A human immune cell weighs the same as a pineapple. Where in the body are these immune cells found?

Every living organism has
The total mass, number, and distribution of immune cells in the human body | PNAS
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2308511120
The Immune System Weighs The Same as a Pineapple, Study Finds : ScienceAlert
https://www.sciencealert.com/the-immune-system-weighs-the-same-as-a-pineapple-study-finds

Human immunity has a subsystem of the immune system called the adaptive immune system , which is a powerful and complex system that acquires antibodies by acquiring immunological memory. Experiments on immune cells are often carried out in mice, and analysis often leads to the assumption that the same reactions are seen in the human immune system, but previous studies attempting to estimate the overall picture of the immune system have only been conducted to a limited extent and generalized to humans.
Immune cells have long-term memory of pain experienced in childhood - GIGAZINE

A study published by Sender et al. in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) in October 2023 characterized the distribution of immune cells in the human body and showed their total number and weight. According to the study, the average human immune system is composed of approximately 1.8 trillion cells, and for an average-sized adult male, it is estimated to weigh about 1.2 kg. Science Alert, a scientific media outlet, likens the weight of about 1.2 kg to 'one pineapple' or 'six hamsters.'
Regarding the types of immune cells, lymphocytes account for about 40% of the total number of immune cells and about 15% of the total mass of immune cells, and neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, also account for a similar proportion. Macrophages , a type of white blood cell that moves like an amoeba, account for about 10% of immune cells in terms of number, but because macrophages are large in size, they account for about 50% of the total cell mass.
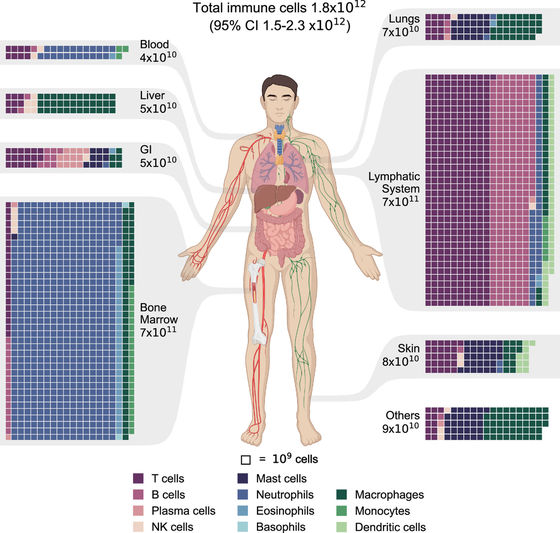
The following shows the distribution of immune cells in the human body. Each square represents 1 billion immune cells, and the color of the square represents the type of immune cell. According to the figure, the immune cells are particularly abundant in the bone marrow, which is dominated by neutrophils (blue), and in the lymphatic system, which is dominated by dark red T cells and light red B cells.
'There is a wealth of research investigating the human immune system from various angles, but to gain a deeper understanding, we needed a comprehensive look at the distribution and mass of different immune cell types,' said Sender, explaining the significance of the research. 'Knowledge of the quantity, distribution and weight of immune cells provides an integrated quantitative view of the immune system and will facilitate the development of research models.'
The researchers also used the adult male estimates to calculate the immune cell counts of adult women and children, mainly based on body type. If a 73kg man in his 20s has a total of 1.8 trillion immune cells, weighing about 1.2kg, then a 60kg adult woman of the same age would likely have about 1.5 trillion immune cells, weighing about 1kg. A 10-year-old child would likely have about 1 trillion immune cells, weighing 600g. However, these estimates should be interpreted with caution, as women are more likely to develop autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, and children's immune systems are more susceptible to change during maturation.
Although it is said that the digestive tract contains the greatest number of immune cells, Sender and his colleagues' analysis showed that most immune cells are not in the digestive tract but in the lymphatic system and bone marrow. The distribution of which organs in the human body have the greatest accumulation of immune cells, as well as information on the type and weight of the cells, clearly have strong links to health and disease, and so require further discovery and analysis.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1e_dh