It turns out that water frost, which was thought to be impossible, falls on Olympus Mons near the equator on Mars
Mars was once covered with water, which is important for life, and it is believed that even today, when the surface water has disappeared , water still exists underground in the form of ice, etc. A new study has discovered that the previously impossible 'water frost' is present on Olympus Mons , the largest volcano in the solar system, and nearby mountains on Mars.
Evidence for transient morning water frost deposits on the Tharsis volcanoes of Mars | Nature Geoscience
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-024-01457-7
Researchers detect water frost on solar system's tallest volcanoes | Brown University
https://www.brown.edu/news/2024-06-10/mars-frost
'We thought it was impossible:' Water frost on Mars discovered near Red Planet's equator | Space
https://www.space.com/mars-water-frost-equator-exomars-tharsis-olympus-mons
In an Extremely Unlikely First, Scientists Found Frost on the Peak of Mars' Volcano at Olympus Mons
https://www.inverse.com/science/frost-mars-mountain-olympus-mons-volcano
Olympus Mons is located in the Tharsis region, which spreads near the equator of Mars, and boasts an elevation of about 27,000 m above the surface of the planet. Near Olympus Mons are a group of huge volcanoes ( the Tharsis Mountains ), including Mons Ascleus , Mons Pavonis , and Mons Arsia .
Adomas Valentinas , a planetary scientist at Brown University in the United States and a doctoral student at the University of Bern in Switzerland at the time, conducted a study analyzing data from the Trace Gas Orbiter, a Mars probe of the European Space Agency (ESA) .
The analysis of more than 30,000 high-resolution color images taken by the Trace Gas Orbiter's Color Stereo Surface Imaging System (CaSSIS) revealed that there is water frost near the summits of Olympus Mons and the Tharsis Mons. This result was verified by the Trace Gas Orbiter's spectrometer (Nadir and Occultation for Mars Discovery ) and the high-resolution stereo camera on the Mars Express probe .
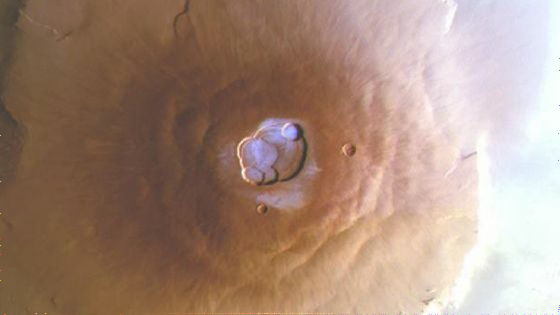
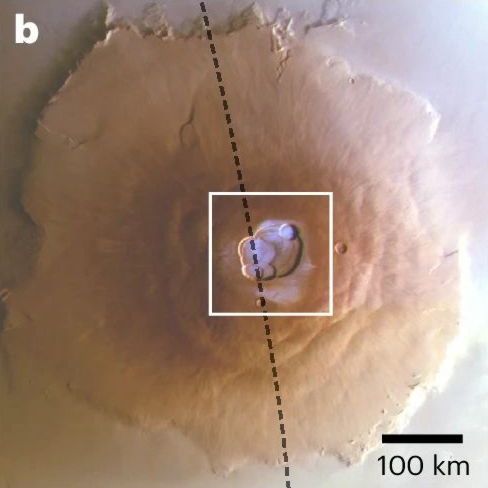
The image below shows frost on the summit of Mount Olympus, taken with a high-resolution camera. The frost that falls on the summits and calderas of volcanoes only occurs during the cold seasons of Mars, and is as thin as a hair, forming only for a few hours around sunrise before it evaporates due to the heat of the sun. Although the layer of frost itself is very thin, the area it covers is quite large, so the total amount of moisture is said to be about 111 million liters (the equivalent of 60 Olympic swimming pools).

When you enlarge the frost area surrounded by a white frame, it looks like this.
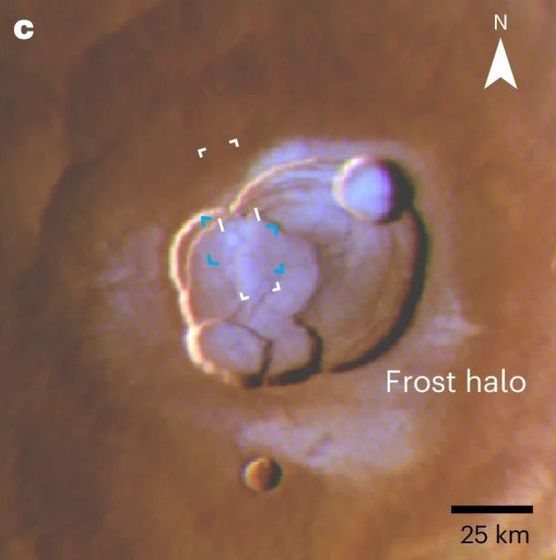
This is an image of the mountain and frost simulated on Olympus Mons. This is the first time that water frost has been found near the Martian equator, and it casts doubt on the Martian climate dynamics that have been thought of up until now.

From an Earth perspective, it would not be surprising if frost formed on the summit of a mountain over 20,000 meters above sea level, even if it was near the equator. However, on Mars, the thin atmosphere causes low atmospheric pressure and sunlight conditions, so the temperature near the summit is not much different from that of the plains, so it was thought that frost would not form even at high altitudes. 'We thought it was unlikely that frost would form near the equator on Mars,' Valentinas said.
The team thinks that air circulation near the summit and through the caldera may be creating a cool, humid climate that can produce frost on cold mornings. 'Ancient Mars may have had precipitation or snow on its volcanoes,' Valentinas said. 'What we're seeing could be the remains of an ancient climate cycle.'
Based on the results of this research, it is expected that modeling how frost forms near the Martian equator will help solve mysteries such as the location of water on Mars and understand the complex dynamics of the Martian atmosphere, which is essential for the search for life.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik