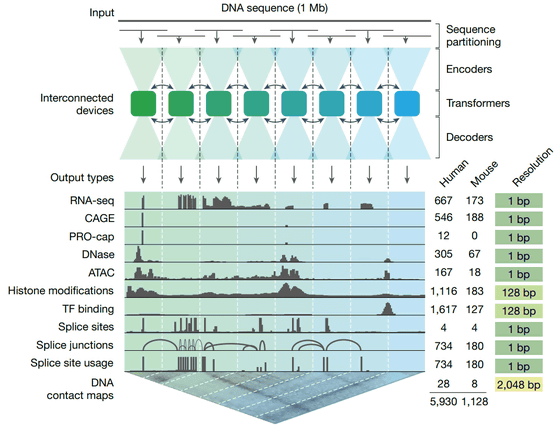
The 11 processes predicted include gene expression such as RNA sequencing , CAGE (cap analyzed gene expression) , and PRO-cap , as well as detailed splicing patterns, chromatin accessibility , histone modifications , transcription factor binding, and a chromatin contact map that represents spatial interactions in the genome.
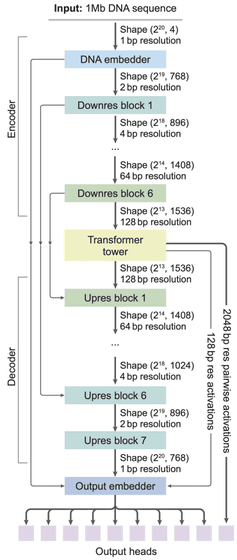
The AlphaGenome architecture is a deep learning model that applies the U-Net structure, which has proven highly effective in the field of image analysis, to genome sequence analysis. This model processes vast DNA sequences of one million bases at a time and employs a hierarchical design that condenses and restores information in stages to decipher the complex regulatory information contained in the blueprint of life.
The Encoder uses convolution to gradually 'summarize' the extremely detailed DNA information, one base at a time, ultimately reducing the information to a resolution of 128 bases, thereby efficiently extracting the overall characteristics of the data.
The Transformer tower uses the summarized information to model the relationships between distant genomic regions, making it possible to accurately capture the interactions between regions that regulate gene function, even if they are located tens of thousands of base pairs apart.
The Decoder then reconstructs the summarized information into single-base units. Based on this summarized information, the system models the relationships between distant genomic regions. For example, even if regions that regulate gene function are located tens of thousands of base pairs apart, the system can accurately capture their interactions.
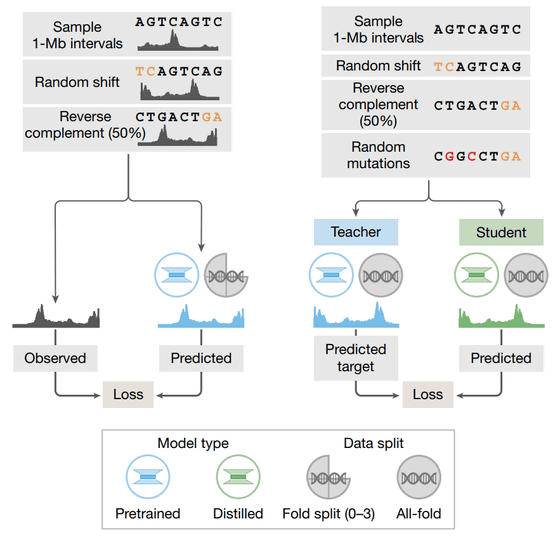
AlphaGenome was trained using both human and mouse genome data and was able to identify changes in gene activity in specific cell types 14.7% more accurately than Borzoi. Additionally, in the task of predicting the sign of eQTL (expression quantitative trait loci), AlphaGenome improved the average auROC (auROC ) of its predecessor, Borzoi, from 0.75 to 0.80, outperforming Borzoi on many evaluation metrics.
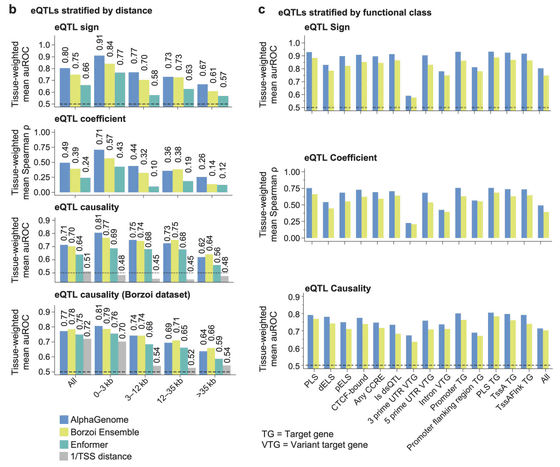
There are also differences in the splicing prediction mechanisms. While Borzoi uses a method to implicitly infer splice sites from RNA-seq coverage data, AlphaGenome is an advancement in that it can directly and explicitly predict splice sites, their utilization, and splice junctions .
In practical terms, AlphaGenome is expected to accelerate the identification of genetic factors that cause disease and the development of new treatments. In particular, it will be a powerful tool for elucidating how mutations in non-coding regions, which account for 98% of the genome but have been difficult to understand, interfere with gene on/off and volume regulation. For example, it is expected to be applied to designing new DNA sequences that activate genes only in specific tissues, pinpointing cancer-causing mutations, and diagnostic research for rare genetic diseases.
Google DeepMind has made AlphaGenome available for non-commercial research use through GitHub, Kaggle, and Hugging Face. An NVIDIA H100 GPU or higher is recommended for running the model, and a mechanism for interacting with the model via a dedicated API is also provided.
google-deepmind/alphagenome_research: Research code accompanying AlphaGenome
https://github.com/google-deepmind/alphagenome_research
AlphaGenome - a google collection
https://huggingface.co/collections/google/alphagenome
Although there are still challenges in predicting individual genomes at the time of writing, AlphaGenome is expected to contribute to a wide range of biological research as a fundamental step toward deciphering the genome's regulatory code and deciphering the blueprint of life.
Related Posts: