The positive and negative effects of coffee on the body

While there are positive research results showing that coffee
Coffee and what it does to your body - BBC World Service - YouTube
One of the original species of coffee is the Arabica coffee tree, native to Ethiopia. The legend goes that around the 9th century, a goat kept by Kaldi of Ethiopia suddenly became excited after eating red berries. Kaldi also ate the same berries and was surprised by how good they tasted. This is said to be the beginning of coffee.

Historically, it is said that
In the 15th century, coffee houses spread throughout the Ottoman Empire and then across Europe over the next few centuries. Philosophers such as Voltaire are said to have drunk dozens of cups of coffee a day, and it is said that without coffee the Enlightenment would not have been possible.

Coffee also fueled the slave trade: in the early 1800s, African slaves produced one-third of the world's coffee in Brazil.

Today, around 2 billion cups of coffee are consumed every day around the world.
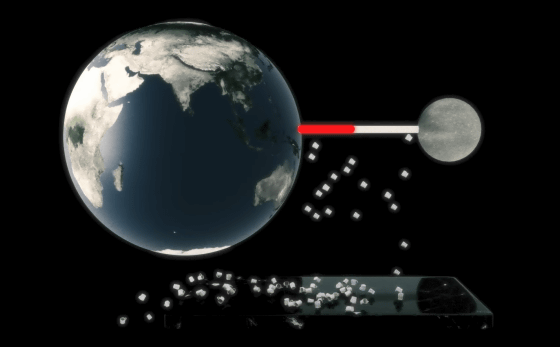
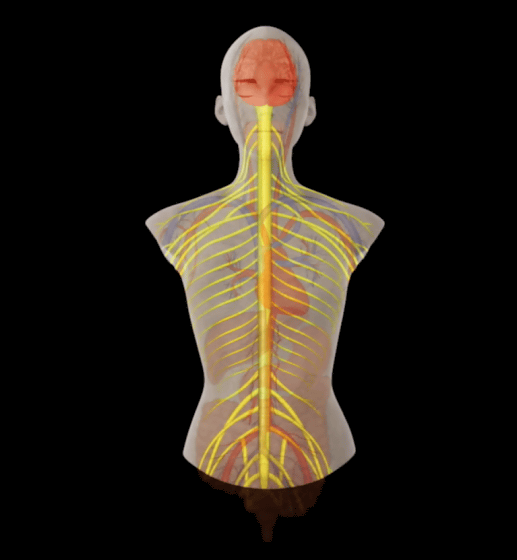
The mechanism by which caffeine in coffee acts on the body is as follows: First, when you drink coffee, various components are absorbed into the bloodstream in the small intestine.
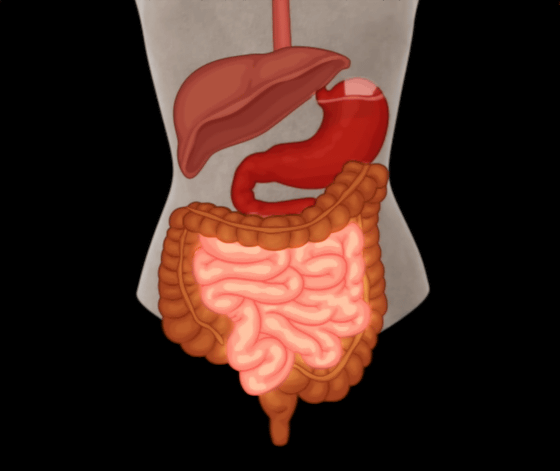
The caffeine is then transported through the bloodstream throughout the body.
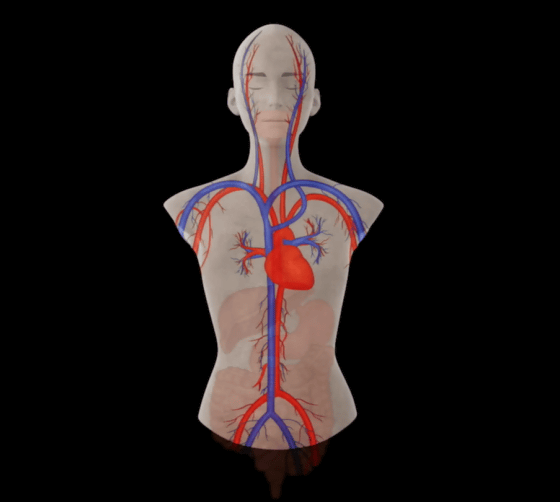
Finally, the caffeine reaches the nervous system.
Caffeine is similar to adenosine and can bind to adenosine receptors. The diagram below shows adenosine as a block and caffeine as a sphere.
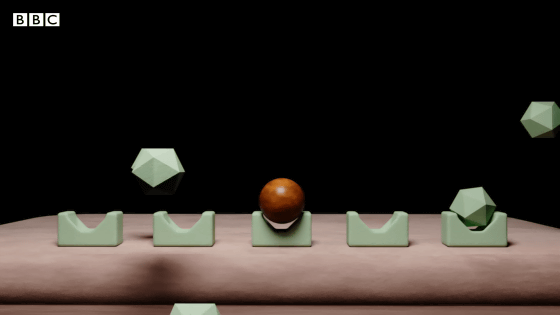
When adenosine binds to adenosine receptors, it has effects such as 'lowering the heart rate,' 'promoting relaxation,' and 'promoting drowsiness. On the other hand, when caffeine binds to adenosine receptors, adenosine cannot bind to those parts, making it difficult for the heart rate to decrease and drowsiness to occur.

Caffeine also has the effect of suppressing fatigue and improving physical performance. For this reason, some athletes take caffeine supplements.

Experts say that cutting back on your caffeine intake in the afternoon will help you get the most out of your caffeine intake the next morning.
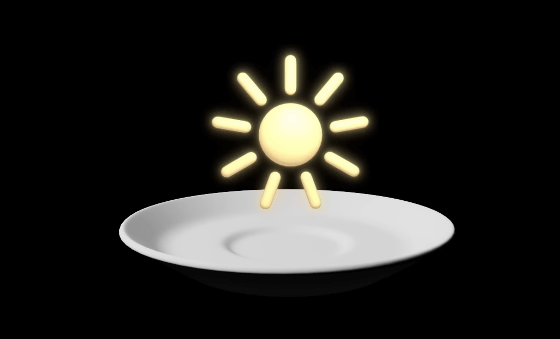
The recommended daily caffeine intake for healthy adults is 400 milligrams, which is equivalent to 4-5 cups of coffee. Drinking more than this amount of coffee can cause side effects such as insomnia, irritability, anxiety, stomach discomfort, nausea, and headaches. Furthermore, consuming 1,200 milligrams of caffeine, equivalent to about 12 cups of coffee, can cause dangerous effects such as seizures.
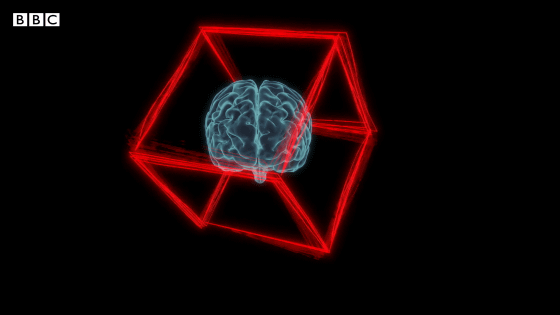
On the other hand, it is also known that drinking coffee in moderation can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, some cancers, and Parkinson's disease.

Related Posts:







