What was the danger of the 'throwing fire extinguisher' used in England in the 19th century?

Fire
The beauty and danger in Victorian Glass Fire Grenades – Museum Crush
https://museumcrush.org/the-beauty-and-danger-in-victorian-glass-fire-grenades/
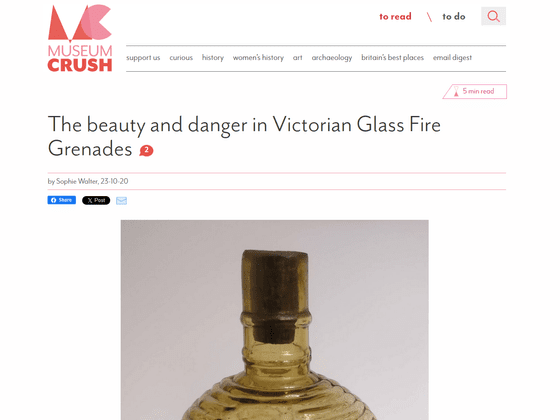
Throwing fire extinguishers, which were introduced in England in the 19th century, are mainly made of glass with company names printed on them, and are typically thrown toward the source of a fire at a fire scene, or when the glass breaks due to heat, the extinguishing agent inside is thrown into a sprinkler system. It was used by hanging it from the ceiling for the purpose of scattering it like this.

It was filled with a mixture of salt water and ammonium chloride. Salt water does not freeze under normal conditions, and heating ammonium chloride produces ammonia, which is said to help suppress fires. However, the effectiveness of extinguishing fires with ammonia produced by heating ammonium chloride was not very good.
Since the beginning of the 20th century,
However, subsequent research has shown that carbon tetrachloride is carcinogenic, and that touching it or inhaling it can cause damage to the lungs, kidneys, and liver. It has been reported.
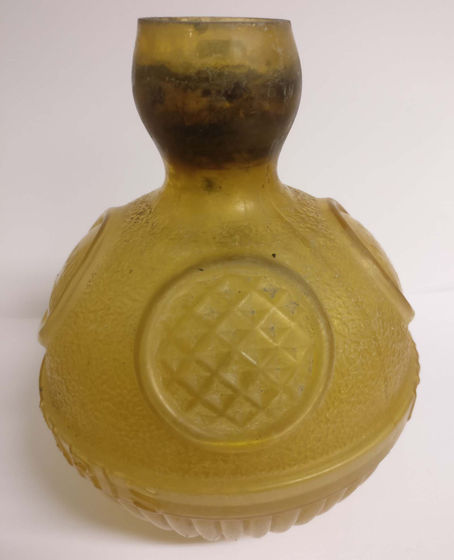

Furthermore, when carbon tetrachloride heated to 200°C to 400°C comes into contact with water, it generates a toxic gas called
According to Museum Crush, which introduces British art, fire extinguishers using carbon tetrachloride were used by the British royal family at the time, and British company Imperial Fire Extinguisher Company said, ``Our fire extinguisher was sold at Sandringham, England . There are records of it being used around 1886.'

Later, as improvements were made, these fire extinguishers changed from being made of colorful glass to being made of clear glass or frosted glass. At the same time, the decorations attached to the glass were gradually removed, and it evolved into something more functional.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1r_ut







