What is a 'packet rate attack,' a type of DDoS attack that has been increasing in recent years?

The Rise of Packet Rate Attacks: When Core Routers Turn Evil - OVHcloud Blog
https://blog.ovhcloud.com/the-rise-of-packet-rate-attacks-when-core-routers-turn-evil/

DDoS attacks have been affecting the availability of online services for many years, with multiple actors using IoT devices and routers to build botnet armies and launch DDoS attacks by injecting malware or exploiting vulnerabilities in those devices.
Most DDoS attacks can be divided into network layer attacks, where a large amount of garbage data is sent to overwhelm the bandwidth, or application layer attacks, where a large number of application requests are sent to overwhelm the CPU or memory, but there are several other DDoS attack techniques, one of which is called a 'packet rate attack.'
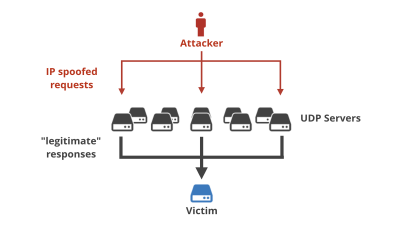
Data sent and received over the Internet is divided into units called packets , and the receiving system must process the source IP address and destination IP address contained in the header of each packet. Packet rate attacks are a method of sending a large number of 'small packets' to a target instead of sending a huge amount of data that overwhelms the bandwidth.

In general, it is more computationally expensive to process many small packets than to process a few large packets. For example, when processing packets using software, each packet means at least one memory access. Even when using hardware, a high packet rate imposes a heavy load. Therefore, for systems that process packet headers, the hardware limit is the packet rate, not the bandwidth.
The goal of packet rate attacks is not to exhaust available bandwidth, but to overload the packet processing engines of network devices close to the destination, typically by disabling load balancers or DDoS mitigation systems in front of the targeted service, causing collateral damage to the larger infrastructure involved, Melio explained.

Packet rate attacks are not new, but for a long time the scale of packet rate attacks has been well below 100 Mpps, but in the past 18 months, there has been a sharp increase in attacks exceeding 100 Mpps. In particular, in April 2024, a record packet rate attack occurred, reaching 840 Mpps, exceeding the highest value ever recorded.
OVHCloud is mitigating the effects of these packet rate attacks while also analyzing the IP addresses from which the attacks were launched. As a result, OVHCloud found that two-thirds of the packets in the packet rate attacks analyzed by OVHCloud came from just four PoPs in the United States, demonstrating the ability of attacking actors to send huge packet rates through a small number of peerings .
In addition, manual analysis of approximately 100 packet rate attacks ranging from 100Mpps to 500Mpps revealed that many of the attacks were coming from a small number of IP addresses. In particular, investigation of the top 70 problematic IP addresses that generated high packet rates revealed that most were MikroTik routers and had configuration web pages exposed on the Internet.
MikroTik routers' operating system, RouterOS, has had several serious vulnerabilities reported in the past few years, so attackers may be exploiting vulnerabilities and improper management interfaces to use these routers for packet rate attacks. Melio also points out that the 'bandwidth test' function in RouterOS may be easily applicable to DDoS attacks.
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Security, Posted by log1h_ik