Meta releases next-generation multimodal AI 'Llama 4,' adopting MoE architecture to boast high performance comparable to competing models

Meta has officially announced its next-generation AI model, the Llama 4 series. The Llama 4 series is comprised of multiple models with different performance, scale, and application ranges, achieving significant performance improvements over the previous generation and rivaling the performance of competing AI models. Its biggest features are its efficient model architecture called '
The Llama 4 herd: The beginning of a new era of natively multimodal AI innovation
https://ai.meta.com/blog/llama-4-multimodal-intelligence/

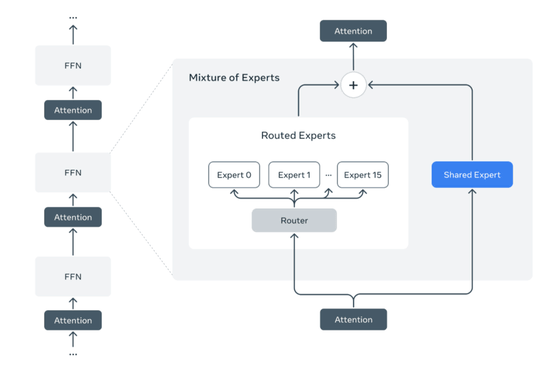
The Llama 4 series is a native multimodal model, designed from the start to handle multiple information formats, including not only text but also images and videos, in an integrated manner. Furthermore, its MoE architecture selectively runs only the most suitable specialized models for each task, known as 'experts,' maintaining high performance while minimizing resource waste.
In addition, Llama 4's underlying technology includes many innovations, such as a new position embedding method called 'iRoPE (Improved Rotary Position Embeddings)' and a new pre-training strategy called 'MetaP (Meta's Progressive Pretraining).' Meta claims that these new technologies are designed to improve the scalability, accuracy, and stability of the model, and are key to Llama 4's improved performance.
First, iRoPE is an improved version of the conventional RoPE (Rotary Position Embedding) that aims to mitigate accuracy degradation in long-text context processing. RoPE is used to incorporate token order information into the transformer, but its performance is known to degrade with long inputs. To address this issue, iRoPE aims to stabilize scaling and inter-token correlation, thereby achieving high-accuracy output even when processing very long code, documents, or conversation histories.

MetaP is a learning method that addresses the learning difficulties of model scaling, making pre-training for Llama 4 more stable and efficient. MetaP uses smaller models and simpler datasets in the early stages of training, and then gradually increases the model size and data complexity, achieving stable convergence and a high-performance final model. Meta claims that MetaP has succeeded in creating a multimodal model capable of integrated understanding and inference.
Furthermore, while typical MoEs have the problem of bias in the selection of expert models, Llama 4 introduces a new routing mechanism that controls diversity and balance in expert selection for each token, which is said to be the key to achieving both high accuracy and efficiency.
At the time of writing, the Llama 4 series includes three models: the Llama 4 Scout, the Llama 4 Maverick, and the Llama 4 Behemoth.

Of the three models, the smallest, 'Llama 4 Scout,' has 17 billion active parameters and 16 experts. With a total of 109 billion parameters, it's lightweight enough to run on a single NVIDIA H100 GPU, yet supports an extremely long context window of 10 million tokens. Furthermore, Meta claims that it outperforms competing models such as Gemma 3, Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite, and Mistral 3.1. Llama 4 Scout is said to be particularly superior in image recognition and text association.
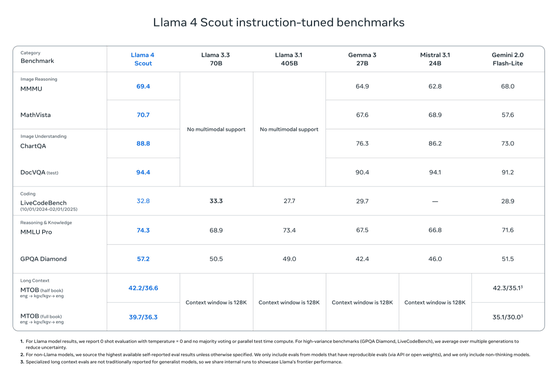
Llama 4 Maverick has 17 billion active parameters and 128 experts, for a total of 400 billion parameters, and can run on a single
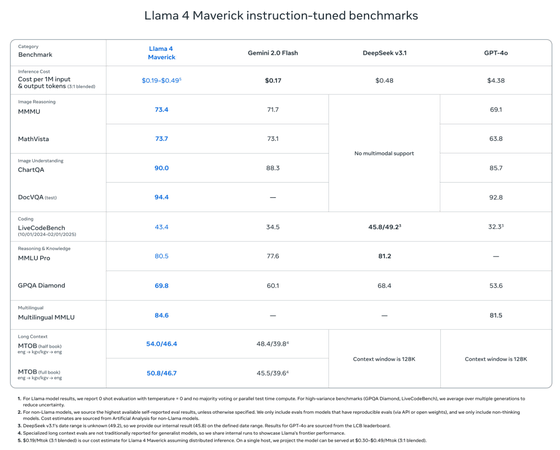
However,
Okay Llama 4 is def a littled cooked lol, what is this yap city pic.twitter.com/y3GvhbVz65
— Nathan Lambert (@natolambert) April 6, 2025
The top-of-the-line model, 'Llama 4 Behemoth,' is a massive model with 288 billion active parameters and 16 experts, totaling 2 trillion parameters. According to Meta, this model has outperformed GPT-4.5 and Claude 3 Sonnet in STEM benchmarks, demonstrating exceptional accuracy in mathematics, programming, and science. However, at the time of writing, the model is still in training and has not yet been released.
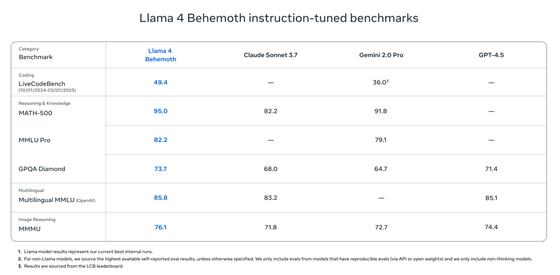
The Llama 4 series supports over 200 languages, with 10 times more multilingual tokens than the previous generation, Llama 3. Meta also says that it has significantly reduced the rejection rate for politically and socially controversial topics and is working to reduce bias.
These new models will be gradually incorporated into Meta's AI assistant, and as of the time of writing, they are available in WhatsApp, Messenger, Instagram, and the web browser version of MetaAI . The models for Llama 4 Scout and Llama 4 Maverick are publicly available on llama.com or Hugging Face , and the research community will soon be able to access them for research purposes.
Related Posts: