Chinese rocket breaks apart after launch, scattering more than 900 pieces of space junk

It has been reported that the Long March 6A rocket launched by China on August 6, 2024, disintegrated in low Earth orbit (LEO), forming a 'debris cloud' made up of a large amount of
Chinese rocket breaks apart after megaconstellation launch, creating cloud of space junk | Space
https://www.space.com/china-megaconstellation-launch-space-junk
China rocket launch creates cloud of space debris in low-Earth orbit | CNN
https://edition.cnn.com/2024/08/09/science/china-rocket-stage-orbital-debris/index.html
The accident in question occurred during the launch of the first 18 satellites of China's satellite broadband network, G60 Starlink. The satellite constellation, also known as the Chinese version of Starlink, is scheduled to launch 1,296 satellites into orbit, with plans to eventually increase the number to 15,000, comparable to SpaxeX's Starlink.
China finally launches satellite for Starlink rival satellite internet 'G60 Starlink' - GIGAZINE

The launch put the satellite into orbit, but part of the rocket carrying the satellite broke apart in space, generating a large amount of space debris.
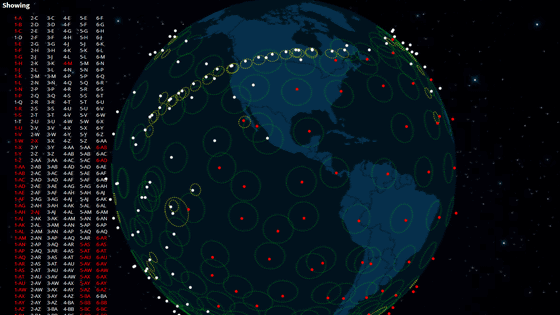
Slingshot Aerospace, a company that develops satellite collision avoidance platforms, said in a statement that its Horus sensor system for tracking moving objects in low energy environments ' detected a series of unexpected bright objects moving along the same orbit as the rocket body and deployed G60 satellite.'

Initially, 50 pieces of debris were discovered, but new pieces have been found one after another since then, and according to LeoLabs, a space debris monitoring service, at least 700 pieces have been discovered, and potentially more than 900 pieces.
The altitude at which the rocket broke up was about 810 km above the Earth's surface, and the International Space Station (ISS) orbits at an altitude of about 408 km above the Earth's surface, so so far there has been no direct impact on the ISS. A spokesperson for the U.S. Space Force said, 'The Space Force has not observed any imminent threats and continues to conduct regular Conjunction Assessments to support the safety and sustainability of the space domain.'
However, it poses a serious threat to LEO satellites below 800 km in altitude, which are increasingly being used for satellite constellations. It is difficult to predict exactly how long the debris will remain in orbit, but experts believe it could last for years, possibly even decades.
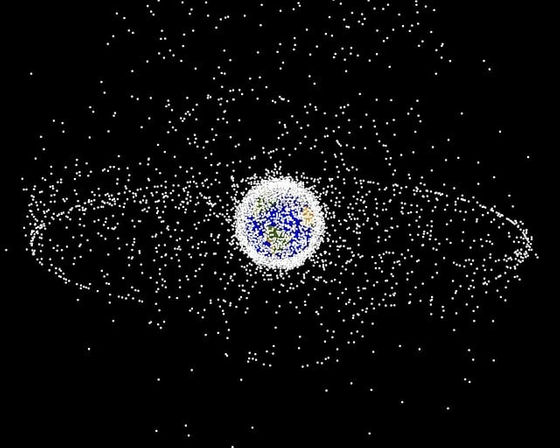

'If even a small percentage of future launches to build China's mega-constellation generate as much debris as this first launch, the amount of space junk in low Earth orbit will become unacceptable,' said Audrey Schaffer, vice president of strategy and policy at Slingshot Aerospace.
This is not the first time that a Chinese rocket has generated a large amount of space debris: on November 12, 2022, the upper stage of another Long March 6A rocket launching a weather satellite exploded, scattering 533 trackable pieces into orbit.
As space development progresses, the amount of orbital debris is also increasing rapidly, raising concerns that it could become a risk for future space exploration. According to the European Space Agency, the number of pieces of debris larger than 10 cm orbiting the Earth is already about 40,500, and the number of pieces larger than 1 mm in diameter has reached 130 million.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1l_ks