Why does running burn more calories than walking?

It may seem obvious that 'running burns more calories than walking,' but it seems a little strange that the calories burned are different when running and walking even when moving the same distance. Clement Leminour, a doctoral student in the Department of Human Movement Sciences
Walking or running: for the same distance, which consumes more energy?
https://theconversation.com/walking-or-running-for-the-same-distance-which-consumes-more-energy-233943
The calorie expenditure associated with any activity is called the 'metabolic cost,' and when running or walking, the metabolic cost is higher than normal because various organs in the body use energy. Metabolic cost can be estimated by analyzing the oxygen and carbon dioxide consumed by the body, and it has been confirmed by this method that 'running burns more calories than walking.'
The difference in metabolic costs between running and walking is mainly due to two factors. The first is that there is a difference in the movement of the body when running and walking, even when moving the same distance.
The following diagram shows the movements of running (top) and walking (bottom), with the positions of the center of gravity indicated by the red and blue dots. When walking, the head and center of gravity remain in almost constant positions, but when running, the head and center of gravity oscillate up and down more.
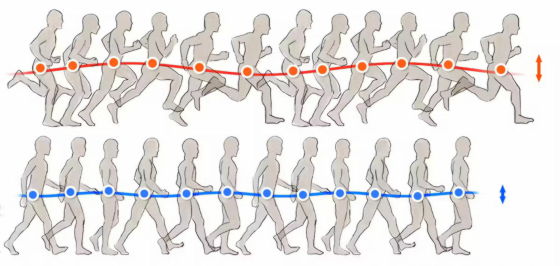
Producing this vertical movement requires more force from the muscles in your legs, which burns more calories but doesn't help you get closer to your destination: When you run, some of your energy is used to move your body up and down instead of forward, so you burn more calories than walking the same distance, Leminneur and his team explained.
The second reason why running has a higher metabolic cost than walking is that running burns more calories after physical exercise than walking.
For example, if you run 3km, your body will be hot and out of breath after you finish. This increase in body temperature and the replenishment of lost energy will cause you to burn more calories than you would at rest for several minutes after running. This is also said to be the reason for the difference in calories burned when running and walking.

From the above, it can generally be said that 'running burns more calories than walking,' but this is based on the assumption that the assumed walking speed is about 2 to 6 km per hour. If you walk at a fairly slow speed of 0.5 km per hour, it will take longer to travel the same distance, and the final calorie consumption may be more than running. This is because living organisms consume a certain amount of calories per unit time regardless of bodily activity, and this calorie consumption necessary to maintain life activities is called
Also, if you walk very fast (over 8km/h), walking may burn more calories than running. This is because running uses the elasticity of not only your muscles but also your tendons, whereas walking uses only muscle power, so above a certain speed running becomes more energy efficient than walking.
The following graph shows the calories burned by walking (blue) and running (red) according to speed. At slower speeds, walking burns fewer calories, but at a point around 8km/h, walking burns more calories than running. This is roughly the same point as when a person on a treadmill that is getting faster and faster switches from walking to running.
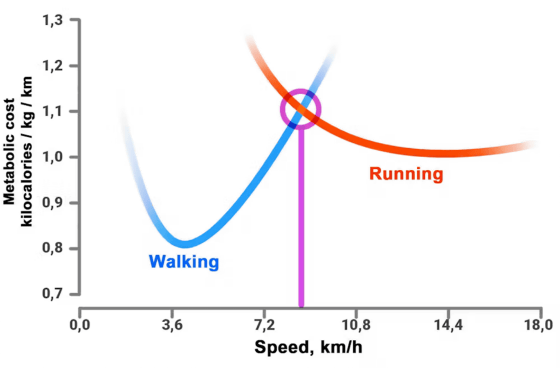
Leminneur and his colleagues concluded, 'In conclusion, running consumes more energy than walking a given distance due to greater oscillations of the center of mass and increased postexercise energy expenditure.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







