Why is it difficult to solve the world's water shortages using technology to turn seawater into freshwater?

It is said that
Why Is Desalination So Difficult? - YouTube
Why Is Desalination So Difficult? — Practical Engineering
https://practical.engineering/blog/2023/6/28/why-is-desalination-so-difficult
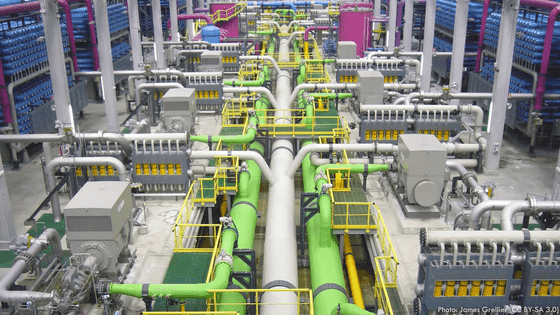
The Carlsbad Desalination Plant in San Diego, California, USA, produces 23,000 cubic meters of fresh water per day.

While most water purification plants purify water from rivers and lakes, the Carlsbad Desalination Plant draws water directly from the ocean.

In addition to the Carlsbad desalination plant, there are more than 18,000 desalination plants operating around the world, consuming about a quarter of all energy used in the water industry. However, desalination plants are only able to produce less than 1% of the world's water demand.
The reason is the salt content of seawater. Generally, seawater contains about 35 grams (35 parts per million) of salt per liter, and the World Health Organization (WHO) stipulates that water with a dissolved solids content of more than 10 parts per million is unacceptable for drinking by consumers. Therefore, in order to turn seawater into drinking water, it is necessary to remove more than 98% of the salt in the water.
To remove salt,

In addition, when seawater is distilled, salts produced during the desalination process accumulate. These deposits have low thermal conductivity and reduce the efficiency of boiling, so they must be removed periodically. However, removing the deposits manually is difficult in large-scale desalination plants.

That's why Middle Eastern desalination plants use a process called ' flash evaporation ,' which minimizes salt buildup by forcing evaporation at temperatures below boiling.
Flash evaporators use a phenomenon called '
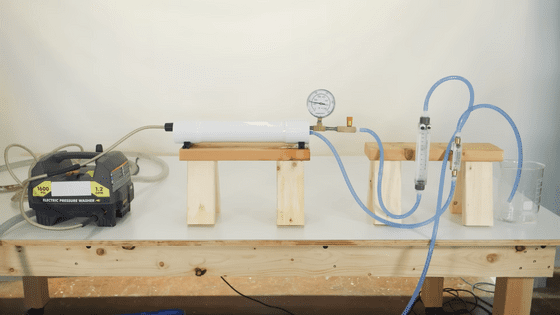
Flash evaporative desalination is much more efficient than distillation – Practical Engineering tests showed it took about five minutes to produce one litre of fresh water – and is why it is the desalination process typically used on ships.

However, like distillation, this desalination process is difficult to scale up. Practical Engineering explains why: 'The amount of electricity required to desalinize one cubic meter of seawater is about 100 kilowatt-hours, which is much more than the amount of electricity required to purify a river.'
In addition to salt, seawater also contains dirt, algae, organic matter, and other contaminants, which can foul the desalination vessel and membranes if desalinized as is. For this reason, all desalination plants remove all substances other than salt at the beginning of the process, which requires a lot of energy and costs.

Furthermore, even if the pretreatment is sufficient, periodic cleaning is still required, at which point the production of freshwater will stop completely.In addition, because the freshwater produced through this process is pure water, the effort of adding additives such as minerals and disinfectants is also required.
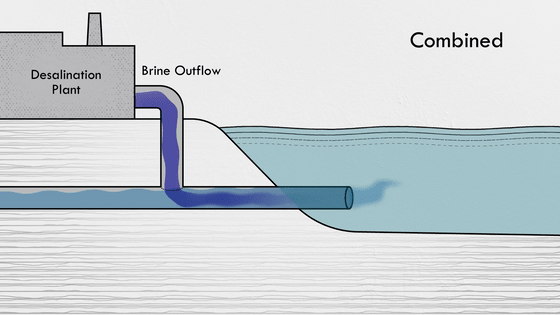
All the salt produced by the desalination process in the flash evaporator is concentrated into a small amount of water, but disposing of the highly saline solution directly back into the ocean would have a detrimental effect on plants and animals near the seabed. For this reason, many plants use diffusers to diffuse the salty solution to dilute it more quickly, or mix the resulting solution with water from other processes, such as the power plant's cooling lines or wastewater, to dilute it before it is released.
Related Posts:







